
- 524 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Economics of Incentives for Inter-firm Innovation
About this book
-->
In the current environment of severe global competition, an uncertain business future as well as shorter product life cycles, companies have a pressing need to develop new products and businesses rapidly. In this book, Professor Yasuhiro Monden expounds on his theories about inter-firm networks and incentive price systems as important mechanisms to encourage innovation.
The author has coined the term incentive price system to explain profit allocation systems which will motivate inter-firm collaboration to develop new customer-pleasing products or businesses. He notes that such a comprehensive concept of incentive price has not been studied in conventional economics but is invaluable for solving various profit allocation problems.
The theories in the book are richly illustrated by many case studies from the automobile, auto-parts, smartphone, semiconductor, convenience store and nuclear power electricity industries. Examples from the automobile industry account for more than half of the case studies because the author has accumulated much practical knowledge and experience from research and related activities in the Japanese automobile industry over several decades.
This book will be of interest to researchers and practitioners of lean or just-in-time production, as well as those involved in related areas such as managerial accounting, managerial economics, corporate finance, organization theory and cooperative game theory.
-->
--> Contents:
- Preface
- Introduction:
- Research Theme, Framework and Summaries of Each Chapter
- Critical Comments on the Traditional Organization and Price Theories
- Innovations for Social Problems:
- Business Innovation in General: Open Innovation Based on the Business Ecosystem
- Environmental Problem: Open Innovation of Eco-Cars Based on the Global Inter-Firm Collaboration
- Wage Difference Problem: Smile Curve and Fair Allocation of the Global Value-Added among Nations
- Inter-Firm Innovations Can Solve the Wage Differentials in the Supply Chain
- Open Inter-Firm Network:
- From Adam Smith's Division of Labor to the Network Organization
- How Can the Open Network Organization be Constructed via M&A?
- Design of " Open " Global Supply Chain
- Robust Supply-Chain for the Disasters
- Incentive System by the Inter-Firm Profit and Loss Allocation:
- How to Value the Intangible Assets for Allocating the Synergy Effect in the Global Inter-Firm Network
- How to Determine the " Acquisition Price " for Purchasing the Firm in M&A
- Risk Sharing and Risk Spreading Based on the " Full Cost-based Transfer Price "
- A Convenience-Store Chain: Cost Sharing and Profit Sharing that Motivate the Inter-Firm Cooperation
- Nuclear Power Electric Company: How Can All Stakeholders "Share the Burdens" of Solving Damage Liability and Business Turnaround?
- Theoretical Analysis of Incentive Price:
- Two Transfer Prices: The Market Price for Balancing Supply and Demand and the Incentive Price for Inter-Firm Collaborations
- Cooperative Game Theory and "Φ stability" for the Profit Allocation by the Cumulative Opportunity Cost Method
- Note on the Management Philosophy for Collaboration:
- Note on Management Philosophy for Inter-Firm Collaboration
-->
--> Readership: Researchers and practitioners who are interested in lean or just-in-time production systems and management. -->
Keywords:Open Innovation;Open Network Organization;Incentive Price System;Inter-firm Collaboration;Supply Chain ManagmentReview:0
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Chapter 1
Research Theme, Framework and Summaries of Each Chapter
1.1.The Theme and Framework of This Book
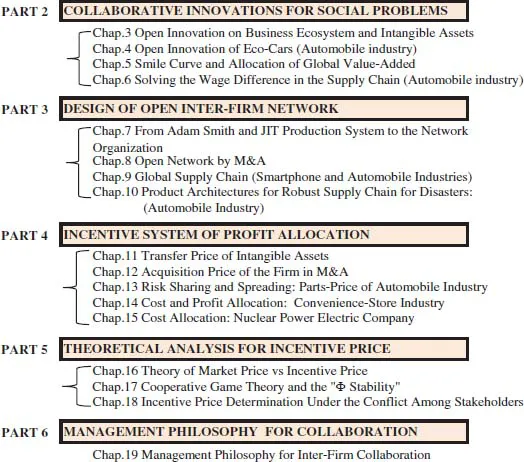
1.1.1.Part 2: Collaborative Innovations
1.1.1.1Innovation by Inter-Firm Collaborations
1.1.1.2Inter-Firm Collaboration
1.1.2.Part 3: Open Inter-Firm Network
1.1.3.Part 4: Incentive System by Profit Allocation
1.1.4.Part 5: Theoretical Analysis of Incentive Prices

1.2.Summaries of Each Chapter of This Book
1.2.1.Part 2: Collaborative Innovations for Social Problems
Table of contents
- Cover
- Halftitle
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- About the Author
- Part 1 Introduction 1
- Part 2 Collaborative Innovations for Social Problems: Business Innovation, Environment and Wage Difference
- Part 3 Design of Open Inter-Firm Network
- Part 4 Incentive System of Profit and Loss Allocation
- Part 5 Theoretical Analysis for Incentive Price
- Part 6 Note on the Management Philosophy on which the Collaboration by the Incentive Price is Based
- References
- Index