
- 352 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Spectroscopic Properties of Natural Flavonoids
About this book
This book offers physical characteristics and spectral data of 150 selected natural compounds arranged according to their chemical structures in various sub-classes. These include natural source, molecular formula, chemical structure, physical characteristics (melting point, molecular weight, and specific rotation) and detailed spectral data (UV, FT-IR, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, 2D-NMR, Mass) along with their assignments for each compound.
Contents:
- Acacetin 7-O-(3-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranoside)
- Aciculatinone
- Afzelin A
- Apigenin-4′- O -(2″- O - p -coumaroyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside
- Bismurrangatin
- Citrumedin-B
- Denticulatain C
- Eriodictyol 7- O -(6″-feruloyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside
- Flemingichromone
- Hirsutissimiside A
- Hovenin B
- Kaempferol 3- O -β-D-apiofuranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside
- Lawsochrysin
- Murrmeranzin
- Noidesol A
- Ormosinol
- Oxytropisoflavan A
- Peregrinumin A
- Phellamurin
- Polygonflavanol A
- Quercetin 4′- O -α-rhamnopyranosyl-3- O -β-D-allopyranoside
- Sophoranone
- Tomentodiplacol
- Tupichinol A
- Vogelin H
- Yunngnin A
- and other papers
Readership: Natural product chemists, synthetic chemists; phytochemists; medicinal chemists; pharmacologists; industrial research groups developing drugs from natural compounds and their analogues; pharmaceutical companies; manufacturers of herbal and ayurvedic medicines and cosmetic products; manufacturers of natural products; advanced and research students.
Key Features:
- This is the first comprehensive guidebook on natural flavonoids. It presents the actual spectral and physical data along with natural sources rather than just references to the data
- This information within will be of great benefit to organic chemists, natural product chemists, synthetic chemists, medicinal chemists and pharmacologists
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Amyrisin B [5,7-dihydroxy-2- (4-((2-hydroxy-3-methylbut-3-en-1-yl)oxy)phenyl)-6-methoxy-4H-chromen-4-one]
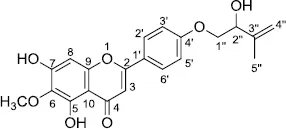
Reference
Amyrisin C [5,7-Dihydroxy-6-methoxy-2-(3-methoxy-4-((3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)oxy)phenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one]
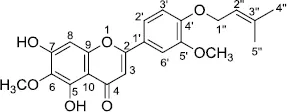
Reference
Angepubebisin
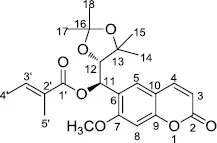
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Abbreviations
- Foreword
- Preface
- Contents
- Acacetin 7-O-(3-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranoside)
- 6″′-O-Acetyl amurensin
- (2R,3R)-2″-Acetyl astilbin [(2R,3R)-5,7,3′, 4′-tetrahydroxyflavanonol 2″-acetylrhamnoside]
- Aciculatinone
- Afzelin A [6,7-(2″,2″-dimethylpyrano)-3,5,4′-trihydroxyflavanone]
- Afzelin C [7,6-(2″,2″-dimethylpyrano)-5-hydroxy-3, 4′-(3,3-dimethylallyloxy)flavone]
- Amyrisin B [5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-((2-hydroxy-3-methylbut-3-en-1-yl)oxy)phenyl)-6-methoxy-4H-chromen-4-one]
- Amyrisin C [5,7-Dihydroxy-6-methoxy-2-(3-methoxy-4-((3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)oxy)phenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one]
