
Bayesian Networks in Fault Diagnosis
Practice and Application
- 420 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Bayesian Networks in Fault Diagnosis
Practice and Application
About this book
Fault diagnosis is useful for technicians to detect, isolate, identify faults, and troubleshoot. Bayesian network (BN) is a probabilistic graphical model that effectively deals with various uncertainty problems. This model is increasingly utilized in fault diagnosis.
This unique compendium presents bibliographical review on the use of BNs in fault diagnosis in the last decades with focus on engineering systems. Subsequently, eleven important issues in BN-based fault diagnosis methodology, such as BN structure modeling, BN parameter modeling, BN inference, fault identification, validation, and verification are discussed in various cases.
Researchers, professionals, academics and graduate students will better understand the theory and application, and benefit those who are keen to develop real BN-based fault diagnosis system.
Contents:
- Fault Diagnosis
- Multi-Source Information Fusion-Based Fault Diagnosis of Ground-Source Heat Pump Using Bayesian Network
- A Data-Driven Fault Diagnosis Methodology in Three-Phase Inverters for PMSM Drive Systems
- A Real-Time Fault Diagnosis Methodology of Complex Systems Using Object-Oriented Bayesian Networks
- A Dynamic Bayesian Network-Based Fault Diagnosis Methodology Considering Transient and Intermittent Faults
- An Integrated Safety Prognosis Model for Complex System Based on Dynamic Bayesian Network and Ant Colony Algorithm
- An Intelligent Fault Diagnosis System for Process Plant Using a Functional HAZOP and DBN Integrated Methodology
- DBN-Based Failure Prognosis Method Considering the Response of Protective Layers for Complex Industrial Systems
- Fault Diagnosis for a Solar-Assisted Heat Pump System Under Incomplete Data and Expert Knowledge
- An Approach for Developing Diagnostic Bayesian Network Based on Operation Procedures
- A DBN-Based Risk Assessment Model for Prediction and Diagnosis of Offshore Drilling Incidents
- A Fault Diagnosis Methodology for Gear Pump Based on EEMD and Bayesian Network
Readership: Researchers, academics, professionals and graduate students in systems engineering, industrial engineering and mechanical engineering.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1.1.Introduction
1.2.Overview of BNs
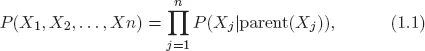
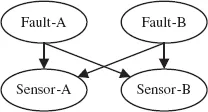
1.3.Procedures of Fault Diagnosis with BNs
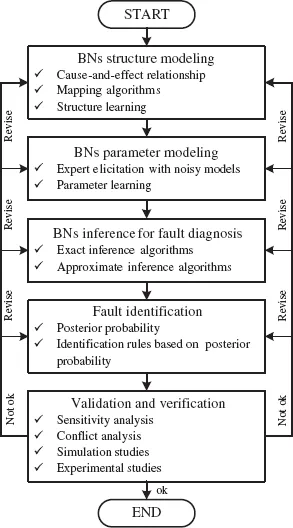
1.3.1.BN structure modeling
Table of contents
- Cover
- Halftitle
- Title
- Copyright
- Preface
- Contents
- 1. Fault Diagnosis
- 2. Multi-Source Information Fusion-Based Fault Diagnosis of Ground-Source Heat Pump Using Bayesian Network
- 3. A Data-Driven Fault Diagnosis Methodology in Three-Phase Inverters for PMSM Drive Systems
- 4. A Real-Time Fault Diagnosis Methodology of Complex Systems Using Object-Oriented Bayesian Networks
- 5. A Dynamic Bayesian Network-Based Fault Diagnosis Methodology Considering Transient and Intermittent Faults
- 6. An Integrated Safety Prognosis Model for Complex System Based on Dynamic Bayesian Network and Ant Colony Algorithm
- 7. An Intelligent Fault Diagnosis System for Process Plant Using a Functional HAZOP and DBN Integrated Methodology
- 8. DBN-Based Failure Prognosis Method Considering the Response of Protective Layers for Complex Industrial Systems
- 9. Fault Diagnosis for a Solar-Assisted Heat Pump System Under Incomplete Data and Expert Knowledge
- 10. An Approach for Developing Diagnostic Bayesian Network Based on Operation Procedures
- 11. A DBN-Based Risk Assessment Model for Prediction and Diagnosis of Offshore Drilling Incidents
- 12. A Fault Diagnosis Methodology for Gear Pump Based on EEMD and Bayesian Network
- Index