![]()
Chapter 1
Introducing Data-driven Content
There is more information being collected today than at any other stage during human existence. As you might expect, a substantial amount of this data can be used for enhancing your existing marketing content, plus creating new marketing material that works harder, plus contributing more towards your professional and business goals.
This wealth of new data poses a substantial threat and untapped opportunity for individuals, practitioners and businesses alike, when it comes ideating and producing effective business and marketing content, as well as keeping in touch of the growing online and offline competition.
To put new data growth into context, every minute Google completes 3.6 million searches, 103 billion spam emails are sent and 69 thousand hours of video is streamed on Netflix, and that’s just the beginning.
Based on IBM data, 90% of all data available to us today were created in the past two years; this equates to 2.5 quintillion bytes of data created every day, demonstrating the rapid changes in data availability, and the business opportunity to leverage this wealth of ever-increasing data for new insights, actions and a competitive company advantage.
Data-driven Content
Data-driven Marketing Content: A Practical Guide empowers you to identify, understand and act on ever-changing data to make meaning from the deep data dilemma.
Everyone can have access to data-driven insights, which can turn mundane, thinner value content into purposeful, positioned marketing materials created with the user in mind, and is able to deliver results regardless of medium, marketing channel or intended audience.
Businesses and practitioners in all industries are at a point where they know there is a need to understand and use data more effectively to create result-based content, but the informational barriers to entry are often high.