- Angepubebisin
- Apigenin-4′-O-(2″-O-p-coumaroyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside
- Apigenin 6-C-[2″-O-(E)-feruloyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl]-8-C-β-D-glucopyranoside
- Apigenin 8-C-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)]-α-D-glucopyranoside
- Apigenosylide C
- Aquisiflavoside [4′,5-dihydroxy-3′,7-dimethoxyflavone 5-O-β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside]
- Artelasticinol
- Artelastoheterol [5,2′,4′,5′-tetrahydroxy-6,7-(2,2-dimethyl-6H-pyrano)-8-prenyl-3-(9-hydroxy)prenyl-flavone]
- Asphodelin A 4′-O-β-D-glucoside
- Bismurrangatin
- Brosimacutin K [(2S)-3′,4′-dihydroxy-7,8- (2,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-4H-pyrano)-flavan]
- Celtiside A [Isoswertisin 8-C-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl- (1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside]
- Celtiside B [7-Methoxyluteolin 8-C-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl- (1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside]
- Citrumedin-B
- Corbulain Ib [2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-3,4,9,10-tetrahydro-3,5-dihydroxy-10-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-(2R,3R,10S)-2H,8H-benzo[1,2-b:3,4-b′]dipyran-8-one]
- Cyanidin 3-O-(2″-(5″′-(E-p-coumaroyl)-β-apiofuranosyl)-β-xylopyranoside)-5-O-β-glucopyranoside
- 7-De-O-methylaciculatin [8-C-β-D-digitoxopyranosylapigenin]
- Delphinidin 3-O-β-galactopyranoside-3′,5′-di-O-β-glucopyranoside
- Denticulatain C
- Denticulatain D
- Devenyol
- (2R,3S)-6,8-Di-C-methyldihydrokaempferol
- (3R)-2′,7-Dihydroxy-3′-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-2′′′, 2′″-dimethylpyrano[5′″,6′″:4′,5′]isoflavan
- (3R)-5,4′-Dihydroxy-2′-methoxy-3′-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-(6″,6″-dimethylpyrano)-(7,6:2″,3″)-isoflavanone
- 5,2′-Dihydroxy-3,6,7-trimethoxyflavone-5-O-β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-β-D-glucopyranoside
- 5,4′-Dihydroxy-8-(3″-methylbut-2″-enyl)-2′″-(4′″-hydroxy-4′″-methylethyl)furano-[4′″,5′″;6,7]isoflavone
- 5,6-Dihydroxy-7,8,4′-trimethoxyflavone
- 5,7-Dihydroxy-6-(2″-hydroxy-3″-methylbut-3″-enyl)-4′-methoxylisoflavone
- 5,7-Dihydroxy-6,8,4′-trimethoxyflavone
- 5,7-Dihydroxy-8-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-4-phenyl-2H-chromen-2-one
- 5,7-Dihydroxy-8,3′,5′-trimethoxyflavone
- 7,4′-Dihydroxy-6,8-dimethoxy-4-phenylcoumarin
- 7,8-Dihydroxy-3-(3-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-pyran-2-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one
- 8,4″-Dihydroxy-3″,4″-dihydrocapnolactone-2′,3′-diol
- (2R,3R)-2-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5-dihydroxy-8,8-dimethyl-2,3-dihydropyrano[2,3-f]-chromen-4(8H)-one
- (2R,3R)-2-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-8-prenyl-chroman-4-one
- 3′,5′-Dimethoxy-[2″,3″:7,8]-furanoflavone
- 7,4′-Dimethylapigenin-6-C-β-glucopyranosyl-2″-O-α-L-arabinopyranoside
- Eriodictyol 7-O-(6″-feruloyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside
- Eriodictyol 7-O-sophoroside [Eriodictyol-7-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1 → 2)-β-D-glucopyranoside]
- 7-O-Feruloylorientin
- Flemingichromone
- Fleminginin
- 3′-Formyl-5,4′-dihydroxy-7-methoxyisoflavone
- 7-O-β-D-Glucopyranosylchamaejasmin
- Griffinoid A
