
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Energy Transfers by Radiation
About this book
Inside industrial furnaces and combustion chambers, energy is essentially exchanged by radiation. It is through the same mechanism that the energy emitted by the Sun spreads through different media to reach the Earth. Developing a sound understanding of the laws underlying energy exchanges by radiation is therefore essential, not only for establishing design equations for industrial equipment, but also for an optimal harvesting of solar energy and a better understanding of climate change phenomena such as the greenhouse effect. Energy Transfers by Radiation establishes the basic laws and equations which support the quantification of energy fluxes transferred between surfaces for situations similar to those usually encountered in industrial processes or in solar energy applications.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1
Origin of Radiation
1.1. Introduction
1.2. The Niels Bohr model
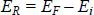
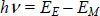
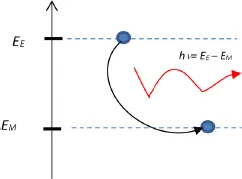
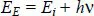
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Introduction
- 1 Origin of Radiation
- 2 Magnitudes Used in Radiation
- 3 Analysis of Radiative Energy Transfers: Black-body Radiation
- 4 Radiant Properties of Real Surfaces
- 5 Radiation Balances between Real Surfaces Separated by a Transparent Medium
- 6 Practical Determination of Shape Factors
- 7 Balances of Radiative Energy Transfers between Black Surfaces
- 8 Balances on Radiative Energy Transfers between Gray Surfaces
- 9 Electrical Analogies in Radiation
- 10 Reduction of Radiating Energy Transfers through Filtering
- 11 Radiative Energy Transfers in Semi-transparent Media
- 12 Exercises and Solutions
- Appendix: Database
- References
- Index
- End User License Agreement