
- 256 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
100 Statistical Tests
About this book
This expanded and updated Third Edition of Gopal Kanji?s best-selling resource on statistical tests covers all the most commonly used tests with information on how to calculate and interpret results with simple datasets.
Each entry begins with a short summary statement about the test?s purpose, and contains details of the test objective, the limitations (or assumptions) involved, a brief outline of the method, a worked example and the numerical calculation.
This new edition also includes:
" A brand new introduction to statistical testing with information to guide the reader through the book so that even non-statistics students can find information quickly and easily
" Real-world explanations of how and when to use each test with examples drawn from wide range of disciplines.
" A useful Classification of Tests table
" All the relevant statistical tables for checking critical values
100 Statistical Tests: Third Edition is the one indispensable guide for users of statistical materials and consumers of statistical information at all levels and across all disciplines.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
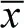
- It is necessary that the population variance σ2 is known. (If σ2 is not known, see the t-test for a population mean (Test 7).)
- The test is accurate if the population is normally distributed. If the population is not normal, the test will still give an approximate guide.
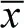

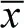
- Both populations must have equal variances and this variance σ2 must be known. (If σ2 is not known, see the t-test for two population means (Test 8).)
- The test is accurate if the populations are normally distributed. If not normal, the test may be regarded as approximate.
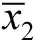
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Half Title Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- feedback
- Contents
- Acknowledgements
- Preface
- List of Common Symbols
- Introduction to the Book
- . Introduction to Statistical Testing
- Examples of Test Procedures
- List of Tests
- Classification of Tests
- The Tests
- List of Tables
- Tables
- References
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app