
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
The must-read summary of Eric Reis' book: `The Lean Startup: How Today’s Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses`
This complete summary of the ideas in Eric Reis' book `The Lean Startup` shows that most startups tend to burn through their resources and then disappear because they never get around to seeing what their potential customers think of what they’re developing. With this accessible summary, you will learn how to do just that in a fast and effective way, using the Build-Measure-Learn loop. In the end, you will be able to offer your customers a fully-featured product, which they will love.
Added-value of this summary:
• Save time
• Understand key concepts
• Expand your business knowledge
To learn more, read `The Lean Startup` and discover how to focus efficiently on what your customer really want.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Summary of The Lean Startup (Eric Ries)
The Lean Startup methodology - Vision
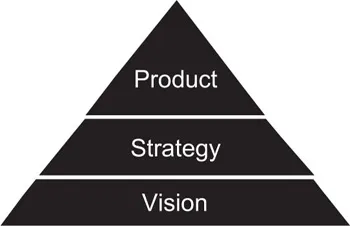
- Someone comes along with a vision which is often a variation of “Let’s go build a thriving business which produces a world-class product that consumers ove.”
- To achieve that vision, a strategy gets developed along the lines of:
- This is the business model we will use.
- Here is our planned product and service lineup.
- We’d like to work with these partners.
- Our competitors will be these firms.
- Our target customers will have these traits.
- The end result of that strategy is a product or service then gets made and sold in the marketplace.
- New customers are being acquired.
- Existing customers are being supported.
- The innovation initiative is happening in the background.
- Fine-tuning of the marketing is going on.
- A decision is being made on whether to change the strategy.
- The product is still being optimized.
institution designed to create a new
product or service under conditions
of extreme uncertainty
- Startups are institutions or bureaucracies whether they like the term or not – they develop processes (often haphazard) for hiring new creative employees, for coordinating their activities, for developing their product and for putting together everything else which will be required to get results. Successful startups are good at processes.
- Startups focus on creating new products and services – by making use of scientific discoveries, new technology, or perhaps repurposing an existing technology for a new use. Sometimes startups will develop new business models which unlock previously hidden value, bring products or services to a new location or to serve a different set of customers. Innovation can take many forms and startups can be formed to commercially harness any of these forms.
- Uncertainty is a given for any startup – which is a challenge because it means most general management tools will not work all that well. These tools are typically intended to be used within an established management structure rather than in the extreme uncertainty in which startups operate. Standard tools like forecasts, yearly budgets, product milestones and detailed business plans don’t work at all well with startups. Different tools are needed when growing a startup.
Table of contents
- Title page
- Book Presentation
- Summary of The Lean Startup (Eric Ries)
- About the Summary Publisher
- Copyright