
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
These volumes teach readers to think beyond apoptosis and describes all of the known processes that cells can undergo which result in cell death
This two-volume source on how cells dies is the first, comprehensive collection to cover all of the known processes that cells undergo when they die. It is also the only one of its kind to compare these processes. It seeks to enlighten those in the field about these many processes and to stimulate their thinking at looking at these pathways when their research system does not show signs of activation of the classic apoptotic pathway. In addition, it links activities like the molecular biology of one process (eg. Necrosis) to another process (eg. apoptosis) and contrasts those that are close to each.
Volume 1 of Apoptosis and Beyond: The Many Ways Cells Die begins with a general view of the cytoplasmic and nuclear features of apoptosis. It then goes on to offer chapters on targeting the cell death mechanism; microbial programmed cell death; autophagy; cell injury, adaptation, and necrosis; necroptosis; ferroptosis; anoikis; pyronecrosis; and more. Volume 2 covers such subjects as phenoptosis; pyroptosis; hematopoiesis and eryptosis; cyclophilin d-dependent necrosis; and the role of phospholipase in cell death.
- Covers all known processes that dying cells undergo
- Provides extensive coverage of a topic not fully covered before
- Offers chapters written by top researchers in the field
- Provides activities that link and contrast processes to each other
Apoptosis and Beyond: The Many Ways Cells Die will appeal to students and researchers/clinicians in cell biology, molecular biology, oncology, and tumor biology.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1
General View of the Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Features of Apoptosis
Abbreviations
| AIF | apoptosis-inducing factor |
| Apaf-1 | apoptotic protease activating factor-1 |
| ATP | adenosine triphosphate |
| BA | bongkrekic acid |
| Bcl-2 | B-cell lymphoma-2 |
| BID | BH3-interacting domain death agonist |
| bp | base pair |
| CAD | caspase-activated DNase |
| c-FLIP | cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein |
| Chx | cyclohexamide |
| CsA | cyclosporine A |
| CTL | cytotoxic T lymphocyte |
| cyt c | cytochrome c |
| DISC | death-inducing signal complex |
| DED | death effector domain |
| endo D | endonuclease D |
| endo G | endonuclease G |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| FADD | Fas-associated death-domain protein |
| FasL | fatty acid synthetase ligand |
| FasR | fatty acid synthetase receptor |
| Gzm-A | granzyme-A |
| Gzm-B | granzyme-B |
| ICAD | inhibitor of caspase-activated DNase |
| Kb | kilobase |
| MEF | mouse embryonic fibroblast |
| MOMP | mitochondrial outer-membrane permeabilization |
| NK | natural killer |
| OMM | outer mitochondrial membrane |
| PCD | programmed cell death |
| PFN | Perforin |
| PT | pore transition |
| RIP | receptor-interacting protein |
| ROCK I | Rho effector protein |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SET | stress-response complex |
| tBID | truncated BID |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| TNFR1 | tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 |
| TRADD | TNF receptor-associated death domain |
| TUNEL | terminal deoxynucleotide tranferase dUTP nick end labeling |
1.1 Introduction
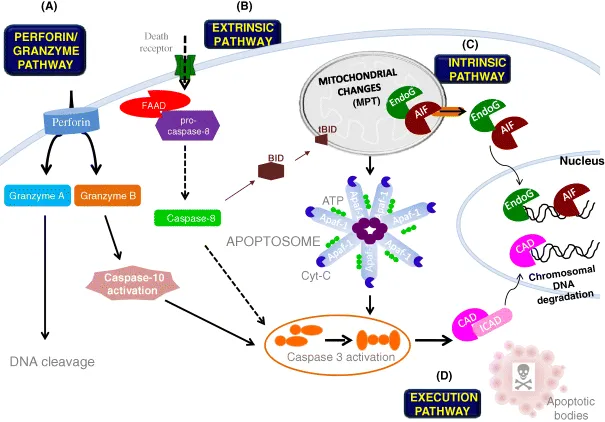
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- List of Contributors
- Chapter 1: General View of the Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Features of Apoptosis
- Chapter 2: Mitochondria in Focus: Targeting the Cell-Death Mechanism
- Chapter 3: Microbial Programmed Cell Death
- Chapter 4: Autophagy
- Chapter 5: Cell Injury, Adaptation, and Necrosis
- Chapter 6: Necroptosis
- Chapter 7: Ferroptosis
- Chapter 8: Anoikis Regulation: Complexities, Distinctions, and Cell Differentiation
- Chapter 9: Cornification
- Chapter 10: Excitotoxicity
- Chapter 11: Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Wallerian Degeneration
- Chapter 12: Pyronecrosis
- Chapter 13: Phenoptosis: Programmed Death of an Organism
- Chapter 14: Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Oxytosis
- Chapter 15: Pyroptosis
- Chapter 16: Paraptosis
- Chapter 17: Hematopoiesis and Eryptosis
- Chapter 18: Cyclophilin D-Dependent Necrosis
- Chapter 19: Role of Phospholipases in Cell Death
- Chapter 20: TRIAD (Transcriptional Repression-Induced Atypical Death)
- Chapter 21: Alkylating-Agent Cytotoxicity Associated with O6-Methylguanine
- Chapter 22: Entosis
- Chapter 23: Mitotic Catastrophe
- Chapter 24: NETosis and ETosis: Incompletely Understood Types of Granulocyte Death and their Proposed Adaptive Benefits and Costs
- Chapter 25: Parthanatos: Poly ADP Ribose Polymerase (PARP)-Mediated Cell Death
- Chapter 26: Methuosis: Drinking to Death
- Chapter 27: Oncosis
- Chapter 28: Autoschizis: A Mode of Cell Death of Cancer Cells Induced by a Prooxidant Treatment In Vitro and In Vivo
- Chapter 29: Programmed Death 1 (PD1)-Mediated T-Cell Apoptosis and Cancer Immunotherapy
- Index
- End User License Agreement