
eBook - ePub
100 Excel Simulations
Using Excel to Model Risk, Investments, Genetics, Growth, Gambling and Monte Carlo Analysis
- 213 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
100 Excel Simulations
Using Excel to Model Risk, Investments, Genetics, Growth, Gambling and Monte Carlo Analysis
About this book
Covering a variety of Excel simulations, from gambling to genetics, this introduction is for people interested in modeling future events, without the cost of an expensive textbook. The simulations covered offer a fun alternative to the usual Excel topics and include situations such as roulette, password cracking, sex determination, population growth, and traffic patterns, among many others.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access 100 Excel Simulations by Gerard M. Verschuuren in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Computer Science & Financial Risk Management. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
- GamblingChapter 1 The Die Is CastAll these simulations are supported by files that you can download from the following website:http://www.genesispc.com/download/simulations100.zip.What the simulation doesWe start with a very simple case of simulation—casting a die (on sheet “Dice” in 1-Gambling.xlsx). In cell A1 is a formula that generates a random number between 1 and 6. According to that outcome, the colored die shows the appropriate number of eyes at their proper locations. Each time the random number changes, the die adjusts accordingly.
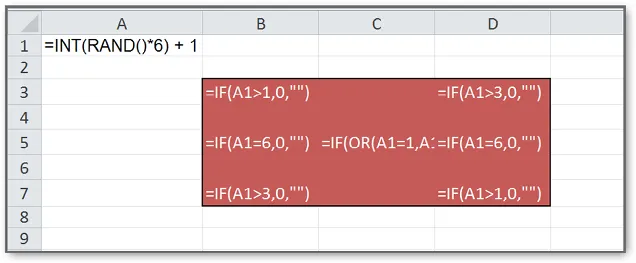
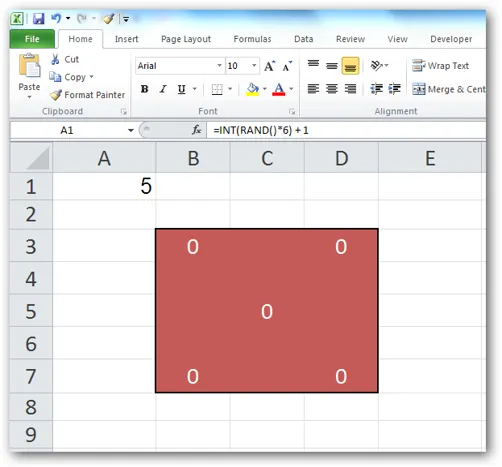 What you need to knowCell A1 has a formula that uses a volatile function called RAND. On each recalculation, this function generates a new random number between 0 and 1. Because we want numbers between 1 and 6, we need to multiply by 6, round the number down by using the INT function, and then add 1 to the end result. More in general: =INT((high-low+1)*RAND()+low).Users of Excel 2007 and later can also use the “easier” function RANDBETWEEN which has two arguments for the lower limit (in this case 1) and the upper limit (in this case 6). I decided not to use that function, because in pre-2007 Excel versions this function was only available through the Analysis Toolpak.To generate a new random number, you either hit the key F9 or the combination of the Shift key and the F9 key. In this file, I would recommend the latter option (Shift F9), since that would only recalculate the current sheet—otherwise you would recalculate all sheets in this file, which may take lots of calculating time.Finally, we need to regulate which eyes should pop up for each new random number. This is done inside some of the die cells by using the IF function. This function is a “decision maker,” which determines whether a specific eye should be on or off.What you need to do
What you need to knowCell A1 has a formula that uses a volatile function called RAND. On each recalculation, this function generates a new random number between 0 and 1. Because we want numbers between 1 and 6, we need to multiply by 6, round the number down by using the INT function, and then add 1 to the end result. More in general: =INT((high-low+1)*RAND()+low).Users of Excel 2007 and later can also use the “easier” function RANDBETWEEN which has two arguments for the lower limit (in this case 1) and the upper limit (in this case 6). I decided not to use that function, because in pre-2007 Excel versions this function was only available through the Analysis Toolpak.To generate a new random number, you either hit the key F9 or the combination of the Shift key and the F9 key. In this file, I would recommend the latter option (Shift F9), since that would only recalculate the current sheet—otherwise you would recalculate all sheets in this file, which may take lots of calculating time.Finally, we need to regulate which eyes should pop up for each new random number. This is done inside some of the die cells by using the IF function. This function is a “decision maker,” which determines whether a specific eye should be on or off.What you need to do
- Type in cell A1: =INT(RAND()*6) + 1. In this case, the function RAND is “nested” inside the function INT (INT eliminates decimals). Nested functions are very common in Excel; for more information, see Appendix 2.
- Type in B3: =IF(A1>1,0,””). The two double quotes in the last argument return an empty string, showing up as nothing.
- Type in D3: =IF(A1>3,0,””).
- Type in B5: =IF(A1=6,0,””).
- Type in D5: =IF(A1=6,0,””).
