
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
Provides students and practitioners with a solid grounding in the theory of chromatography, important considerations in its application, and modern instrumentation.
- Highlights the primary variables that practitioners can manipulate, and how those variables influence chromatographic separations
- Includes multiple figures that illustrate the application of these methods to actual, complex chemical samples
- Problems are embedded throughout the chapters as well as at the end of each chapter so that students can check their understanding before continuing on to new sections
- Each section includes numerous headings and subheadings, making it easy for faculty and students to refer to and use the information within each chapter selectively
- The focused, concise nature makes it useful for a modular approach to analytical chemistry courses
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
CHAPTER 1
Many “real-world” samples are mixtures of dozens, hundreds, or thousands of chemicals. For example, medication, gasoline, blood, cosmetics, and food products are all complex mixtures. Common analyses of such samples include quantifying the levels of drugs – both legal and illegal – in blood, identifying the components of gasoline as part of an arson investigation, and measuring pesticide levels in food.
FUNDAMENTALS OF CHROMATOGRAPHY
Chromatography is a technique that separates the individual components in a complex mixture. Fundamental intermolecular interactions such as dispersion, hydrogen bonding, and dipole–dipole forces govern the separations. Once separated, the solutes can also be identified and quantified. Because of its ability to separate, quantify, and identify components, chromatography is one of the most important instrumental methods of analysis, both in terms of the number of instruments worldwide and the number of analyses conducted every day.
1.1 THEORY
Chromatography separates components in a sample by introducing a small volume of the sample at the start, or head, of a column. A mobile phase, either gas or liquid, is also introduced at the head of the column. When the mobile phase is a gas, the technique is referred to as gas chromatography (GC) and when it is a liquid, the technique is called liquid chromatography (LC). Unlike the sample, which is injected as a discrete volume, the mobile phase flows continuously through the column. It serves to push the molecules in the sample through the column so that they emerge, or “elute” from the other end.
Two particular modes of LC and GC, known as reversed-phase liquid chromatography (RPLC) and capillary gas chromatography, account for approximately 85% of all chromatographic analyses performed each day. Therefore, we focus on these two techniques here and leave discussions of specific variations to the chapters that describe LC and GC in greater detail.
In GC, the mobile phase, which is typically He, N2, or H2 gas, is delivered from a high-pressure gas tank. The gas flows through the column toward the low-pressure end. The column contains a stationary phase. In capillary GC, the stationary phase is typically a polymer film that is 0.25–5 µm thick (see Figure 1.1a). It is coated on the interior walls of a fused silica capillary column with an inner diameter of approximately 0.5 mm or smaller. The column is usually 10–60 m (30–180 ft) long.
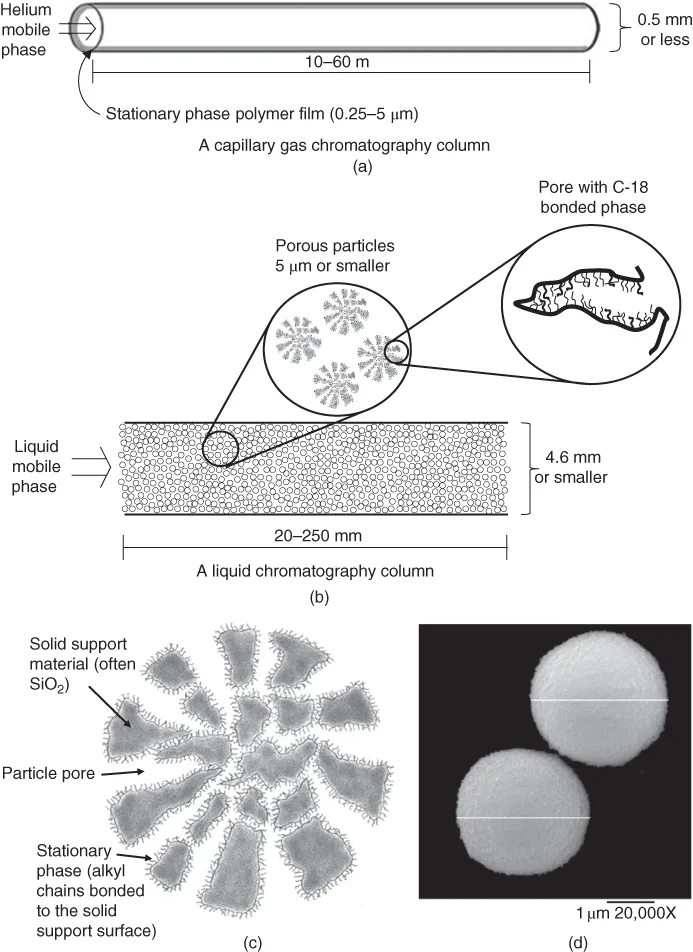
Figure 1.1 Representations of typical capillary gas (a) and liquid (b) chromatography columns. Figure (c) is a depiction of a cross section of a porous particle (shaded areas represent the solid support particles, white areas are the pores, and the squiggles on the surface are bonded alkyl chains. Figure (d) is an scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of actual 3 µm liquid chromatography porous particles. Note that the lines across the particle diameters have been added to the image and are not actually part of particles. (Source: Alon McCormick and Peter Carr. Reproduced with permission of U of MN.). It is worth taking time to note the different dimensions involved. For the GC columns, they range from microns (10−6 m) for the thickness of the stationary phase, to millimeters (10−3 m) for the column diameter, up to tens of meters for the column length. Note also that LC columns are typically much shorter than GC columns (centimeter versus meter).
RPLC is the most common mode of liquid chromatography. In RPLC, the mobile phase is a solvent mixture such as water with acetonitrile (CH3CN) that is forced through the column using high-pressure pumps. The column is typically made of stainless steel, has an inner diameter of 4.6 mm or smaller, and is only 20–250 mm (1–10 in.) in length (see Figure 1.1b). However, unlike most GC columns, most LC columns are packed with tiny spherical particles approximately 5 µm in diameter or smaller, as shown in Figure 1.1c and d. When rubbed between your fingers, the particles feel like talc or other fine powders. The particles are not completely solid, but rather are highly porous, with thousands of pores in each particle. The pores create cavities akin to caves within the particle....
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- COPYRIGHT
- Table of Contents
- PREFACE
- CHAPTER 1: FUNDAMENTALS OF CHROMATOGRAPHY
- CHAPTER 2: GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY
- CHAPTER 3: LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY
- SOLUTIONS
- INDEX
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Chromatography by Mark F. Vitha in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Physical Sciences & Analytic Chemistry. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.