
Simulating Copulas: Stochastic Models, Sampling Algorithms, And Applications (Second Edition)
Stochastic Models, Sampling Algorithms, and Applications
- 356 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Simulating Copulas: Stochastic Models, Sampling Algorithms, And Applications (Second Edition)
Stochastic Models, Sampling Algorithms, and Applications
About this book
-->
The book provides the background on simulating copulas and multivariate distributions in general. It unifies the scattered literature on the simulation of various families of copulas (elliptical, Archimedean, Marshall-Olkin type, etc.) as well as on different construction principles (factor models, pair-copula construction, etc.). The book is self-contained and unified in presentation and can be used as a textbook for graduate and advanced undergraduate students with a firm background in stochastics. Besides the theoretical foundation, ready-to-implement algorithms and many examples make the book a valuable tool for anyone who is applying the methodology.
--> Contents:
- Introduction
- Archimedean Copulas
- Marshall–Olkin Copulas
- Elliptical Copulas
- Pair Copula Constructions
- Sampling Univariate Random Variables
- The Monte Carlo Method
- Further Copula Families with Known Extendible Subclass
- Appendix: Supplemental Material
-->
--> Readership: Advanced undergraduate and graduate students in probability calculus and stochastics, practitioners who implement models in the financial industry and scientists. -->
Copula;Simulation;Monte Carlo;Random Vector;Dependence Model Key Features:
- Explicit focus on stochastic representations of copulas in contrast to an analytical perspective
- Easy-to-implement simulation schemes given as pseudo code
- Explicit focus on high-dimensional models
- Focus on applicability of models, e.g. to portfolio credit risk or insurance
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Introduction
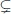
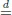
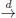
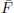
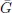


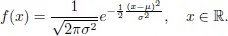
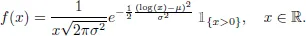
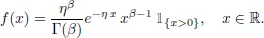
Table of contents
- Cover
- Halftitle
- Series Editors
- Title
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Preface
- Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Archimedean Copulas
- 3. Marshall–Olkin Copulas
- 4. Elliptical Copulas
- 5. Pair Copula Constructions
- 6. Sampling Univariate Random Variables
- 7. The Monte Carlo Method
- 8. Further Copula Families with Known Extendible Subclass
- Appendix A Supplemental Material
- Bibliography
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app