For companies to succeed, they need to act fast and confident that the practical and strategic marketing content decisions they make, combined with the resource they deploy, are going to deliver end results faster and more frequently.
This is where Data-driven Marketing Content: A Practical Guide helps.
This book explores the data-driven content opportunity, shares practical tips and expertise generated over thousands of business and marketing content projects and empowers you to make more successful content choices.
As you use this guide you will find chapter summaries, important term definitions and practical tips and advice, helping you to delve further into material that interests you the most, remove informational barriers sooner and digest information faster.
The Data-driven Content Process
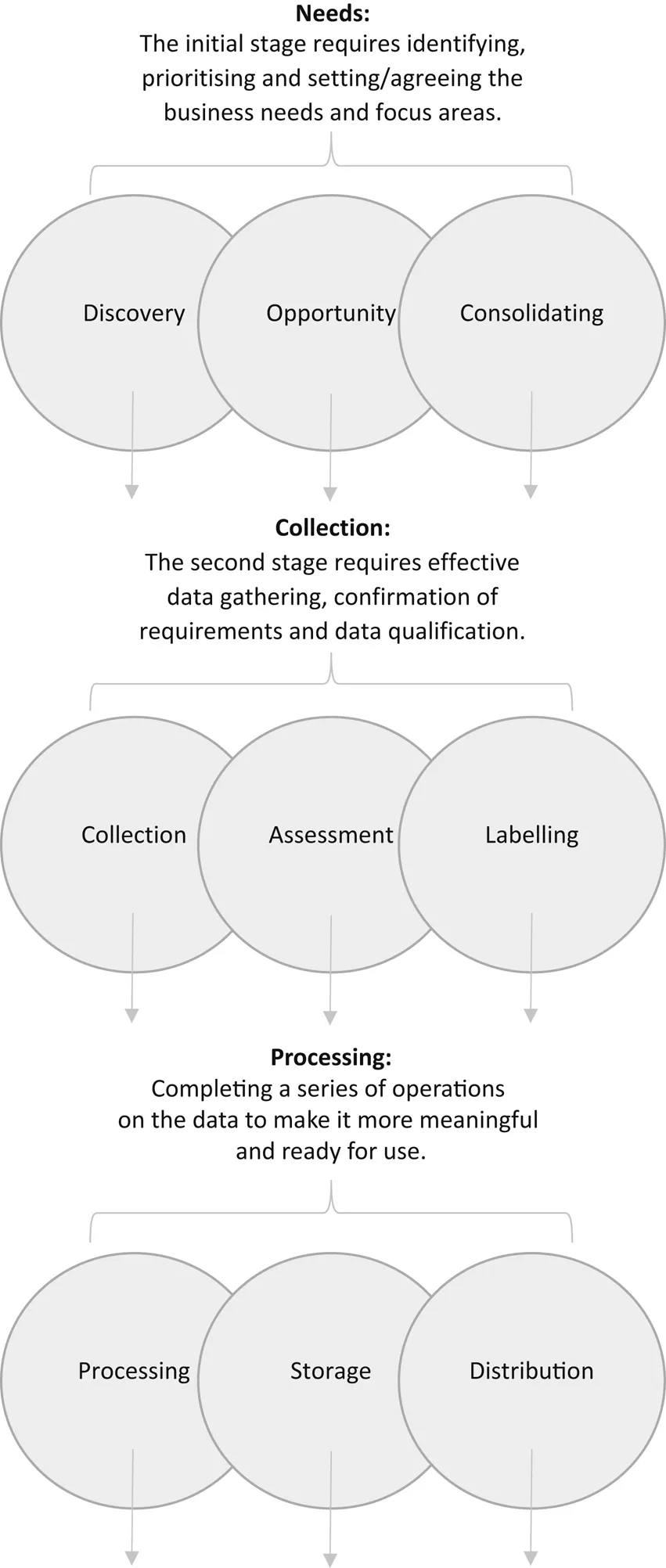
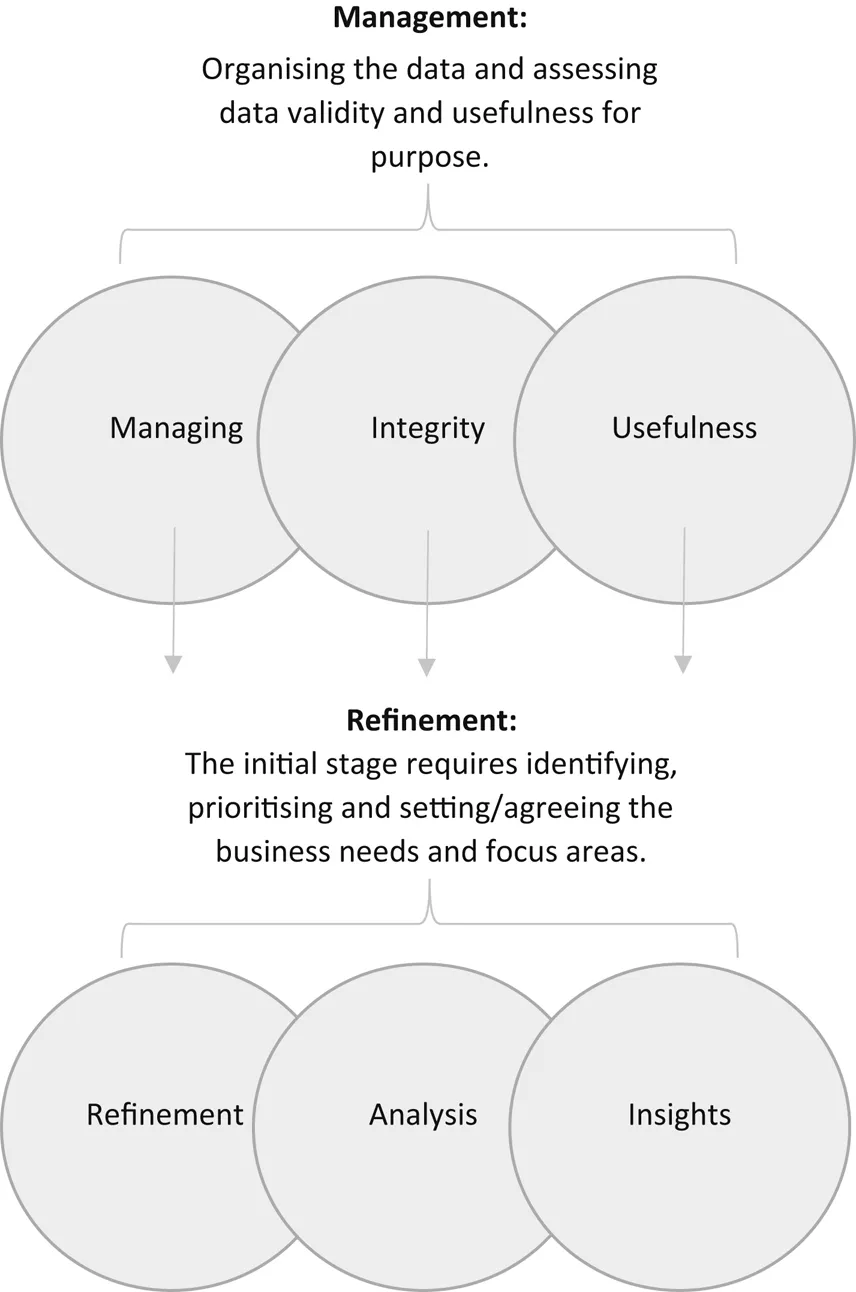
The data-driven content process to follow when developing a repeatable system for marketing content creation that works can be effectively segmented into five stages:
- Needs: data discovery, opportunity and consolidating needs
- Collection: data collection, assessment and labelling
- Processing: data processing, storage and distribution
- Management: data managing, integrity and usefulness
- Refinement: data refinement, analysis and insights
Over the next few sections, we provide visualisations of this process in action, plus each segment previously referred to is discussed in greater detail.
Needs: Data Discovery, Opportunity and Consolidating Needs
The needs stage of the data-driven content process centres on the end user goals, objectives and desired outcomes from the data.
By putting clearly defined business data needs in place and matching these with solution-orientated outcomes and objectives, it becomes possible to outline expectations and describe practically what a successful data-led project looks like.
