
Ordinary Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems
Volume II: Boundary Value Problems
- 344 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Ordinary Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems
Volume II: Boundary Value Problems
About this book
The authors give a systematic introduction to boundary value problems (BVPs) for ordinary differential equations. The book is a graduate level text and good to use for individual study. With the relaxed style of writing, the reader will find it to be an enticing invitation to join this important area of mathematical research. Starting with the basics of boundary value problems for ordinary differential equations, linear equations and the construction of Green's functions are presented clearly.
A discussion of the important question of the existence of solutions to both linear and nonlinear problems plays a central role in this volume and this includes solution matching and the comparison of eigenvalues.
The important and very active research area on existence and multiplicity of positive solutions is treated in detail. The last chapter is devoted to nodal solutions for BVPs with separated boundary conditions as well as for non-local problems.
While this Volume II complements Volume I: Advanced Ordinary Differential Equations, it can be used as a stand-alone work.
Contents:
- Introduction to Boundary Value Problems
- Linear Problems and Green's Functions
- Existence of Solutions I
- Existence of Solutions II
- Solution Matching
- Comparison of Smallest Eigenvalues
- BVP's for Functional Differential Equations
- Positive Solutions
- Boundary Data Smoothness
- Nodal Solutions of BVP's fpr PDE's
Readership: Undergraduate and graduate students as well as researchers who are interested in ordinary differential equations.
Key Features:
- This book is unique in that the title is descriptive of its contents, it addresses a range of questions that are timely and provides avenues for additional research, and the exercises and examples nicely illustrate the theory
- There are literally hundreds of researchers who work in the field of boundary value problems for ordinary differential equations, for functional differential equations, and for finite difference equations. This book touches each of those topics, in more depth for some, and only on the surface for others
- BVPs for functional differential equations are discussed in a separate chapter that can be omitted in a first reading
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Chapter 1
Introduction to Boundary Value Problems
1.1Introduction

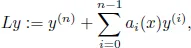
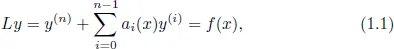
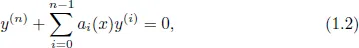
1.2Disconjugacy

Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Preface
- Contents
- 1. Introduction to Boundary Value Problems
- 2. Linear Problems and Green’s Functions
- 3. Existence of Solutions I
- 4. Existence of Solutions II
- 5. Solution Matching
- 6. Comparison of Smallest Eigenvalues
- 7. BVP’s for Functional Differential Equations
- 8. Positive Solutions
- 9. Boundary Data Smoothness
- 10. Nodal Solutions of BVP’s for ODE’s
- Index