
- 164 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Step through loading GIS data, creating GIS data, styling GIS and making maps with QGIS following a simple narrative that will allow you to build confidence as you progress.
Key Features
- Work with GIS data, a step by step guide from creation to making a map
- Perform geoprocessing tasks and automate them using model builder
- Explore a range of features in QGIS 3.4, discover the power behind open source desktop GIS
Book Description
QGIS is a user friendly, open source geographic information system (GIS). The popularity of open source GIS and QGIS, in particular, has been growing rapidly over the last few years. This book is designed to help beginners learn about all the tools required to use QGIS 3.4.
This book will provide you with clear, step-by-step instructions to help you apply your GIS knowledge to QGIS. You begin with an overview of QGIS 3.4 and its installation. You will learn how to load existing spatial data and create vector data from scratch. You will then be creating styles and labels for maps. The final two chapters demonstrate the Processing toolbox and include a brief investigation on how to extend QGIS.
Throughout this book, we will be using the GeoPackage format, and we will also discuss how QGIS can support many different types of data.
Finally, you will learn where to get help and how to become engaged with the GIS community.
What you will learn
- Use existing data to interact with the canvas via zoom/pan/selection
- Create vector data and a GeoPackage and build a simple project around it
- Style data, both vector and raster data, using the Layer Styling Panel
- Design, label, save, and export maps using the data you have created
- Analyze spatial queries using the Processing toolbox
- Expand QGIS with the help of plugins, model builder, and the command line
Who this book is for
If you know the basic functions and processes of GIS, and want to learn to use QGIS to analyze geospatial data and create rich mapping applications, then this is the book for you.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Expanding QGIS 3
- Model builder
- Plugins
- Python command line
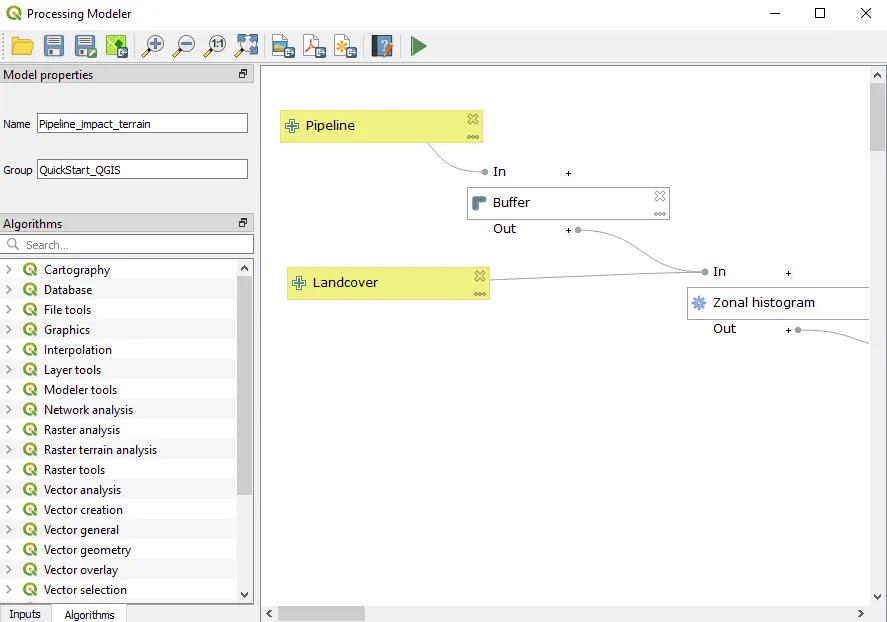
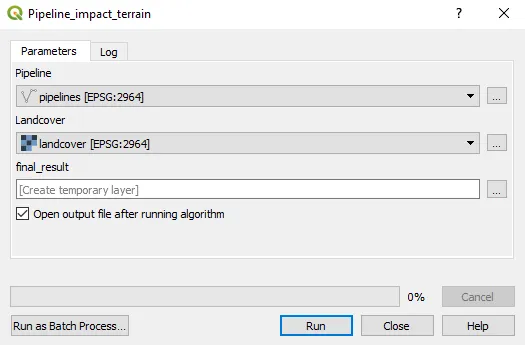
Model builder
Plugins in QGIS
Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright and Credits
- Dedication
- About Packt
- Contributors
- Preface
- Getting Started with QGIS 3
- Loading Data
- Creating Data
- Styling Data
- Creating Maps
- Spatial Processing
- Expanding QGIS 3
- Other Books You May Enjoy