
- 268 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Numeracy for Teaching
About this book
`The stated aim of this book is to help teacher-trainees prepare for the numeracy test all new entrants to the profession now have to pass. Any trainee worried about the test should find this a useful resource…. As in similar books by Derek Haylock, the mathematical content is written in a clear and accessible style? - Mike Askew, Times Educational Supplement
Quotes from the author?s students
`The book is excellent. I think it will present students and others with a valuable resource, not only to help with the QTS test, but also for teaching. I could see myself using it on "dip-in-as-necessary" basis?.
`The practice questions were really helpful for checking and consolidating learning. The material was useful for the QTS test, particularly the mental calculations. Many thanks for letting me work through your sample material. I cannot begin to tell you how much more I have learnt! This has definitely made me feel more confident about passing the QTS numeracy skills test! I have definitely demonstrated to myself from this material that my ability to complete calculations mentally has increased. I can calculate faster and with some accuracy now!?
`Comprises a very helpful resource for students who are obliged to succeed in passing the QTS numeracy test in order to gain QTS. It should provide a valuable resource for students to increase their confidence as well as their competence? - Mathemtics in Schools
This book is designed to help teacher-trainees prepare for the Qualified Teaching Standards numeracy test that must now be passed by all entrants to the teaching profession. The author focuses especially on weaknesses in numeracy often observed in adults, and in teacher-trainees in particular. As far as possible, this mathematics is set in the professional context of teaching, drawing on statistics and other data from individual schools, the DfEE and the Qualifications and Curriculum Agency (QCA).
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Check-Up

| a) | A quarter of the pupils in my class have free school meals. |
| b) | Three-quarters of the pupils in my class do not have free school meals. |
| c) | Seven out of eight pupils in primary schools like their teacher. |
| d) | This year our school had to employ a supply teacher 17 days out of 20. |
| e) | Four-fifths of the lessons observed by Ofsted in our school were good or very good. |
| f) | A total of 273 pupils out of 300 achieved at least one GCSE at grade C or above. |
Answers to check-up 1
| a) 25% of the pupils… | b) 75% of the pupils… | c) 87.5% of primary pupils… |
| d) 85% of the days… | e) 80% of the lessons… | f) 91% of the pupils… |
Discussion and explanation of check-up 1



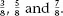
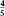
See also…
- Per cent means ‘for each hundred’ (e.g. 35% means ‘35 out of 100’)
- A proportion can be written as a percentage, by working out the equivalent number out of a hundred (e.g. ‘7 out of 20’ is ‘35 out of 100’, which is 35%; ‘240 out of 300’ is ‘80 out of 100’, which is 80%).
- The percentage equivalents of many simple proportions (such as ) should be memorised.
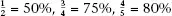
Further practice
| 1.1 | Work out the equivalent percentages for the following fractions and then commit them all to memory! |
| 1.2 | A pupil... |
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Contents
- Read this first
- Check-up 1: Mental calculations, changing proportions to percentages
- Check-up 2: Mental calculations, changing more proportions to percentages
- Check-up 3: Decimals and percentages
- Check-up 4: Understanding data presented in tables
- Check-up 5: Two-way tables for comparing two sets of data
- Check-up 6: Bar charts and frequency tables for discrete data
- Check-up 7: Bar charts for grouped discrete data
- Check-up 8: Bar charts for continuous data
- Check-up 9: Finding a fraction of a quantity
- Check-up 10: Fractions to decimals and vice versa
- Check-up 11: Expressing a percentage in fraction notation
- Check-up 12: The commutative laws
- Check-up 13: The associative laws
- Check-up 14: The distributive laws
- Check-up 15: Using a four-function calculator, precedence of operators
- Check-up 16: Using a four-function calculator for money calculations
- Check-up 17: Using the memory on a four-function calculator
- Check-up 18: Using a calculator to express a proportion as a percentage
- Check-up 19: Rounding answers
- Check-up 20: Very large and very small numbers
- Check-up 21: Mental calculations, multiplication strategies
- Check-up 22: Mental calculations, division strategies
- Check-up 23: Mental calculations, finding a percentage of a quantity
- Check-up 24: Finding a percentage of a quantity using a calculator
- Check-up 25: Adding and subtracting decimals
- Check-up 26: Mental calculations, adding lists
- Check-up 27: More multiplication strategies
- Check-up 28: More division strategies
- Check-up 29: Multiplication with decimals
- Check-up 30: Division with decimals
- Check-up 31: Using approximations to check your answers
- Check-up 32: Mental calculations, time
- Check-up 33: Knowledge of metric units of length and distance
- Check-up 34: Knowledge of metric units of area and solid volume
- Check-up 35: Knowledge of other metric units
- Check-up 36: Mental calculations, money
- Check-up 37: Simplifying ratios
- Check-up 38: Sharing a quantity in a given ratio
- Check-up 39: Increasing or decreasing by a percentage
- Check-up 40: Expressing an increase or decrease as a percentage
- Check-up 41: Finding the original value after a percentage increase or decrease
- Check-up 42: Calculating means
- Check-up 43: Modes
- Check-up 44: Medians
- Check-up 45: Upper and lower quartiles
- Check-up 46: Measures of spread, range and inter-quartile range
- Check-up 47: Box-and-whisker diagrams
- Check-up 48: More box-and whisker diagrams
- Check-up 49: Percentiles
- Check-up 50: Reading scatter graphs
- Check-up 51: Scatter graphs and correlation
- Check-up 52: Conversion graphs
- Check-up 53: Interpreting pie charts
- Check-up 54: Substituting into formulas
- Check-up 55: Weighted means
- Check-up 56: Combining means or percentages from two or more sets of data
- Check-up 57: Understanding cumulative frequency graphs
- Check-up 58: Cumulative frequency graphs, finding the median and quartiles
- Check-up 59: Line graphs for representing data over time
- Check-up 60: Bar charts for comparing two sets of data
- Check-up 61: The notion of value-added
- Check-up 62: Interpreting value-added graphs
- Answers to Further Practice Questions
- Sources of Data
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app