
eBook - ePub
Digital Signal Processing
- 168 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Digital Signal Processing
About this book
This book covers the fundamentals of digital signal processing (DSP) in a concise format, accessible to anyone with a technical background, enabling the reader for further DSP training, research, and development.
The authors explore many subjects, including discrete time (digital) signals and systems, with emphasis on linear shift invariant (LSI) systems; Fourier and the z transforms; signal sampling and analog-to-digital (A/D) conversion. The book ends with examples of DSP techniques applications to practical problems from several areas.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
CHAPTER 1
DISCRETE-TIME SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS
1.1 INTRODUCTION
A discrete-time signal is a sequence of values usually representing the behavior of a physical phenomenon. In electrical engineering problems, those values are samples of a continuous-time-varying electrical signal taken at uniform rate, called sampling rate or sampling frequency. The inverse of the sampling rate is called sampling interval or sampling period. Figure 1.1 shows the graphical representations of a continuous-time signal and its discrete-time uniformly sampled version. For the latter, time is normalized by the sampling period becoming the index n. This can be stated as:

where T is the sampling period.
In practice, continuous-time or analog signals are electrical events (voltage or current) representing the behavior of some physical phenomenon such as speech or temperature as a function of time. Devices known as transducers are utilized to convert physical variations (of pressure or temperature, for example) into voltage or electrical current changes, thus creating an electrical signal. To be digitally processed, electrical signals have to be sampled, time discretized, quantized, and encoded, thus becoming a digital signal.
Therefore, a digital signal is a discrete-time signal, as represented in Figure 1.1(b), for which the amplitude is quantized, that is, it is constrained to assume values in a finite set. Quantization is usually accomplished by rounding or truncating the amplitude sample to the nearest value in the discrete set. It is always present in digital signal processing, as samples must be stored in finite length registers. Chapter 3 analyzes the sampling and quantization processes.
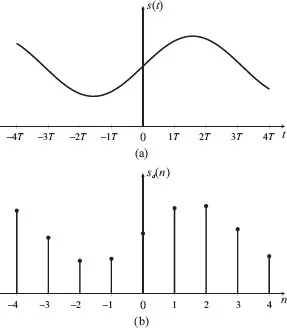
Figure 1.1. (a) Continuous-time signal s(t), (b) Discrete-time signal sd(n) = s(nT).
In this chapter, we present the main properties of discrete-time signals, demonstrate how those signals are affected by operations on the independent variable, and introduce some signals that are important in digital signal processing.
1.2 PROPERTIES OF DISCRETE-TIME SIGNALS
Most properties of continuous-time (analog) signals are also common to discrete-time (digital) signals. In this section, we review some relevant properties to digital signal processing.
1.2.1 PERIODICITY
A discrete-time signal is periodic if there exists an integer N such that:

for any value of n. The integer N is called the period of the signal.
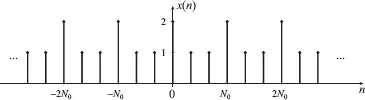
Figure 1.2. Discrete-time periodic signal (segment) with period N0.
Equation 1.2 holds for any integer multiple of N. Figure 1.2 shows a periodic signal where N0 is the smallest value that period N can assume, called fundamental period. Thus, this signal is periodic for any period N = kN0, k integer. Equation 1.2, thus, generalizes to:
1.2.2 POWER AND ENERGY
The energy of a discrete-time signal x(n) is defined as:

The average ...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half-title Page
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Contents
- List of Figures
- List of Tables
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- 1 Discrete-Time Signals and Systems
- 2 Discrete-Time Signal Transforms
- 3 Sampling and Analog To Digital Conversion
- 4 Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform
- 5 Digital Filters
- 6 Applications
- Recommended Readings
- About the Author
- Index
- Backcover
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Digital Signal Processing by João Marques de Carvalho, Edmar Candeia Gurjao, Luciana Ribeiro Veloso, Carlos Danilo Miranda Regis in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Computer Science General. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.