- Griffinoid D
- (+)-Hexanoyllomatin
- Hildegardiol [(3R)-6,2′-dihydroxy-7-methoxy-4′,5′-methylenedioxyisoflavan]
- Hirsutissimiside A [formononetin 7-O-β-D-(6″-ethylmalonyl)-glucopyranoside]
- Hovenin A
- Hovenin B
- Hovenin C
- (2R)-5-Hydroxy-7,8-dimethoxy flavanone-5-O-β-D-glucopyranoside
- (2S)-3′-(2-Hydroxy-3-methylbut-3-enyl)licoflavone-4′-methyl ether
- 2′-Hydroxy-3,4-dimethoxy-[2″,3″:4′,3′]-furanochalcone
- 2′-Hydroxy-6,4′,6″,4′″-tetramethoxy-[7-O-7″]-bisisoflavone
- 5-Hydroxy-3,7-dimethoxy-4′-prenyloxyflavone
- 5-Hydroxy-6,8-dimethoxy-3′,4′-methylenedioxyflavone
- 5-Hydroxy-7,8,2′,4-tetramethoxyflavone
- 5-Hydroxy-8,8-dimethyl-4-phenyl-9,10-dihydropyrano [2,3-f]chromen-2(8H)-one
- 7-Hydroxy-4′-methoxy-3′-(3-hydroxy-3-methyl-trans-but-1-enyl)-5′-(3-methylbut-2-enyl) flavanone
- 7-Hydroxy-6,4′-dimethoxy-isoflavonequinone
- 7-Hydroxy-6-methoxy-3,8-bis(3-methyl-2-butenyl)coumarin
- 6-Hydroxyluteolin 7-O-laminaribioside [6-hydroxyluteolin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)-β-D-glucopyranoside]
- Irilone 4′-O-[β-D-glucopyrano-(1→6)-O-β-D-glucopyranoside]
- Kaempferol 3-O-β-D-apiofuranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside
- Khonklonginol A [3,5-Dihydroxy-4′-methoxy-6″,6″-dimethylpyrano(2″,3″:7,6)-8-(3′″,3″′-dimethylallyl) flavanone]
- Khonklonginol E [3,5-Dihydroxy-4′-methoxy-6″,6″-dimethylpyrano(2″,3″:7,6)-8-(3′″,3′″-dimethyl-2′″, 3″′-dihydroxypropyl)flavanone]
- Khonklonginol F [3,5-Dihydroxy-4′-methoxy-6″, 6′-dimethylpyrano(2″,3″:7,6)-8-(3′″;, 3″′-dimethylallyl)flavone]
- Kurzphenol B
- Lawsochrysin (5-hydroxy-6-n-pentyl-7-n-pentyloxyflavone)
- Lawsonaringenin [4′,5-dihydroxy-7-(4″-pentenyloxy)flavanone]
- Licoflavanone-4′-O-methyl ether
- Liquiritigeninyl-(I-3,II-3)-naringenin
- Luteolin 7-O-[6″-(3′″-hydroxy-4′″-methoxy cinnamoyl)]-β-D-glucopyranoside
- Lyratin B
- Malvidin 3-O-[6-O-(3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl)-β-glucopyranoside]
- 3-Methoxy-(3″,4″-dihydro-3″,4″-diacetoxy)-2″, 2″-dimethylpyrano-(7,8:5″,6″)-flavone
- 7-Methoxy-2″-O-(2′″-methylbutyryl)orientin
- 6-Methoxykaempferol-3-O-β-D-gentiobioside [6-methoxy-3,5,7,4′-tetrahydroxyflavon 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→6)-O-β-D-glucopyranoside]
- 5-Methoxyl-4,2′-epoxy-3-(4′,5′-dihydroxyphenyl)-linear pyranocoumarin
- (2R,3R)-6-Methylaromadendrin 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside
- 3′,4′-Methylenedioxy-[2″,3″:7,8]-furanoflavonol
- N-8-Methylquercetin-3-O-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→6)]-β-D-galactopyranosyl])-3-hydroxypiperidin-2-one
- Murrmeranzin
- Naringenin 5-methyl ether
- Nervilifordin A [Rhamnocitrin-3-O-β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-glucopyranoside]
- Nervilifordin E [4′-O-β-D-glucopyranosylrhamnetin-3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(4→1)-β-D-glucopyranoside]
- Noidesol A
- Ormosinol [5,7,2′,4′-tetrahydroxyl-6,8,5′-tri-(γ,γ-dimethylallyl) isoflavanone]
- Ormosinoside [Isoprunetin-7-O-β-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside
- Oxytropisoflavan A
- Pavietin
- Pelargonidin 3-(2″-(6′″-E-sinapoyl-β-glucopyranosyl)-6″-(E-p-coumaroyl)-β-glucopyranoside)-5-β-glucopyranoside
- 5,6,2′,5′,6′-Pentamethoxy-3′,4′-methylenedioxyflavone
- Peregrinumin A [Acacetin-7-O-(2,3-O-diacetyl-α-L-rhamnosyl)-(1→6)-β-D-glucoside]
- Phellamurin
