
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
OLED Displays and Lighting
About this book
Explains the fundamentals and practical applications of flat and flexible OLEDs for displays and lighting
Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) have emerged as the leading technology for the new display and lighting market. OLEDs are solid-state devices composed of thin films of organic molecules that create light with the application of electricity. OLEDs can provide brighter, crisper displays on electronic devices and use less power than conventional light-emitting diodes (LEDs) or liquid crystal displays (LCDs) used today. This book covers both the fundamentals and practical applications of flat and flexible OLEDs.
Key features:
- Covers all of the aspects necessary to the design and manufacturing of OLED displays and lighting.
- Explains the fundamental basic technologies and also related technologies which might contribute to the next innovation in the industry.
- Provides several indications for future innovation in the OLED industry.
- Includes coverage of OLED vacuum deposition type and solution type materials.
The book is essential reading for early career engineers developing OLED devices and OLED related technologies in industrial companies, such as OLED device fabrication companies.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
History of OLEDs
Summary
Active research and development of OLEDs (organic light emitting diodes) started in 1987, when Tang and VanSlyke of Eastman Kodak showed that a bright luminance was obtained in an OLED device with two thin organic layers sandwiched between anode and cathode. Since their report, OLEDs have been an attractive field from scientific and practical points of view because OLEDs have great potentials in practical applications such as displays and lighting.This chapter describes the history of the OLED.Key words
History, Tang, Kodak, Friend, Forrest, Kido, Adachi
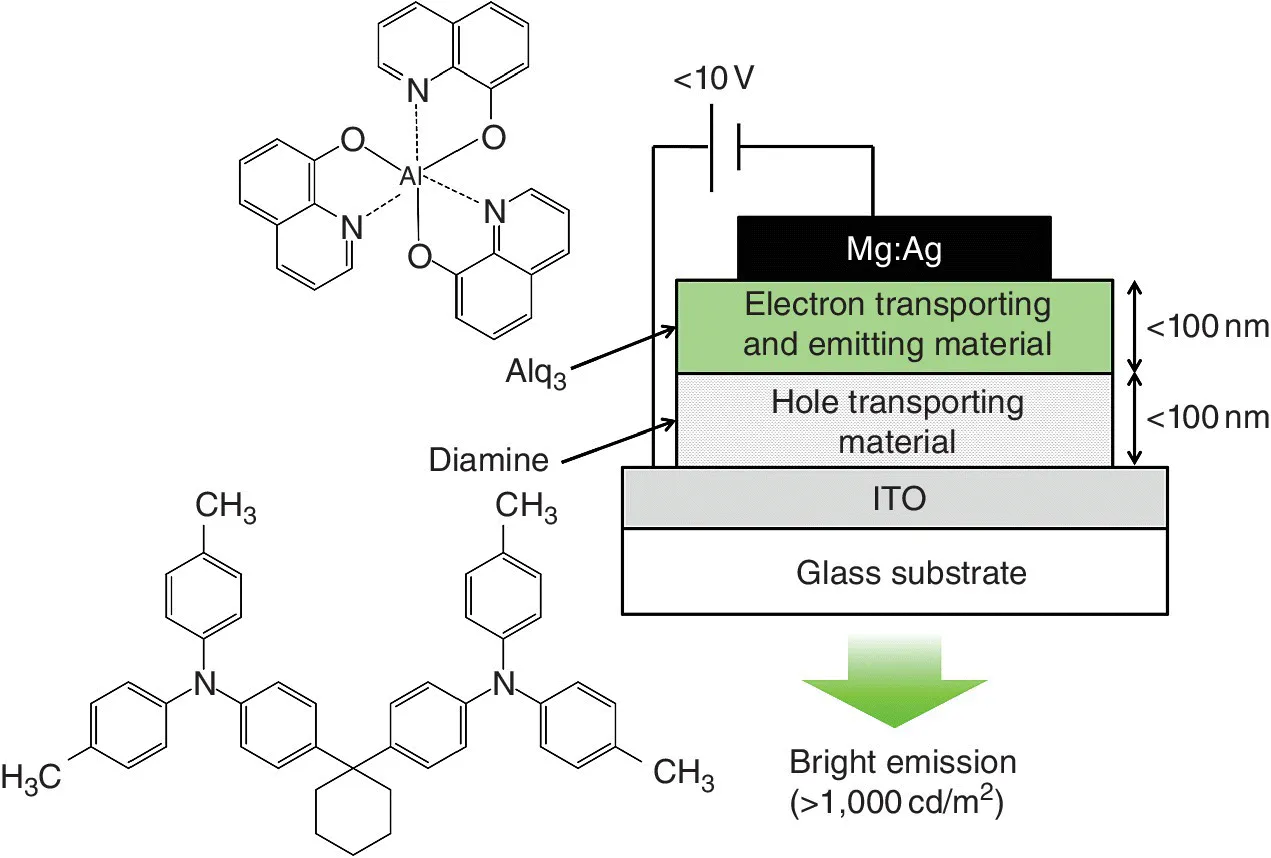
| 1987 | Invention of two‐layered OLED with a bright emission (Eastman Kodak / Tang and VanSlyke) [3] (Fig. 1.1) |
| 1990 | Invention of polymer OLED (Cavendish Lab. / Burroughes et al. of Friend’s group) [4] |
| 1994 | First report of white OLED (Yamagata Univ. / Kido et al.) [5] |
| 1997 | World’s first commercial OLED (Pioneer) [6] (Fig. 1.2) (Passive‐matrix monochrome OLED display with bottom emission structure and vacuum deposited small molecular fluorescent materials) |
| 1998 | Invention of phosphorescent OLED (Princeton Univ./ Baldo et al. of Thompson and Forrest’s group) [7] |
| 1999 | Prototype of a full‐color polymer AM‐OLED display fabricated by ink‐jet printing (Seiko‐Epson) [8] |
| 2001 | Prototype 13″ full‐color AM‐OLED display (Sony) [9] (Fig. 1.4) |
| 2002 | Invention of multi‐photon OLED (Yamagata Univ./Kido et al.) [10] |
| Prototype 17″ full‐color polymer AM‐OLED display fabricated by ink‐jet printing (Toshiba) [11] | |
| 2003 | World’s first commercial polymer OLED display (Philips) [12] |
| World’s first commercial active‐matrix OLED display (SK Display) [13] | |
| 2006 | Prototype of 3.6″ full‐color polymer AM‐OLED display with the world’s highest resolution (202 ppi) fabricated by ink‐jet printing (Sharp) [14] |
| 2007 | World’s first application of AM‐OLED displays for main displays of mobile phones (Samsung) [15] |
| World’s first commercial AM‐OLED‐TV (Sony) [16] (Fig. 1.5) | |
| 2009 | Invention of TADF (thermally activated delayed fluorescence) (Kyushu Univ. / Endo et al. of Adachi’s group) [17] |
| 2010 | World’s largest OLED display wit... |
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- 1 History of OLEDs
- 2 Fundamentals of OLEDs
- 3 Light Emission Mechanism
- 4 OLED Materials
- 5 OLED Devices
- 6 OLED Fabrication Process
- 7 Performance of OLEDs
- 8 OLED Display
- 9 OLED Lighting
- 10 Flexible OLEDs
- 11 New Technologies
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app