
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Power System Wide-area Stability Analysis and Control
About this book
An essential guide to the stability and control of power systems integrating large-scale renewable energy sources
The rapid development of smart grids and the integration of large scale renewable energy have added daunting new layers of complexity to the long-standing problem of power system stability control. This book offers a systematic stochastic analysis of these nonlinear problems and provides comprehensive countermeasures to improve power system performance and control with large-scale, hybrid power systems.
Power system stability analysis and control is by no means a new topic. But the integration of large scale renewable energy sources has added many new challenges which must be addressed, especially in the areas of time variance, time delay, and uncertainties. Robust, adaptive control strategies and countermeasures are the key to avoiding inadequate, excessive, or lost loads within hybrid power systems. Written by an internationally recognized innovator in the field this book describes the latest theory and methods for handling power system angle stability within power networks. Dr. Jing Ma analyzes and provides control strategies for large scale power systems and outlines state-of-the-art solutions to the entire range of challenges facing today's power systems engineers.
- Features nonlinear, stochastic analysis of power system stability and control
- Offers proven countermeasures to optimizing power system performance
- Focuses on nonlinear time-variance, long time-delays, high uncertainties and comprehensive countermeasures
- Emphasizes methods for analyzing and addressing time variance and delay when integrating large-scale renewable energy
- Includes rigorous algorithms and simulations for the design of analysis and control modeling
Power System Wide-area Stability Analysis and Control is must-reading for researchers studying power system stability analysis and control, engineers working on power system dynamics and stability, and graduate students in electrical engineering interested in the burgeoning field of smart, wide-area power systems.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Basic Theories of Power System Security Defense
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Power System Reliability and Stability
1.2.1 Reliability of Power System
1.2.1.1 Adequacy
- LOLD (loss of load probability) refers to the probability that the system cannot meet load demand in a given time interval, that is, (1.1)where Pi is the probability of the system being at state i. S is the complete set of system states in which the system cannot meet load demand in the given time interval.
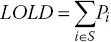
- LOLE (loss of load expectation) refers to the expected number of hours or days when the system cannot meet load demand in a given time interval, that is, (1.2)where Pi is the probability of the system being at state i, S is the complete set of system states in which the system cannot meet load demand in the given time interval, and T is the number of hours or days in the given time interval.
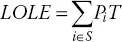
- LOLF (loss of load frequency) refers to the number of times when the system cannot meet load demand in a given time interval, that is, (1.3)where Fi is the probability of the system being at state i and S is the complete set of system states in which the system cannot meet load demand in the given time interval.
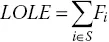
- LOLD (loss of load duration) refers to the average time duration when the system cannot meet load demand in a given time interval, that is, (1.4)where LOLE is loss of load expectation and LOLF is loss of load frequency.
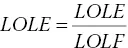
- EDNS (expected demand not supplied) refers to the expected reduction of load demand power due to generation capacity shortage or power grid constraints in a given time interval, that is, (1.5)where Pi is the probability of the system being at state i, Ci is the reduced load power at state i, and S is the complete set of system states in which the system cannot meet load demand in the given time interval.
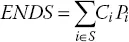
- EENS (expected energy not supplied) refers to the expected reduction of load demand energy due to generation capacity shortage or power grid constraints in a given time interval, that is, (1.6)where Pi is the probability of the system being at state i, Fi is the probability of the system being at state i, Di is the time duration (in days) at state i, Ci is the reduced load power at state i, S is the complete set of system states in which the system cannot meet load demand in the given time interval, and T is the number of hours in the given time interval.
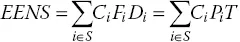
1.2.1.2 Security
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- About the Author
- Preface
- 1 Basic Theories of Power System Security Defense
- 2 Power System Analysis and Control Theory
- 3 Wide‐Area Information Monitoring
- 4 Stability Analysis of Stochastic System
- 5 Stability Analysis of Time‐Delay System
- 6 Wide‐area Robust Control
- 7 Wide‐Area Adaptive Control
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app