
Blockchain for Business 2019
A user-friendly introduction to blockchain technology and its business applications
- 258 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Blockchain for Business 2019
A user-friendly introduction to blockchain technology and its business applications
About this book
Your one-stop guide to blockchain technology and its business applications
Key Features
- Assimilate blockchain services such as Ethereum and Hyperledger to transform industrial applications
- Know in and out of blockchain technology to understand various business use cases
- Understand various common and not-so-common challenges faced in blockchain development
Book Description
Blockchain for Business 2019 is a comprehensive guide that enables you to bring in various blockchain functionalities to extend your existing business models and make correct fully-informed decisions. You will learn how decentralized applications are transforming numerous business sectors that are expected to play a huge role in the future. You will see how large corporations are already implementing blockchain technology now. You will then learn about the various blockchain services, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Hyperledger, and others to understand their use cases in a variety of business domains. You will develop a solid fundamental understanding of blockchain architecture.
Moving ahead, you will get to grips with the inner workings of blockchain, with detailed explanations of mining, decentralized consensus, cryptography, smart contracts, and many other important concepts. You will delve into a realistic view of the current state of blockchain technology, along with its issues, limitations, and potential solutions that can take it to the next level.
By the end of this book, you will all be well versed in the latest innovations and developments in the emerging blockchain space.
What you will learn
- Understand the fundamentals of blockchain and how it was developed
- Gain a good understanding of economic concepts and developments
- Develop a base for concepts such as cryptography, computer networking, and programming
- Understand the applications of blockchain and its potential impact on the world
- Become well versed with the latest developments in the blockchain space
- Explore blockchain frameworks, including decentralized organizational structures, networks, and applications
Who this book is for
This book is for financial professionals, business executives, managers, and enthusiasts who are interested in getting well-versed with blockchain technology in various business domains. This book will help boost your existing business models using blockchain services. No prior experience of blockchain is required.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Five Forces of Bitcoin - #1 Blockchain
- Introduction to Bitcoin's five forces
- The first force – blockchain
- Different types of blockchain
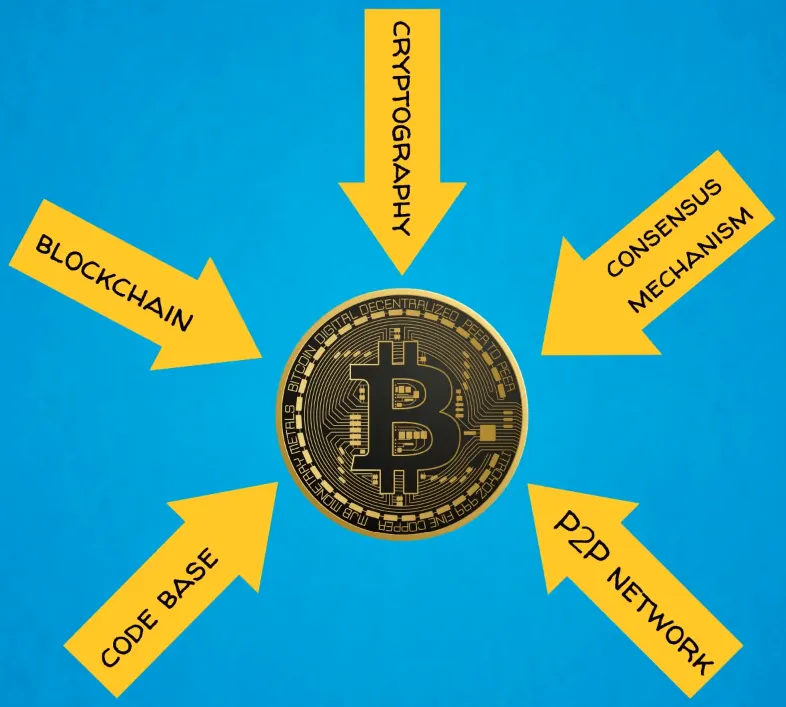
Introduction to Bitcoin's five forces
- Blockchain or distributed ledger technology (DLT)
- Cryptography
- Consensus mechanism rooted in game theory, which, in this case, is Proof-of-Work
- Peer-to-peer network
- Software code base
The first force – blockchain
Why blockchain is better
How blockchain works
Different types of blockchain
- Public or permission-less blockchains
- Private or permissioned blockchains
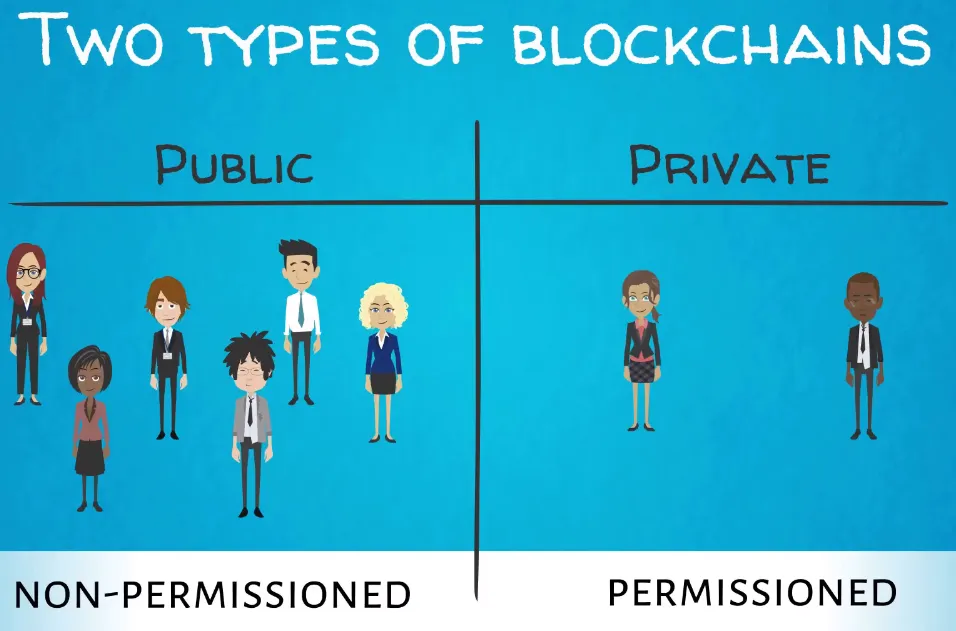
Public blockchains

Private blockchains
Value of blockchain
Areas where blockchain can be handy
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright and Credits
- About Packt
- Contributors
- Preface
- Bitcoin, Blockchain, and Cryptoassets
- A Brief History of Money
- The Birth of Bitcoin and the Advantages of a Decentralized Payment System
- Five Forces of Bitcoin - #1 Blockchain
- Five Forces of Bitcoin - #2 Cryptography
- Five Forces of Bitcoin - #3 Consensus Algorithm
- Five Forces of Bitcoin - #4 P2P Network
- Five Forces of Bitcoin - #5 Software Code Base
- How Ethereum Took the Idea of Blockchain to the Next Level
- Ethereum - A Global Platform for Decentralized Applications
- Blockchains Focused on Specific Sectors and Use Cases
- Corporate Blockchains
- The Disruptive Potential of Blockchain Technology
- Blockchain and AI
- Current Issues and Potential Solutions to Take Blockchain to the Next Level
- Other Books You may Enjoy