
eBook - ePub
High Performance Phthalonitrile Resins
Challenges and Engineering Applications
- 147 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
High Performance Phthalonitrile Resins
Challenges and Engineering Applications
About this book
This book not only introduces the chemistry and physicochemical properties of phthalonitrile resins, but also describes strategies for crosslinking and structural modification. The authors explore blends and composites of phthalonitriles with other high-performance polymers and give an outlook on the future of the field.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access High Performance Phthalonitrile Resins by Augustine Dhanya,Satheesh Chandran,Dona Mathew,C.P. Reghunadhan Nair in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Ciencias físicas & Ciencia medioambiental. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1 Phthalonitriles and state-of-the-art high-performance thermosets
1.1 Introduction to high-performance polymer systems
Rapid pace of advances in modern science and technology demand newer and special materials. Meeting these requirements depends, to a great extent, on the ability to develop tailored materials. High-performance polymers and composites are highly versatile and they can be tuned to the desired forms/formulations to meet the ever-increasing demands of modern technology. The application of polymer has crossed the barriers of household to enter high-tech areas such as electrical, electronics, aerospace and communication satellite-mediated ultra-fast communication. Space and interplanetary travel became a reality, thanks to the phenomenal growth in polymer materials.
High-performance polymers have found widespread utility in everyday life to high-end applications. They have revolutionised the outlook of industrial and aerospace arena and literally materialised the major requirements such as weight reduction and minimal energy dissipation. These are accomplished by architecting monomers and polymers with tailorable functionality, reactivities and backbones. By virtue of the higher strength-to-weight ratio, many polymer matrix composites could outsmart metallic structures [1, 2, 3].
By definition, high-performance polymers are used in applications that demand service at elevated temperatures while maintaining their structural integrity. Chemical resistance and retention of physical and mechanical properties at high temperature are highly essential. Development of heat-resistant polymers and high-performance polymer matrix composites that can function above 250 °C for long duration has been an area of interest for more than a decade. The ability of polymers to attain structural features such as heterocyclic, rigid backbones after cross-linking makes them suitable candidates for applications in extreme thermal conditions. Typically, high-performance polymers display a glass transition temperature (Tg) of >200 °C and a melting temperature of >450 °C [4, 5, 6, 7, 8].
As mentioned earlier, the increased demand for high-performance materials in modern aircrafts and space vehicles could lead to explorations for widening their temperature withstanding capability at still higher temperature regimes. Today, there are many advanced thermosets and thermoplastics that exhibit excellent thermal performance even at very stringent conditions. Some of the notable systems are thermosets such as epoxies, phenolic resins, bismaleimides (BMI), cyanate esters, polyimides (PI), polymerised monomeric reactant (PMR), phenolic triazine (PT) resins and thermoplastics like polyether sulfone (PES), polyether ether ketone (PEEK), polyetherimide (PEI) and polyether nitrile [9, 10, 11, 12, 13]. The latest thermoset entry in this array is phthalonitrile (PN) resins.
Prelude to the discussion on PN polymers and their chemistry and technology, it is felt appropriate to have a brief discussion on the state-of-the-art thermally stable polymeric resins.
1.2 State-of-the-art high-performance polymers
1.2.1 Phenol formaldehyde resins
Phenolic resins are synthesised by the step-growth polymerisation of formaldehyde and phenol in the presence of an acid or a base catalyst. Novolacs are formed under acidic conditions with an excess of phenol to formaldehyde (HCHO) stoichiometry (1.5–1.7) in the feed, whereas resoles are synthesised under basic conditions with an excess of formaldehyde (phenol: HCHO = 1:1.6) in the feed [14, 15, 16]. Novolac requires the presence of cross-linking agents such as hexamethylene tetramine, whereas resoles can be cured by heating [17, 18, 19]. Synthetic schemes for novolac and resoles are shown in Schemes 1.1 and 1.2 respectively.
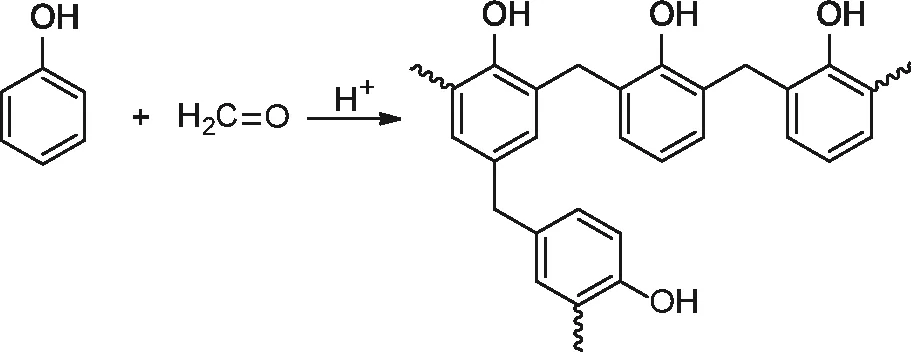

The advantages of phenolic resins include excellent dimensional stability with a constant usage temperature range of 150–160 °C, excellent resistance to chemicals, moisture, heat and fire. The main areas of application include insulation products, abrasive and friction lining materials. Because of their high aromatic content, phenolic resins absorb a lot of heat for their thermal degradation, and hence it is used as an ablative material in re-entry spacecarfts. Phenolic resins are also used as an alternative to conventional precursor (pitch and tar) materials for the production of carbon-based engineering materials (e.g., glassy carbon, carbon fibres and carbon–carbon composites) [14, 20, 21].
Generally, phenolic-type resin systems undergo polymerisation through condensation-type polymerisation reaction. This causes defects in their composites as composites are prone to voids caused by the release of certain other molecules such as water vapour and formaldehyde during cure leading to the premature failures at the point of their application. Hence, phenolics have the inherent drawback of poorer mechanical properties than those of epoxies and most other high-performance resins. An additional step to be included in the phenolic composite processing ensures the removal of water molecules by venting, and this can mainly be employed only for compression-type mouldings. Therefore, phenolics are not typically processed using resin transfer moulding (RTM), which is the most common type of composite moulding employed for thermosets. To alleviate these shortcomings, phenolic resins with addition-curable nature were developed and well accepted. Addition-curable phenolics with different chemical modification are available...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface
- Contents
- List of Abbreviations
- 1 Phthalonitriles and state-of-the-art high-performance thermosets
- 2 Basic Chemistry and general remarks
- 3 Structure–property relationships
- 4 Self-catalysed phthalonitriles
- 5 Phthalonitrile blends and composites
- Index