
- 389 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
The increasing interest in graphene, due to its unique properties and potential applications, is sparking intense research into chemically derived graphene. This book provides a comprehensive overview of the recent and state-of-the-art research on chemically derived graphene materials for different applications.
Starting with a brief introduction on chemically derived graphene, subsequent chapters look at various fascinating applications such as electrode materials for fuel cells, Li/Na-ion batteries, metal–air batteries and Li-S batteries, photocatalysts for degradation of pollutants and solar-to-fuels conversion, biosensing platforms, and anti-corrosion coatings. The emphasis throughout this book is on experimental studies and the unique aspects of chemically derived graphene in these fields, including novel functionalization methods, particular physicochemical properties and consequently enhanced performance.
With contributions from key researchers, the book provides a detailed resource on the latest progress and the future directions of chemically derived graphene for students and researchers across materials science, chemistry, nanoengineering and related fields.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
*E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]
1.1 General Background of Graphite and Its Derivatives
| Product | Graphite | Graphene | Graphite oxide | Graphene oxide | Chemically derived graphene |
| Form | Layered structure (>10 layers) | Monolayer carbon atom | Layered structure with expanded interlayer spacing | Monolayer structure with many defects | Monolayer structure with some defects |
| Powder form | Film | Paste/powder | Suspension/powder | Suspension/powder | |
| Elemental composition | C | C | C, O, H | C, O, H | C, O, H |
| Density (g cm−3) | 2–2.3 | ∼0.77 mg m−2 | Depends on defects | Depends on defects | Depends on defects |
| Electrical conductivity (S m−1) | 2–3 × 105 (in-plane) | 106 (in plane) | Nearly insulator | Nearly insulator | 4600–5880 |
| 3 × 102 (cross-plane) | |||||
| Thermal conductivity (W m−1 K−1) | 2000 (in-plane) 20 (cross-plane) | 5300 (in-plane) | N/A | 1.68–2.21 (in-plane) | 61 (in-plane), 0.09 (cross-plane) |
| Young’s modulus | N/A | 1.06 TPa | N/A | 290–470 GPa | 6.3 GPa |
| Basic synthesis method | Exists in nature | Micromechanical exfoliation, chemical vapor deposition, epitaxial growth, chemically derived methods | Hummers method, Staudenmaier method, Brodie method | Thermal, chemical, electrochemical, exfoliation of graphite oxide | Chemical oxidation–exfoliation–reduction of graphite, liquid exfoliation, solid exfoliation by ball milling, intercalation–exfoliation |
| Main applications | Pencils, batteries, refractories, steel making, brake linings | Fundamental research, semiconductor, energy storage, screen, optoelectronic applications | Intermediate product of CDG, biomedicine, catalysis | Intermediate product of CDG, biomedicine, energy storage, catalysis, environmental protection, sensor, optoelectronic applications | Semiconductor, energy storage, catalysis, optoelectronic applications, biomedicine |
1.2 Preparation Methods and State-of-the-art Research Progress
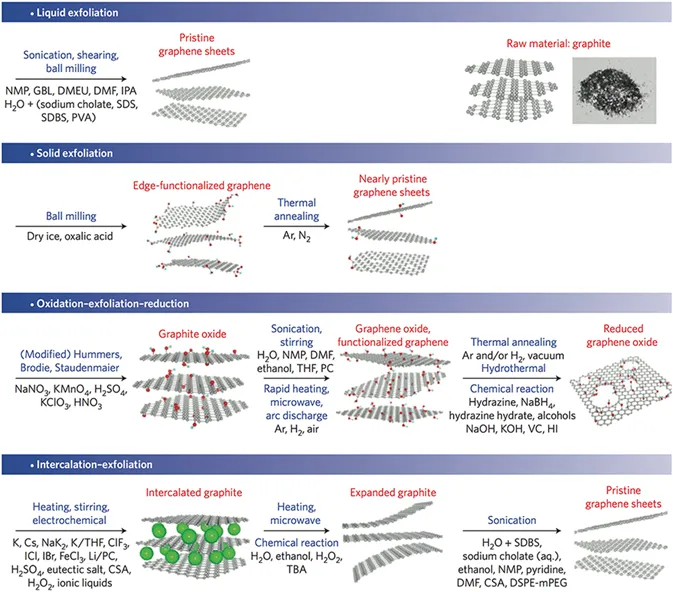
1.2.1 Chemical Oxidation–Exfoliation–Reduction of Graphite
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Preface
- Contents
- Chapter 1 Introduction to Chemically Derived Graphene
- Chapter 2 Preparation and Characteristics of Edge-functionalized Graphene Nanoplatelets and Their Applications
- Chapter 3 Functionalization of Chemically Derived Graphene as Electrode Materials for Fuel Cells
- Chapter 4 Functionalization of Chemically Derived Graphene for Solar Energy Conversion
- Chapter 5 Functionalization of Chemically Derived Graphene for Photocatalysis
- Chapter 6 Graphene-based Materials as Electrodes for Li/Na-ion Batteries
- Chapter 7 Functionalization of Chemically Derived Graphene as Electrode Materials for Metal–Air Batteries
- Chapter 8 Application of Graphene Derivatives in Lithium–Sulfur Batteries
- Chapter 9 Functionalization of Chemically Derived Graphene for High-performance Supercapacitors
- Chapter 10 Functionalization of Chemically Derived Graphene for Flexible and Wearable Fiber Energy Devices
- Chapter 11 Chemically Derived Graphene for Water Purification and Gas Separation
- Chapter 12 Chemically Derived Graphene for Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensing
- Chapter 13 Principle, Properties, and Applications of Graphene and Graphene Oxide as Anticorrosion Coating Materials
- Subject Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app