
Summary: The Strategy Paradox
Review and Analysis of Raynor's Book
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
The must-read summary of Michael Raynor's book: `The Strategy Paradox: Why Committing to Success Leads to Failure (and What to Do About It).
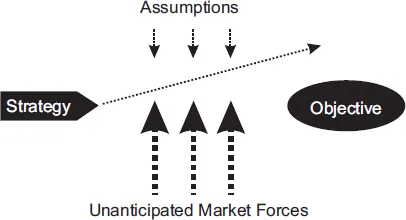
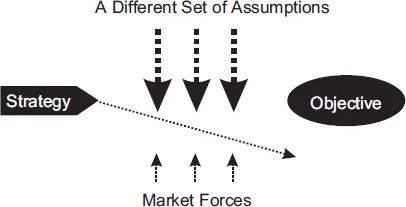
This complete summary of the ideas from Michael Raynor's book `The Strategy Paradox` shows that whenever you develop a strategy to achieve a specific objective, you are also automatically making some implicit assumptions about what the future market forces will be. If that forecast of future market conditions turns out to be incorrect, then your strategy which had a reasonable chance of success might turn out to be an absolute failure. In his book, the author explains that this is the essence of the strategy paradox. This summary explains how to hedge your strategic bets by creating a number of strategic options which can be harnessed depending on the actual marketplace conditions and the four phases of the strategic flexibility process.
Added-value of this summary:
• Save time
• Understand key concepts
• Expand your knowledge
To learn more, read `The Strategy Paradox` and discover the key to protecting your business from failure.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Summary of The Strategy Paradox (Michael Raynor)
The Problem – The Strategy Paradox
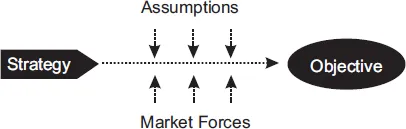
- Most firms accept a lower rate of return by executing a strategy which is not entirely optimized one way or another. This gives them a better chance of survival as the marketplace evolves. These firms don’t maximize their profits because they don’t put all their eggs in the one basket but nor are they bankrupted when the marketplace changes.
- Other companies try and become more adaptable so they can change their strategy as the market shifts. This is fine as long as the firm can continue to change at the same pace as the environment changes. There are however problems when some parts of the organization need to change faster while other parts need to change more sedately. That can cause some serious internal challenges.
- Some companies try and forecast what the market conditions will be like in the future and integrate that into their strategies. That’s fine when you get it right but it is impossible to forecast the future correctly indefinitely. Sooner or later (and probably sooner), your forecasts will end up being wrong. The marketplace has so many random factors which need to be taken into account you just can’t tell whether your predictions will end up being correct or not, even if you have a great track record of past success in forecasting the future. Besides which, an even more fundamental question is do you really want to commit all your resources to back your forecast about what’s going to happen in the future to the hilt?
- Other companies manage strategic uncertainty by using their hierarchies. Different levels of the hierarchy deal with different levels of strategic uncertainty. This typically tends to work out something along these lines:
- The board of directors specify the corporation’s overall exposure to strategic uncertainty and marketplace risk.
- Senior managers hedge the various risks and ensure all options remain viable.
- Operating divisional managers commit to a specific strategy but also work to avoid catastrophes should key assumptions turn out to be invalid.
- Functional managers are charged with delivering short-term results in this quarter or this financial year. They are typically so busy doing that they have little time to be...
Table of contents
- Title page
- Book Presentation
- Summary of The Strategy Paradox (Michael Raynor)
- About the Summary Publisher
- Copyright