
Green Chemistry for Surface Coatings, Inks and Adhesives
Sustainable Applications
- 440 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Green Chemistry for Surface Coatings, Inks and Adhesives
Sustainable Applications
About this book
Many modern surface coatings and adhesives are derived from fossil feedstocks. With fossil fuels becoming more polluting and expensive to extract as supplies dwindle, industry is turning increasingly to nature, mimicking natural solutions using renewable raw materials and employing new technologies.
Highlighting sustainable technologies and applications of renewable raw materials within the framework of green and sustainable chemistry, circular economy and resource efficiency, this book provides a cradle-to-cradle perspective. From potential feedstocks to recycling/reuse opportunities and the de-manufacture of adhesives and solvents, green chemistry principles are applied to all aspects of surface coating, printing, adhesive and sealant manufacture.
This book is ideal for students, researchers and industrialists working in green sustainable chemistry, industrial coatings, adhesives, inks and printing technologies.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
*E-mail:[email protected]
This chapter by way of an introduction gives a big picture overview of the importance of adhesives and sealants and the need for green chemistry. Global drivers for change are considered, which are inter-related to our need for materials but also the challenges of ‘doing the right thing’ for a sustainable 21st Century. The biobased adhesives and sealants market is growing commensurate with the need for more materials. More publications are now appearing in the literature with respect to biobased and renewable resources in the context of green chemistry. The latter is explored in this chapter, which defines the 12 principles and discusses green metrics and solvents. Green chemistry is linked to sustainability and the combination of the two often leads to life cycle assessment or analysis.
1.1 Introduction: Drivers for Change
1.2 Biobased Markets and Trends5
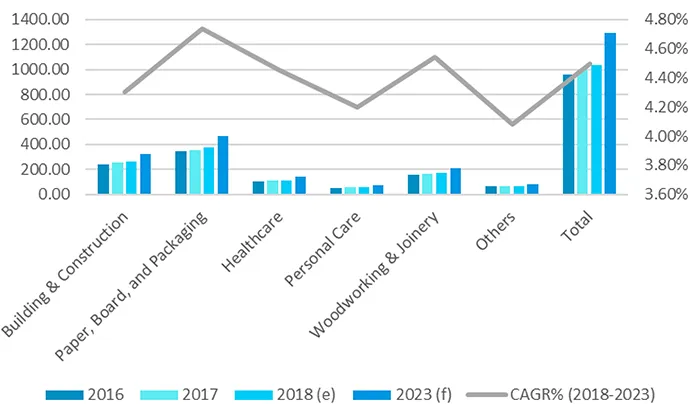
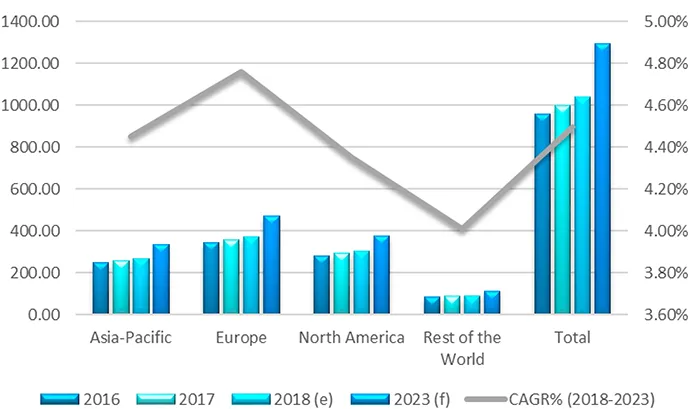
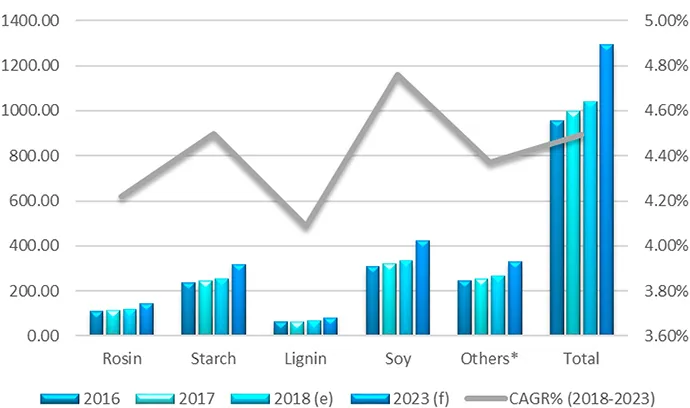
1.3 Circular Economy, SDGs, Waste, and Legislation
| SDG | Overview and action |
| 1 | No poverty: |
| End poverty in all its forms everywhere. | |
| 2 | Zero hunger: |
| End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture. | |
| 3 | Good health and well-being: |
| Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages. | |
| 4 | Quality education: |
| Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all. | |
| 5 | Gender equality: |
| Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls. | |
| 6 | Clean water and sanitation: |
| Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all. | |
| 7 | Affordable and clean energy: |
| Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all. | |
| 8 | Decent work and economic growth: |
| Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all. | |
| 9 | Industry, innovation and infrastructure |
| Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation. | |
| 10 | Reduced inequality: |
| Reduce inequality within and among countries. | |
| 11 | Sustainable cities and communities: |
| Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable. | |
| 12 | Responsible consumption & production: |
| Ensure sustainabl... |
Table of contents
- Cover
- halftitle
- Series Editor
- Title
- Copyright
- Preface
- Contents
- Chapter 1 Green Chemistry Principles and Global Drivers for Sustainability – An Introduction
- Chapter 2 Green Solubility for Coatings and Adhesives
- Section 1: Natural Adhesive and Surface Coating Concepts
- Section 2: Biobased Binders and Additives
- Section 3: Sustainable Adhesive and Surface Coating Technologies
- Subjected Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app