
eBook - ePub
Blockchain
An Illustrated Guidebook to Understanding Blockchain
- 256 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Blockchain
An Illustrated Guidebook to Understanding Blockchain
About this book
Blockchain should be easy to understand, but the so-called "experts" always explain it in such a complicated way! Through 200 original illustrations, this book provides simple explanation of Blockchain technology: what Blockchain is and how it works. This book will help you, understand everything about Blockchain, including:
- The Origin,
- The Theory,
- The People,
- The Application,
- The Brief History of Blockchain
- And many more fundamental aspects of blockchain!
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Blockchain by Xu Mingxing, Ying Tian, Jiyue Li, Jie Liu in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Business & Entrepreneurship. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1.
THE ORIGINS OF BLOCKCHAIN
Definition and the Inevitability behind the Contingency
FinTech is a phenomenal concept. As the Internet and technical industries register rapid growth, innovative programs of the FinTech industry also are witnessing singular development, among which Blockchain technology is undoubtedly the most eye-catching. Blockchain is one of the most promising industries over the next five years, as well as an emerging field in which many financial institutions and leading banks around the world are competing and pouring investments.
Speaking of Blockchain, the problems we’d like to discuss first involve some whys: Why is it so popular? Why do people believe that it can change the world? Before starting this chapter, I have read many books concerning this technology, like Blockchain Revolution, Blockchain Finance, Commercial Blockchain, Blockchain Society, and Blockchain Reshapes Economy and the World, in which many specialists illustrate reasons why Blockchain can boom. They present different perspectives, including economics, commercial development, human history, and technological change. I even get caught up in the glamour of Blockchain after perusing these excellent works. Therefore, I’m going to explain the origins of Blockchain and its uses from the following four perspectives: the evolution of the ledger, value transfer, credit cost, and technical innovation.

Fig. 1-1: Bookkeeping in the Paleolithic Age.
THE EVOLUTION OF THE LEDGER: THE RISE AND FALL OF THE ACCOUNT BOOK
“Distributed ledger” is the most representative word to define Blockchain, the most cutting-edge phenomenal concept in the 21st century. First, from the perspective of the evolution of the ledger, let’s explore the following two questions: Why was Blockchain invented? and How does distributed ledger technology have the power to transform our economy and society?

Fig. 1-2: Bookkeeping in the embryonic stage: portraying and sketching.
Back in the Paleolithic period, people kept accounts (like the number of animals they hunted or ate every day) in their heads tens of thousands of years ago. However, as the number of people in tribes grew, their productivity became higher, leading to producer surplus. At the same time, the economic demand of people was so complex that keeping accounts in mind no longer sufficed, and improved bookkeeping was needed.
Therefore, people invented two methods: simple characterization and pictorial drawing, which meant recording with various symbols and awing things that had happened, respectively. This was the beginning of bookkeeping.

Fig. 1-3: The origins of bookkeeping: keeping records by tying knots.
However, symbols and drawings, with their taxing and space-occupied features, also failed to keep pace with the growing demand for bookkeeping. Under such circumstances, maintaining records by tying knots was invented. This well-known method was documented in historical texts and secondary school history textbooks and defined forms of recording objects, quantity measure, and final results. In addition, several principles of book entry could also be found as used by this method. Thus, it was almost known as the origin of the account book.
In late primitive society, productivity reached a new high, surplus products increased, and the division among agriculture, animal husbandry, and handicrafts expanded, which contributed to the invention of words. Characters and other narrative forms were adopted as ways to record tallies, in which income and expenses were recorded in chronological order.

Fig. 1-4: The end of primitive society: current accounts.
By the early 5th century BC, the economic boom in slavery societies of ancient Greece and Rome made it possible for journal accounts and cash books in running accounts. With the classification of time, the names of products and people, and currency capital, these account books were very similar to the ledger of an account. This phase was known as the “single-entry bookkeeping period.”

Fig. 1-5: Single-entry bookkeeping.
Now, let’s move to the generally recognized double-entry bookkeeping. Double-entry bookkeeping, which has been widely adopted in China, originated from the Longmen account at the end of the Ming Dynasty and early Qing Dynasty and later developed into four-element bookkeeping. The earliest double-entry bookkeeping in the West can be traced back to the 12th and 13th century and was widely used by bankers and merchants. The double-entry system could not only calculate operating costs, but also produce capital and profits, ensuring the continuous operation of companies.

Fig. 1-6: Double-entry bookkeeping period.
The 19th century witnessed the explosive development of information technology. At that time, as an individual no longer served as the owner and operator of a company and the work to be dealt with became more complex, all officials had the demand of checking account books. For example, if I were the largest shareholder of a company but unwilling to operate it, then I could employ a professional manager to do this job.
At the end of a year when the financial report showed that my bonus share was 10 million yuan, I would say that I wanted to check the account book. However, the account book recorded that the money spent on advertisements stood at 30 million yuan, much more than my annual salary, which made me doubt the accuracy of this ledger.
To be prudent, I employed an accountant certified by a third party and asked him to be responsible for bookkeeping. It was the surging demand for accounting and distrust between the owner and the operation of a company that led to the appearance of accountants. Since then, the rapid spread of computer technology brought accounting to a new stage—Computerized Accounting.

