
The SAGE Handbook of Remote Sensing
- 568 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
The SAGE Handbook of Remote Sensing
About this book
Remote Sensing acquires and interprets small or large-scale data about the Earth from a distance. Using a wide range of spatial, spectral, temporal, and radiometric scales Remote Sensing is a large and diverse field for which this Handbook will be the key research reference.
Organized in four key sections:
• Interactions of Electromagnetic Radiation with the Terrestrial Environment: chapters on Visible, Near-IR and Shortwave IR; Middle IR (3-5 micrometers); Thermal IR ; Microwave
• Digital sensors and Image Characteristics: chapters on Sensor Technology; Coarse Spatial Resolution Optical Sensors ; Medium Spatial Resolution Optical Sensors; Fine Spatial Resolution Optical Sensors; Video Imaging and Multispectral Digital Photography; Hyperspectral Sensors; Radar and Passive Microwave Sensors; Lidar
• Remote Sensing Analysis - Design and Implementation: chapters on Image Pre-Processing; Ground Data Collection; Integration with GIS; Quantitative Models in Remote Sensing; Validation and accuracy assessment;
• Remote Sensing Analysis - Applications: LITHOSPHERIC SCIENCES: chapters on Topography; Geology; Soils; PLANT SCIENCES: Vegetation; Agriculture; HYDROSPHERIC and CRYSOPHERIC SCIENCES: Hydrosphere: Fresh and Ocean Water; Cryosphere; GLOBAL CHANGE AND HUMAN ENVIRONMENTS: Earth Systems; Human Environments & Links to the Social Sciences; Real Time Monitoring Systems and Disaster Management; Land Cover Change
Illustrated throughout, an essential resource for the analysis of remotely sensed data, the SAGE Handbook of Remote Sensing provides researchers with a definitive statement of the core concepts and methodologies in the discipline.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1 Remote Sensing Scale and Data Selection Issues
Keywords
- remote sensing data
- scale
- spectral scale
- spatial scale
- temporal scale
- radiometric scale.
Introduction
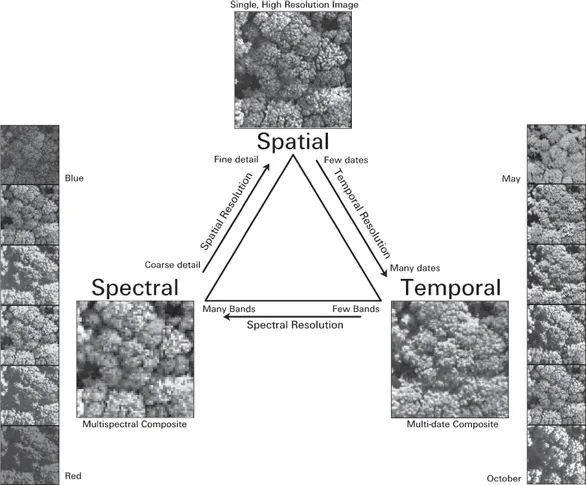
Source: Figure reproduced from T. Key, T. Warner, J. McGraw, and M. A. Fajvan, 2001. A comparison of multispectral and multitemporal imagery for tree species classification. Remote Sensing of Environment 75: 100–112.
- The scale problem, which focuses on how results may vary as the size of the aggregation units (pixels, in the typical remote sensing analysis) varies.
- The zoning (or aggregation) problem, which focuses on how the results may vary as the shape, orientation and position of the units vary, even as the number of aggregation units is held constant.
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Acknowledgements
- Contents
- Preface
- Notes on Contributors
- Section I Introduction
- 1 Remote Sensing Scale and Data Selection Issues
- 2 Remote Sensing Policy
- Section II Electromagnetic Radiation and the Terrestrial Environment
- 3 Visible, Near-IR, and Shortwave IR Spectral Characteristics of Terrestrial Surfaces
- 4 Interactions of Middle Infrared (3–5 μm) Radiation with the Environment
- 5 Thermal Remote Sensing in Earth Science Research
- 6 Polarimetric SAR Phenomenology and Inversion Techniques for Vegetated Terrain
- Section III Digital Sensors and Image Characteristics
- 7 Optical Sensor Technology
- 8 Fine Spatial Resolution Optical Sensors
- 9 Moderate Spatial Resolution Optical Sensors
- 10 Coarse Spatial Resolution Optical Sensors
- 11 Airborne Digital Multispectral Imaging
- 12 Imaging Spectrometers
- 1 Active and Passive Microwave Systems1
- 14 Airborne Laser Scanning
- Section IV Remote Sensing Analysis: Design and Implementation
- 15 Radiometry and Reflectance: From Terminology Concepts to Measured Quantities
- 16 Pre-Processing of Optical Imagery
- 17 Surface Reference Data Collection
- 18 Integrating Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems
- 19 Image Classification
- 20 Quantitative Models and Inversion in Optical Remote Sensing
- 21 Accuracy Assessment
- Section V Remote Sensing Applications
- A. Lithospheric Sciences
- 22 Making Sense of the Third Dimension through Topographic Analysis
- 23 Remote Sensing of Geology
- 24 Remote Sensing of Soils
- B. Plant Sciences
- 25 Remote Sensing for Studies of Vegetation Condition: Theory and Application
- 26 Remote Sensing of Cropland Agriculture
- C. Hydrospheric and Cryospheric Sciences
- 27 Optical Remote Sensing of the Hydrosphere: From the Open Ocean to Inland Waters
- 28 Remote Sensing of the Cryosphere
- D. Global Change and Human Environments
- 29 Remote Sensing for Terrestrial Biogeochemical Modeling
- 30 Remote Sensing of Urban Areas
- 31 Remote Sensing and the Social Sciences
- 32 Hazard Assessment and Disaster Management Using Remote Sensing
- 33 Remote Sensing of Land Cover Change
- Section VI Conclusions
- 34 A Look to the Future
- Appendix. Acronyms
- Index