![]()
Part I
Operations Management
![]()
Chapter 1
Product and Service Innovation
Learning Objectives
1.Understand the meaning of innovation.
2.Understand the meaning of product and service.
3.Understand the application of product and service innovation.
4.Case studies on the application of product and service.
Introduction
A product is not just a specific commodity, an intangible service is also a product. Hence, physical goods, service, experiences, people, places, rights, concepts, and creative ideas are all part of a product. Section 1.2 of this chapter discusses the procedures entrepreneurs should adopt in commercializing a product during the development process of a new product. Section 1.3 presents the service-related issues and introduces service quality model. Case studies are then used to discuss how different companies use science and technology to improve service quality. Finally, section 1.4 introduces two research methods, KANO model and TRIZ theory. We introduced these two research methods because KANO model can be used to analyze the relationship between product attributes and customer satisfaction; and the TRIZ theory helps to provide a systematic and theoretical framework for solutions to the problems (Domb, 1998). At the same time the TRIZ theory also helps researchers and innovators to develop more feasible results (Ruchti and Livotov, 2001; Su et al., 2008). These two methods are useful scientific analysis methods for the development phase of product and service innovation when starting a business.
1.1.The Meaning of Innovation
Innovation means “change,” which is to apply a new concept on a product or service (Huang and Hong, 2005). Robbins and Coulter (2002) pointed out that innovation is the process of translating new ideas into useful products and services. Certo (2003) believed that innovation is the integration of technological and management innovation, by merging new ideas into products, processes, and organizational policies. In addition, Huang and Hong (2005) pointed out that innovation is a form of value conviction. With information technology (IT) and other technologies, innovation turns creativity into specific ideas, and then creates special products, technologies, and services. We may sum up the three characteristics of innovation, as follows:
1.Innovation is a concept, an idea.
2.Innovation is transformed into products, services, processes, and so on with the help of technology.
3.Innovation can be applied on various levels including intangible services, processes, policies, or tangible products and equipment.
Porter’s (1991) Five Forces Analysis shows that the competitive advantage of a corporation in the marketplace is not only affected by their own ability, but also by upstream companies, downstream companies, competitors, and potential competitors. When companies come up with innovative ideas, they seek suggestions through discussions within the organization or outside the organization. If the innovative ideas of a company are decided via discussions within the organization, it is called closed innovation. On the other hand, a company will be affected by the flow of the organization’s internal staff, the stimulation of the organization’s external partners and the number of upstream and downstream companies. When a company is affected by the above factors, it promotes a company from closed innovation into open innovation.
As the market environment is rapidly changing, enterprises need to be able to adjust their strategy and layout accordingly and timely in order to become more competitive in the market. Therefore, companies cannot be cut off from external resources, but must be able to keep up the interaction with the outside world for providing more added value to the company’s products (Li et al., 2012). The concept is similar with open innovation which advocates that companies make use of external resources to create higher value (Chesbrough, 2007).
Case 1 IBM embracing free software Linux
Chesbrough (2003) pointed out that IBM was known for its internal technology development and therefore, appeared to people as a mysterious company. With the changes in the market environment, IBM changed its attitude and started to accept external partners such as free software Linux. After IBM accepted Linux, IBM received hundreds of software patents, and their annual patent licensing income went up to US$10 billion.
1.2.The Meaning of Product
1.2.1.The meaning of product
Kotler and Armstrong (2004) pointed out that a product can meet consumers’ desire or need. A product is anything that we can buy and use from the market which includes physical goods, services, experiences, worlds, people, places, interests, and creative ideas. Under the broad meaning of a product, we will introduce the levels, classification, and development processes of a product accordingly.
1.2.1.1.Levels of product
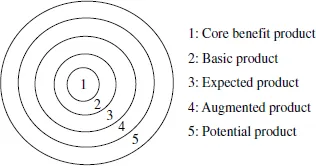
Kotler (1999) pointed out that a product can be divided into five levels according to their form and meaning, namely, core benefit product, basic product, expected product, augmented product, and potential product. In terms of graphical representation see Figure 1.1, followed by the description of the five points:
1.Core benefit product
The core benefit of a product refers to the fundamental core attributes that make a customer purchase and use the product. For example, when consumers buy mobile phones, the function of the phone is part of the core benefit of the product. Or when a consumer purchases a travel package, the safety of the customer’s journey is part of the core benefit of the product.
Figure 1.1Levels of a product
2.Basic product
A basic product refers to products that can turn the core benefit into a product with specific features. Using the same example of the mobile phone, the basic product of a mobile phone is its high call quality and aesthetic design.
3.Expected product
Expected product is the expected extra benefit when consumers purchase a product. For instance, when a customer buys a mobile phone the aesthetic design and product warranty are its expected product.
4.Augmented product
Augmented product is a product’s differentiation. For instance, sales can provide gifts and consulting services to attract consumers to buy a specific mobile phone.
5.Potential product
A potential product is a product that can meet consumers’ additional and future needs. For instance, if we combine mobile phones and solar power so that customers can rely on both the power charge and solar charging function, this technology can enhance consumers’ needs to use a phone with long battery life.
From the above we can see that “core benefit product” and “basic product” are the basic elements to meet consumers’ demand for a product or a service. “Expected product,” “augmented product” and “potential product” are the parts which can create added value. Therefore, in establishing new businesses, it is recommended that the design of “core benefit product” and “basic product” are a basic requirement to meet consumers’ demand in design of products and services. If the entrepreneurs want to create more added value for customers, they can focus on “expected product,” “augmented product,” and “potential product.”
Case 2 Snowflake ice: Charmy
Charmy, a food company with 15 franchises in the whole world has established “Charmy House” snowflake ice flagship shop in Kaohsiung. Unlike the traditional ice store, Charmy House consumers can enjoy a comfortable environment with French windows and green streets. You can say that consumers not only eat the delicious ice cream, but also enjoy a comfortable atmosphere when they visit the shop.
Snowflake ice which is as fine as snowflake is made of smashed ice. Charmy is successful in producing this kind of ice. If consumers hold a tray filled with fine ice pieces and breathe out through their mouth, the ice will dance like snowflakes. It shows how meticulously Charmy makes the ice.
Another innovation is that snowflake ice itself has added flavors. Consumers can have red or yellow snowflake ice besides the white snowflake ice. In addition, Charmy developed salty ice cream with such flavors as meat floss and ham. All the innovations on snowflake ice enhanced the added value for consumers when they taste it.
Currently Charmy is planning to develop a packed snowflake ice service for customers to enjoy DIY at home. What makes this packed service special is that consumers can buy packed ice only and freeze it in their refrigerator. Whenever they want to have a taste of snowflake ice, they just need to add fruits, jams, and other seasonings to it and they can have a taste of a unique homemade snowflake ice.
Charmy offers a variety of flavored snow ice, comfortable dining space, and convenient DIY snowflake ice, undoubtedly enhancing the product’s added value to consumers.
In this case, Charmy satisfied consumers’ basic requirements (i.e, “core benefit product,” “basic product”) on food products, f...