
- 272 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Essentials of Ophthalmology: For Medical School and Beyond is a concise reference text for the medical undergraduates and residents, but the contents will also benefit family physicians who really are the first line of eye-care givers in the community.
Highly illustrated with 200 colour clinical pictures and illustrations, the book is written by the multi-disciplinary faculty of the Department of Ophthalmology, National University Health System, Singapore. The authors constantly asked themselves 'how much is too much' and deliberately attempted to weed out any 'excess' for the benefit of the target readers. The content is written in a point format with lucid language.
Emphasis has been focused on information that constitutes essential ophthalmic 'core conditions and problems' of the current medical undergraduate curriculum. Every section in the book has 'learning objectives' and a 'take home message' to facilitate quick learning. The book embraces a practical guide to the study of ocular diseases, basic methods of investigations and treatment where applicable.
Contents:
- Basic Anatomy of the Eye, Adnexa and Visual Pathways (Jeyabal Preethi, Koh Teck Chang Victor)
- Cornea and External Eye Diseases (Chai Hui Chen Charmaine, Anna Marie Tan Wee Tien, Ray Manotosh)
- Cataract (Chai Hui Chen Charmaine, Anna Marie Tan Wee Tien, Ray Manotosh)
- Glaucoma (Koh Teck Chang Victor, Chen Ziyou David)
- Uveitis (Chan Hwei Wuen, Dawn Lim Ka-Ann)
- Vitreoretinal Disorders (Yuen Yew Sen, Paul Zhao Song Bo)
- Oculoplastics (Stephanie Ming Young, George Thomas Naveen, Shantha Amrith, Gangadhara Sundar)
- Paediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus (Lam Sing Harn Janice, Cheryl Ngo Shufen)
- Neuro-Ophthalmology (Lin Hui'en Hazel Anne, Clement Tan Woon Teck)
- Principles and Practice of Low Vision Rehabilitation (Daniel Bohan)
- Clinical Approaches:
- Approach to Leukocoria (Lam Sing Harn Janice)
- Clinical Pathway for Chronic Visual Loss (Jeyabal Preethi, Koh Teck Chang Victor)
- Clinical Pathway for Acute Visual Loss (Lin Hui'en Hazel Anne)
- Diagnostic Flowchart in an Acute Red Eye (Chai Hui Chen Charmaine, Anna Marie Tan Wee Tien, Ray Manotosh)
- Neuro-ophthalmology Approaches (Lin Hui'en Hazel Anne)
- Pupil Examination (Lin Hui'en Hazel Anne)
- Clinical Examinations:
- Approaches to Visual Acuity (Jeyabal Preethi, George Naveen Thomas)
- Cover Test (Lam Sing Harn Janice)
- Normal Fundus Examination (Yuen Yew Sen)
- Visual Fields by Confrontation (Lin Hui'en Hazel Anne)
Readership: Medical undergraduates, residents, primary eye-care providers.
Key Features:
- The book is designed to incorporate knowledge and skills to prepare the undergraduate medical students for their NUS rotation within Ophthalmology
- The content is written in summarized point format with lucid language that is supplemented with more than 200 high resolution clinical pictures and illustrations
- Atlas of coloured images which illustrates concepts, anatomy, conditions, treatment and common complications related to the Asian population
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Chapter 1
BASIC ANATOMY OF THE EYE, ADNEXA AND VISUAL PATHWAYS
1.1Basic Anatomy
Sclera
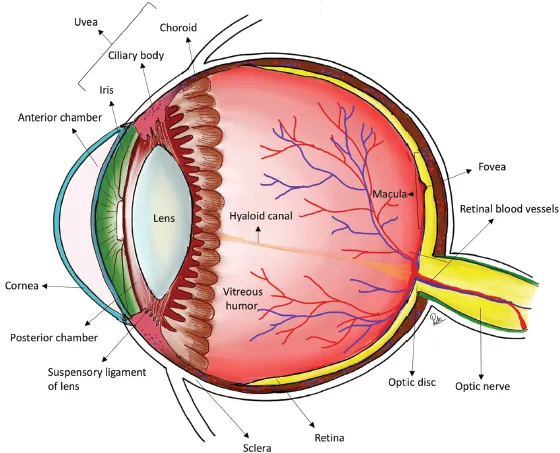


Uveal tissue



Retina
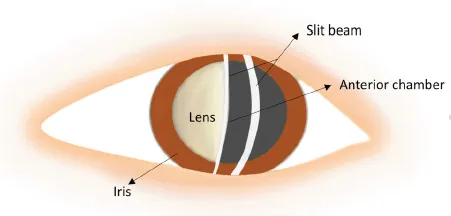
1.2Cornea
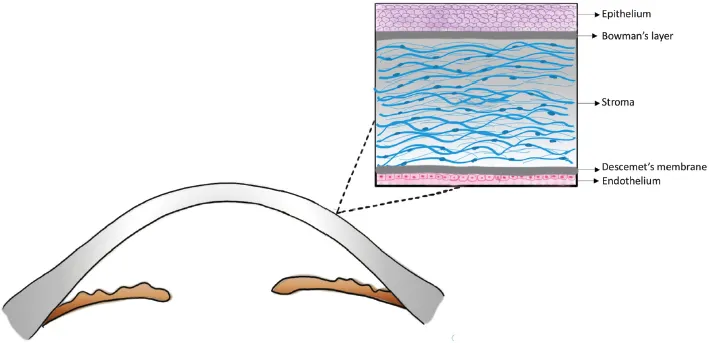
Epithelium
Bowman’s Layer
Stroma
Descemet’s Membrane
Endothelium
Nerve Supply of the Cornea
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Contents
- Foreword
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- About the Editors
- List of Contributors
- Chapter 1 Basic Anatomy of the Eye, Adnexa and Visual Pathways
- Chapter 2 Cornea and External Eye Diseases
- Chapter 3 Cataract
- Chapter 4 Glaucoma
- Chapter 5 Uveitis
- Chapter 6 Vitreoretinal Disorders
- Chapter 7 Oculoplastics
- Chapter 8 Paediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus
- Chapter 9 Neuro-Ophthalmology
- Chapter 10 Principles and Practice of Low Vision Rehabilitation
- Chapter 11 Clinical Approaches
- Chapter 12 Clinical Examinations
- Glossary
- Index