- Type in B7: =IF(A1>3,0,””).
- Type in D7: =IF(A1>1,0,””).
- Type in C5: =IF(OR(A1=1,A1=3,A1=5),0,””). In this case, the function OR is nested inside IF. The function OR returns “true” if any of the enclosed arguments is “true.”
- If you want to see all formulas at once, hit Ctr ~ (the tilde can be found below the Esc key). This shortcut toggles the sheet, back and forth, between value-view and formula-view.
Chapter 2 Casting Six Dice
What the simulation does
Open file 1-Gambling.xlsx on sheet “6-Dices.” This time we have six different dice. Each die “listens” to a random number above it, to its left.
The settings for each die are similar to what we did in Simulation 1. The number of eyes for each die is plotted in a column chart below the dice.
A die that shows six eyes gets marked with a color. When there are at least 2 dice in a row with six eyes, all dice get marked at the same time.

What you need to know
There is not much new on this sheet. The main difference is that we need 6 different cells with a RAND function in order to control the...
Table of contents
- Gambling
- Chapter 2 Casting Six Dice
- Chapter 3 Frequencies
- Chapter 4 Roulette Machine
- Chapter 5 Gambler’s Ruin
- Chapter 6 Random Walk
- Chapter 7 Gambling Strategy
- Chapter 8 Cracking a Password
- Statistics
- Chapter 10 The Mean of Means
- Chapter 11 Sampling
- Chapter 12 The Normal Distribution
- Chapter 13 Normalizing
- Chapter 14 Repeats
- Chapter 15 Confidence Margins
- Chapter 16 Power Curves
- Chapter 17 Hidden Peaks
- Chapter 18 Sampling Sizes
- Chapter 19 Quality Control
- Genetics
- Chapter 21 Sex Determination
- Chapter 22 Radiation and Mutation
- Chapter 23 Mendel
- Chapter 24 Hardy-Weinberg Law
- Chapter 25 Genetic Drift
- Chapter 26 Lethal Homozygote
- Chapter 27 Reduced Vitality
- Chapter 28 Two Selective Forces
- Chapter 29 Balanced Equilibrium
- Chapter 30 Molecular Clock
- Chapter 31 DNA Sequencing
- Financial
- Chapter 33 Risk Analysis
- Chapter 34 Missing or Exceeding Targets
- Chapter 35 Two-Dimensional Filters
- Chapter 36 Scenarios
- Chapter 37 Moving Averages
- Chapter 38 Return on Investment
- Chapter 39 Employee Stock Options
- Chapter 40 Value at Risk
- Chapter 41 Asian Options
- Chapter 42 Black-Scholes Model
- Expansion
- Chapter 44 Extrapolation
- Chapter 45 Predator-Prey Cycle
- Chapter 46 Homeostasis
- Chapter 47 Taking Medication
- Chapter 48 Population Pyramid
- Chapter 49 Titration
- Chapter 50 EC50 Determination
- Chapter 51 Converter
- Chapter 52 Conditional Training
- Chapter 53 Epidemics
- Monte Carlo Simulations
- Chapter 55 Brownian Motion
- Chapter 56 A Traffic Situation
- Chapter 57 Uncertainties in Sales
- Chapter 58 Exchange Rate Fluctuations
- Chapter 59 Cost Estimates
- Chapter 60 Market Growth
- Chapter 61 Integration with Monte Carlo
- Iterations
- Chapter 63 Win or Lose?
- Chapter 64 Circular Gradients
- Chapter 65 Single-Cell Arrays
- Chapter 66 Data Management
- Chapter 67 Solving Equations
- Chapter 68 Least Squares Method
- Chapter 69 Combining Scenarios
- Chapter 70 Logistics
- Extras
- Chapter 72 Graph Manipulation
- Chapter 73 Detecting Outliers
- Chapter 74 False Positives
- Chapter 75 Probability of Beliefs
- Chapter 76 Unbiased Sampling
- Chapter 77 Numbering Records
- Chapter 78 Fiscal Year
- Chapter 79 Stock Market
- Chapter 80 Forecasting Temperatures
- Miscellanea
- Chapter 82 Graph Manipulation
- Chapter 83 Simulation of a Slot Machine
- Chapter 84 Letter Game
- Chapter 85 A Hawk-Dove Simulation
- Chapter 86 Flock Behavior
- Chapter 87 Simulation of Sick Cases
- Chapter 88 Ehrenfest’s Urn Simulation
- Chapter 89 Two Monte Carlo Integrations
- Chapter 90 Randomness in Gene Pools
- Chapter 91 Random Mating
- Chapter 92 Differences in Fitness
- Chapter 93 Loan Simulation
- Chapter 94 Stock Volatility
- Chapter 95 S&P 500 Performance
- Chapter 96 Scenario Risks
- Chapter 97 Temperature Fluctuations
- Chapter 98 Juror Selection
- Chapter 99 Waiting Time Simulation
- Chapter 100 Project Delays
- Appendices
- Nested functions
- What-If Tables
- Simulation Controls