Fig. 1-7: The 19th century: The appearance of accountants.
In a world of informatization, digitalization, and intelligence, although methods of bookkeeping are continually improved and innovated, we are still faced with such issues as information asymmetry and trust crisis. Put simply, how can you trust the account kept by an accountant or audit to provide correct information? Do you ever wonder if your company may collude with accounting firms to cook the books? Now, Blockchain offers us a new way to solve such issues—the underlying application of Bitcoins, which can be seen as a shared distributed ledger.
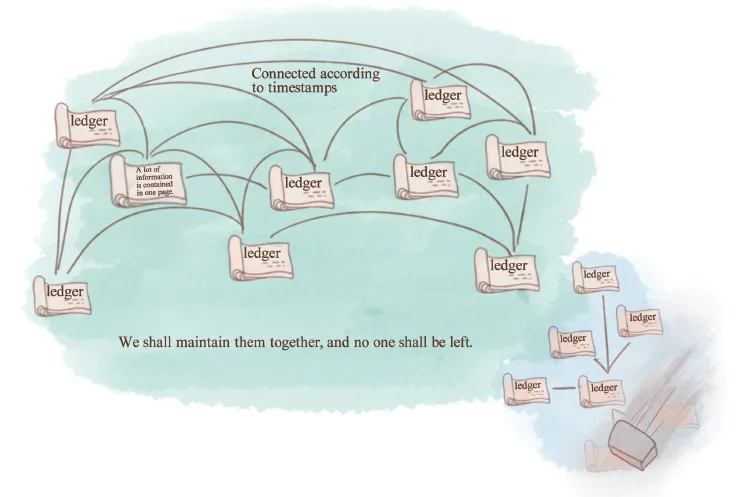
Fig. 1-8: The distributed ledger.
As a distributed ledger, Blockchain has the following features:
First, Blockchain is a huge ledger, in which every block can be regarded as a page, with a new page, including one or several entries, to be added for every new block.
Second, it is an encrypted and sequential ledger. All record information will be packaged into encrypted and time-stamped blocks, which are formed into a chronological, general account.
Third, it is a decentralized ledger that is jointly maintained by users in the network.
History has witnessed great changes in recording accounts. Now, thanks to technology, Blockchain has become the latest and most trustworthy form of bookkeeping.
VALUE TRANSFER: WHAT TO EXPECT AFTER THE INTERNET
The Internet, a concept that everyone is familiar with, has penetrated into every aspect of our lives. It serves as the information superhighway that can transmit all information with high speed and low cost except currency, a particular kind of information. Blockchain, however, is able to address this issue as a value transmission network.
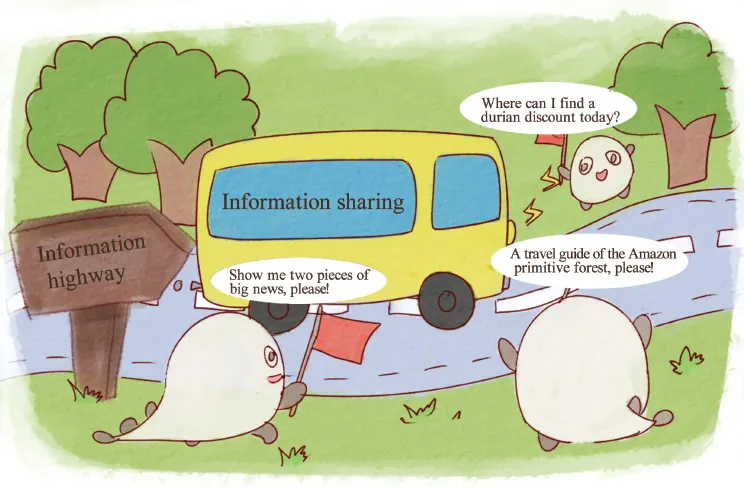
Fig. 1-9: The dawn of the Internet.
Do you remember the story of the Internet? In 1993, the United States announced the establishment of National Information Infrastructure, a new project that was designed to build an information superhighway and enabled all Americans to share and use information resources. This is the rudiment of today’s Internet world.
Nowadays, everyone can produce information and spread it easily and swiftly. The rapid transmission of all information brings us to an age of information explosion. In order to satisfy people’s need for diverse information, information transmission technologies continuously innovate, as evidenced by Cloud Drive and Automatic Network Replenishment.
It also begins to dawn on people that although most information like videos, photos, and audios can be used through copying and pasting, for some messages, reproduction is impossible and meaningless.
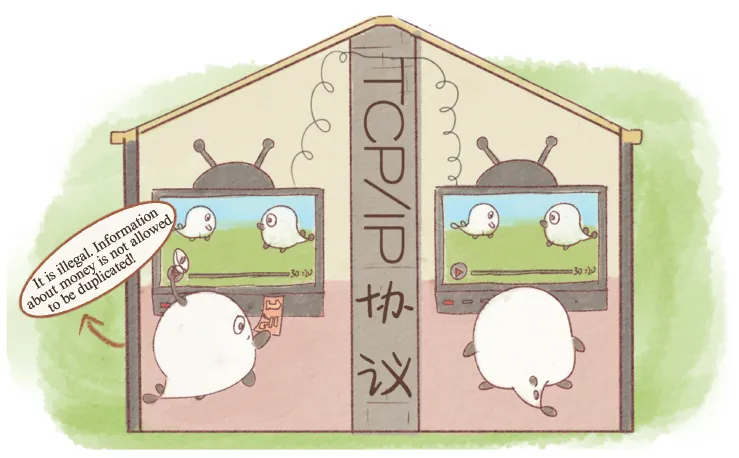
Fig. 1-10: How to transfer value.
For instance, it is impossible for payment to be completed through copying money. Instead, this process involves transferring money from payment accounts to collection accounts. A video can be posted on different websites and sha...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Contents
- Preface by Wang Wei
- Introduction by Guo Yuhang
- Chapter One: The Origins of Blockchain
- Chapter Two: The Theory
- Chapter Three: The People
- Chapter Four: The Application
- Chapter Five: The Equipment
- Appendix
- Acknowledgments