
Ensemble Machine Learning Cookbook
Over 35 practical recipes to explore ensemble machine learning techniques using Python
- 336 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Ensemble Machine Learning Cookbook
Over 35 practical recipes to explore ensemble machine learning techniques using Python
About this book
Implement machine learning algorithms to build ensemble models using Keras, H2O, Scikit-Learn, Pandas and more
Key Features
- Apply popular machine learning algorithms using a recipe-based approach
- Implement boosting, bagging, and stacking ensemble methods to improve machine learning models
- Discover real-world ensemble applications and encounter complex challenges in Kaggle competitions
Book Description
Ensemble modeling is an approach used to improve the performance of machine learning models. It combines two or more similar or dissimilar machine learning algorithms to deliver superior intellectual powers. This book will help you to implement popular machine learning algorithms to cover different paradigms of ensemble machine learning such as boosting, bagging, and stacking.
The Ensemble Machine Learning Cookbook will start by getting you acquainted with the basics of ensemble techniques and exploratory data analysis. You'll then learn to implement tasks related to statistical and machine learning algorithms to understand the ensemble of multiple heterogeneous algorithms. It will also ensure that you don't miss out on key topics, such as like resampling methods. As you progress, you'll get a better understanding of bagging, boosting, stacking, and working with the Random Forest algorithm using real-world examples. The book will highlight how these ensemble methods use multiple models to improve machine learning results, as compared to a single model. In the concluding chapters, you'll delve into advanced ensemble models using neural networks, natural language processing, and more. You'll also be able to implement models such as fraud detection, text categorization, and sentiment analysis.
By the end of this book, you'll be able to harness ensemble techniques and the working mechanisms of machine learning algorithms to build intelligent models using individual recipes.
What you will learn
- Understand how to use machine learning algorithms for regression and classification problems
- Implement ensemble techniques such as averaging, weighted averaging, and max-voting
- Get to grips with advanced ensemble methods, such as bootstrapping, bagging, and stacking
- Use Random Forest for tasks such as classification and regression
- Implement an ensemble of homogeneous and heterogeneous machine learning algorithms
- Learn and implement various boosting techniques, such as AdaBoost, Gradient Boosting Machine, and XGBoost
Who this book is for
This book is designed for data scientists, machine learning developers, and deep learning enthusiasts who want to delve into machine learning algorithms to build powerful ensemble models. Working knowledge of Python programming and basic statistics is a must to help you grasp the concepts in the book.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Statistical and Machine Learning Algorithms
- Multiple linear regression
- Logistic regression
- Naive Bayes
- Decision trees
- Support vector machines
Technical requirements
Multiple linear regression
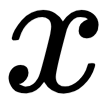



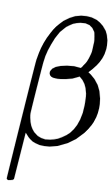
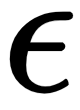



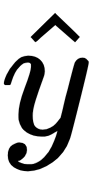
by



Getting ready
# import os for operating system dependent functionalities
import os
# import other required libraries
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Set your working directory according to your requirement
os.chdir(".../Chapter 4/Linear Regression")
os.getcwd()
df_housingdata = pd.read_csv("Final_HousePrices.csv") How to do it...
- First, we'll take a look at the variables and the variable types:
# See the variables and their data types
df_housingdata.dtypes
- We'll then look at the correlation matrix. The corr() method computes the pairwise correlation of columns:
# We pass 'pearson' as the method for calculating our correlation
df_housingdata.corr(method='pearson')
- Besides this, we'd also like to study the correlation between the predictor variables and the response variable: ...
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright and Credits
- About Packt
- Foreword
- Contributors
- Preface
- Get Closer to Your Data
- Getting Started with Ensemble Machine Learning
- Resampling Methods
- Statistical and Machine Learning Algorithms
- Bag the Models with Bagging
- When in Doubt, Use Random Forests
- Boosting Model Performance with Boosting
- Blend It with Stacking
- Homogeneous Ensembles Using Keras
- Heterogeneous Ensemble Classifiers Using H2O
- Heterogeneous Ensemble for Text Classification Using NLP
- Homogenous Ensemble for Multiclass Classification Using Keras
- Other Books You May Enjoy
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app