- (2R)-Phellodensin-F
- Pisonianone [5,7,2′-Trihydroxy-6-methoxy-8-methylisoflavone]
- Pisonivanol [(2R,3R)-3,7-dihydroxy-5,6-dimethoxyflavanone]
- Pisonivanone [(2S)-5,7,2′-trihydroxy-8-methylflavanone]
- Platyisoflavanone A [(S)-5,7-dihydroxy-2′,4′-dimethoxy-3′-(3″-methylbut-2″-enyl)-isoflavanone]
- Polygonflavanol A
- Pongamone A [7-(γ,γ-Dimethylallyloxy)-8,4′-dimethoxy-isoflavone]
- Pongamone C [(2S)-3′,4′-Methylenedioxy-6-γ, γ-dimethylallylpyrano [5″,6″:7,8]-flavanone]
- Praeroside VI [cis-Khellactone-3′-O-β-D-apiofuranosyl (1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside]
- Protoapigenone
- Quercetin 3-O-[2′″,6″′-O-diacetyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside]
- Quercetin-3-O-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→6)]-β-D-galactopyranosyl]-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside
- Quercetin 3-O-β-D-apiofuranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside
- Quercetin 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-4″,6″-digallate[2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5, 7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl-4,6-bis-O-α-D-(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl) glucopyranoside]
- Quercetin 4′-O-α-L-arabinofuranoside [2-Hydroxy-4-O-α-L-(3,5,7-trihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-2-yl) phenylarabinofuranoside]
- Quercetin 4′-O-α-rhamnopyranosyl-3-O-β-D-allopyranoside
- Rotundaflavone Ia
- Sarcandracoumarin
- Sarmenoside VII [Limocitrin 3-O-(6-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl)-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside]
- Siamenol A
- Sophoranone [3,5,7,3′-Tetrahydroxy-2′,4′-dimethoxy-5′-prenylisoflavanone]
- Sophoronol A
- Sophoronol C
- Terpurinflavone [7-Acetoxy-8-(3″-acetoxy-2″, 2″-dimethyltetrahydro-4″-furanyl)flavone]
- 2,3′,4,4′-Tetrahydroxy-3,5′-diprenylchalcone
- 5,7,3′,4′-Tetrahydroxy-3,6-diprenylflavone
- 5,7,2′,2′-Tetrahydroxyflavone 7-O-β-D-glucuronopyranoside
- (2S)-5,7,3′,4′,-Tetramethoxyflavanone
- Tomentodiplacol
- (2R,3R)-3,4′,7-Trihydroxy-3′-prenylflavanone
- (3S)-2′,4′,5-Trihydroxy-[5″-(1,2-dihydroxy-1-methylethyl)-dihydrofurano(2″,3″:7,8)]-isoflavanone
- (3S)-7,2′,4′-Trihydroxy-5,5′-dimethoxy-6-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-isoflavan
- 5,2′,4′-Trihydroxy-7-methoxy-5″-(3-methylbuten-2-yl) isoflavone
- 5,7,2′-Trihydroxy-8-methoxyflavone 7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside
- 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-8-p-hydroxybenzyldihydroflavonol
- (2S)-6,3′,4′-Trimethoxy-[2″,3″:7,8]-furanoflavanone
- 4′,5,6-Trimethoxyisoflavone-7-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→4)-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranosyl(1→3)-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→6)]-β-D-glucopyranoside
- Tupichinol A [(2R,3R)-3,4′-Dihydroxy-7-methoxy-8-methylflavan]
- Tupichinol E [3,5,4′-Trihydroxy-7-methoxy-8-methylflavone]
- Tupichinol F [5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3-methoxy-8-methylflavone]
- Vogelin H [7,4′-Dihydroxy-8-(γ, γ-dimethylallyl)-2″ξ-(4″-hydroxyisopropyl)dihydrofurano [1″,3″:5,6]isoflavone]
- Vogelin I [7,4′-Dihydroxy-8-[(2′″ξ,3′″-dihydroxy-3″′-methyl)butyl]-2″,2″-dimethyl-3″,4″-dehydropyrano [1″,4″:5,6]isoflavone]
- Yunngnin A
- Yunngnoside A [Apterin monoacetate]