
- 304 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
-->
This book covers the elementary school mathematics curriculum common in most parts of the world. Its aim is to serve educators (teachers and parents) as a guide for teaching mathematics at elementary school level. The book focuses both on content knowledge and on pedagogical content knowledge. It bridges the gap between fundamental mathematical principles and good teaching practices. It also offers the reader a glimpse on how mathematicians perceive elementary mathematics and presents ideas for specific mathematical activities.
Volume 2 focuses on content taught in the higher grades of elementary school. It covers the following topics: multiplication and division of multi-digit numbers, divisibility and primality, divisibility signs, sequences, fractions and their representations, and fraction arithmetic.
-->
Request Inspection Copy
-->
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Chapter 31
Fraction Multiplication


31.1Numbers and multiplication revisited
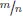
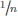
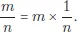
31.1.1The number concept revisited
Table of contents
- Cover
- Halftitle
- Title
- Copyright
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- Contents
- 19. Multiplication of Multi-Digit Numbers
- 20. Division of Multi-Digit Numbers
- 21. The Order of Operations
- 22. Division with a Remainder
- 23. Prime and Composite Numbers
- 24. Common Multiples and Common Divisors
- 25. Divisibility Rules
- 26. Sequences
- 27. Fractions
- 28. Quotients of Natural Numbers
- 29. Fraction Comparison
- 30. Fraction Addition and Subtraction
- 31. Fraction Multiplication
- 32. Fraction Division
- Index
- Common Core Index