
- 172 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
A quick start guide to visualize your Elasticsearch data
Key Features
- Your hands-on guide to visualizing the Elasticsearch data as well as navigating the Elastic stack
- Work with different Kibana plugins and create effective machine learning jobs using Kibana
- Build effective dashboards and reports without any hassle
Book Description
The Elastic Stack is growing rapidly and, day by day, additional tools are being added to make it more effective. This book endeavors to explain all the important aspects of Kibana, which is essential for utilizing its full potential.
This book covers the core concepts of Kibana, with chapters set out in a coherent manner so that readers can advance their learning in a step-by-step manner. The focus is on a practical approach, thereby enabling the reader to apply those examples in real time for a better understanding of the concepts and to provide them with the correct skills in relation to the tool. With its succinct explanations, it is quite easy for a reader to use this book as a reference guide for learning basic to advanced implementations of Kibana. The practical examples, such as the creation of Kibana dashboards from CSV data, application RDBMS data, system metrics data, log file data, APM agents, and search results, can provide readers with a number of different drop-off points from where they can fetch any type of data into Kibana for the purpose of analysis or dashboarding.
What you will learn
- Explore how Logstash is configured to fetch CSV data
- Understand how to create index patterns in Kibana
- Become familiar with how to apply filters on data
- Discover how to create ML jobs
- Explore how to analyze APM data from APM agents
- Get to grips with how to save, share, inspect, and edit visualizations
- Understand how to find an anomaly in data
Who this book is for
Kibana 7 Quick Start Guide is for developers new to Kibana who want to learn the fundamentals of using the tool for visualization, as well as existing Elastic developers.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Introducing Kibana
- Configure Beats to monitor system metrics, database metrics, and log metrics
- Configure APM to monitor your application metrics and issues if your application platform is supported
- Configure the JDBC plugin of Logstash to pull RDBMS data into Elasticsearch to make it available to Kibana for creating visualizations on KPIs
- There are different third-party plugins that help us to get data from those sources, for example, you can use the Twitter plugin to get Twitter feeds
- You can create alerts for certain thresholds, so that whenever that situation occurs, you get alerts so you don't have to continuously monitor the application
- You can apply machine learning on your data to get data anomalies or future trends by analyzing the current dataset
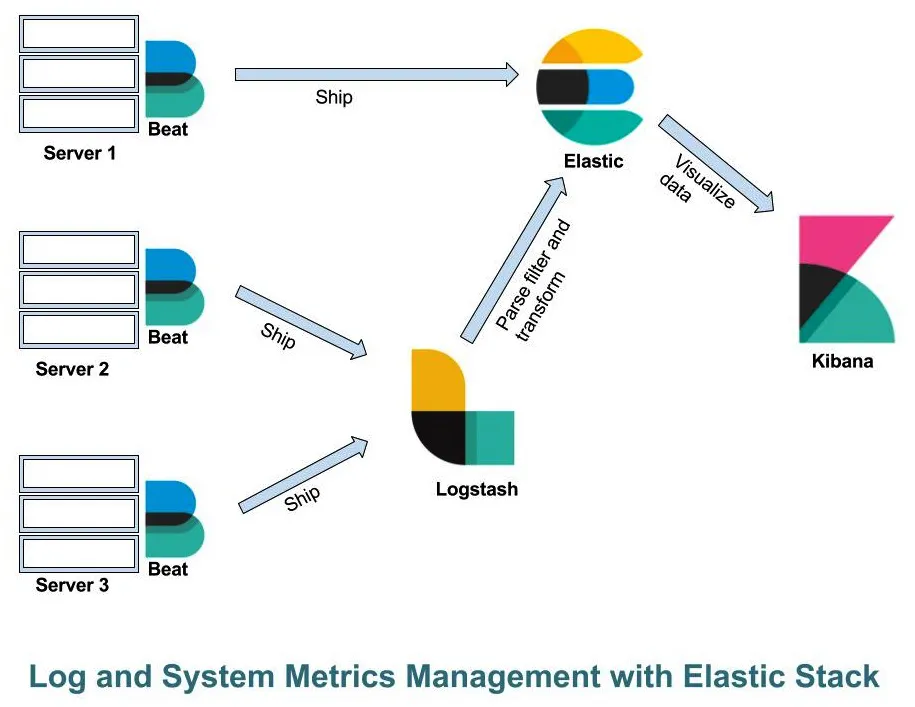
Elastic Stack
- Elasticsearch: We can store data in Elasticsearch.
- Logstash: A data pipeline that we can use to read data from various sources, and can write it to various sources. It also provides a feature to filter the input data before sending it to output.
- Kibana: A graphical user interface that we can use to do a lot of things, which I will cover in this chapter.
- Beats: Lightweight data shippers that sit on different servers and send data to Elasticsearch directly or via Logstash:
- Filebeat
- Metricbeat
- Packetbeat
- Auditbeat
- Winlogbeat
- Heartbeat
Elasticsearch
- Java
- PHP
- Perl
- Python
- .NET
- Ruby
- JavaScript
- Groovy
In fuzzy queries, we match words even then if there's no exact match for the spelling. For example, if we try to search a word with the wrong spelling, we can get the correct result using fuzzy search.
- Cluster: A collection of one or more nodes that work together is known as a cluster. By default, the cluster name is elasticsearch, which we can change to any unique name.
- Node: A node represents a single Elasticsearch server, which is identified by a universally unique identifier (UUID).
- Index: A collection of documents where each document in the collection has a common attribute.
- Type: A logical partition of the index to store more than one type of document. Type was supported in previous versions and is deprecated from 6.0.0 onward.
- Document: A single record in Elasticsearch is known as a document.
- Shard: We can subdivide the Elasticsearch index into multiple pieces, which are called shards. During indexing, we can provide the number of shards required.
Logstash
input
{
file
{
path => "/var/log/apache2/access.log"
}
}
filter
{
grok
{
match => {message => "%{COMBINEDAPACHELOG}"}
}
}
output
{
elasticsearch
{
hosts => "localhost"
}
}
Grok is a tool that we can use to generate structured and queryable data by parsing unstructured data.
Kibana
- Discover your data by exploring it
- Analyze your data by applying different metrics
- Visualize your da...
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright and Credits
- Dedication
- About Packt
- Contributors
- Preface
- Introducing Kibana
- Getting Data into Kibana
- Exploring Data
- Visualizing Data
- X-Pack with Machine Learning
- Monitoring Applications with APM
- Kibana Advanced Tools
- Other Books You May Enjoy
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app