This ‘needs phase’ determines the attention of the collection stage.
Collection: Data Collection, Assessment and Labelling
Only once business data needs have been identified and agreed, can the collection stage begin.
Whilst it is likely you have a number of data discovery points in place already, it is necessary to take a step back from what’s already present and contemplate what can potentially become available to fulfil your business data requirements. This provides a more comprehensive data collection body of work and expected improved foundation for future insights derived.
In most cases you will have silos of disparate business intelligence and data, which will require collecting into a single place. This assists you in the recombination of separate data points and sources for added and unique gains.
Once the data collection is at a required level of completion, you will need to review its accuracy, usefulness and compatibility for purpose. This can be a fairly succinct process and likely fairly subjective.
Practical Tip. As a quick tip, it is worth encouraging wider teams, staff and stakeholder involvement at this time. It is much easier to modify and add to data sets now rather than retrospectively.
When combining data sets and gathering information in a single database, you need to label everything. Labelling data is about making data meaningful and informative. Sharing suggested labels, and gathering wider team input through crowdsourcing feedback is critical for future usability and insights.
Processing: Data Processing, Storage and Distribution
As you may have noticed, the steps within the data-driven content process tend to overlap and integrate between phases.
The data processing phase considers the usefulness of the information derived from the data.
This functional step takes raw data and transforms them into processed information which is effectively stored for repeat use and distributed to the end users.
With each step of the process, you need to reflect on the successful application of the completed phase, re-evaluate whether it has delivered on all of the priority areas and needs identified then confirm this with stakeholders and end users.
You will want to limit assumed positive outcomes as much as possible while you progress to encourage data integrity later on.
Management: Data Managing, Integrity and Usefulness
Organising and managing your data is concerned with ensuring the data you have meet the current, changing and ongoing needs or your organisation.
Fundamental characteristics of this body of work include the ongoing maintenance of the data, the integrity of it and making sure it is fit for purpose.
Data management and assessed usefulness of work can often sit more effectively with key staff who are also end users of the data. This is primarily due to the fact that it will be their changing needs and outputs that are fundamentally dependant on the data usefulness.
Data integrity will usually be reliant upon the development and IT teams, accountable for data collection and processing; however, a feedback loop needs to be in place for any user to improve the value and usefulness from the data by reporting back to relevant departments: bugs, refinement, improvements and ideas.
The more that the wider company is included at the early stages of data-driven content, the easier it is to expedite the process and include these type of approaches within wider company departments and the business culture as a whole.
Refinement: Data Refinement, Analysis and Insights
The end goal of data refinement is the development of an integrated data source, which has successfully combined previous separate and dispersed data sets into a final product ready for new use.
Part of this stage involves creating commonality between the data points and the removal of vulnerabilities so that the data have a shared purpose and usefulness for gleaming fresh insight and analysis from.
It can be beneficial to consider this final part of the data-driven content process as an outcome, which refines data potential into information ready for analysis, insights and actions.
The Data-driven Content Process Chart
Fig. 1.1 gives you the visual representation of the data-driven content process in action.
Fig. 1.1.The Data-driven Content Process Chart.
Overcoming the Big Data Gulf
The quandary that this rapid influx of data is causing is that the super brands are able to invest heavily into turning these data into meaningful insight and immediate next actions; however, this is creating an ever-increasing gulf with the remaining 99% of businesses.
This big data gulf is no more present anywhere else than when it comes to creating effective business and marketing content that delivers on its objectives. The gap is more noticeable online, and this is reflected in this guide, but it is not exclusively so.
If you want to create digital marketing content that works, reflects the changing needs of your audience, and delivers results regardless of device and channel, big data is the competitive advantage you are not yet maximising.
It’s important to mention at this time that data-driven content is not only about marketing content but also a changing approach towards creating any purposeful business content online or offline.
Big Data
Big data is a term most businesses and marketing professionals will have heard frequently over the past few years, with growing momentum and buzzword popularity since 2015. As you might expect, the term ‘big data’ can mean many things to various people; however, for the purposes of this book:
‘Big data refers to large data sets that can be analysed, interrogated and processed in order to provide new meaning, value and understanding.’
Big data can be structured and unstructured, qualitative and quantitative, and is all encompassing.
A key characteristic to keep in mind with big data is the combination of ‘high-volume’ data accessibility and the potential to deliver increased data-driven advantages and insights (primarily to businesses).
Another point to acknowledge is that big data is less about isolated quantities of data, rather an added focus on what you are able to do with the data to make better strategic and tactical decision-making.
The end goal being making more out of every piece of content you create, whether this is for marketing purposes or broader company needs.
The Fundamentals of Big Data
There are four fundamental characteristics to take note of with regard to big data, commonly referred to as ‘The Four V’s’.
You may find other sources citing ‘value’ as a fifth ‘V’, but this is a self-explanatory and an assumed feature, plu...