
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Chemistry Essentials For Dummies
About this book
Chemistry Essentials For Dummies (9781119591146) was previously published as Chemistry Essentials For Dummies (9780470618363). While this version features a new Dummies cover and design, the content is the same as the prior release and should not be considered a new or updated product.
Whether studying chemistry as part of a degree requirement or as part of a core curriculum, students will find Chemistry Essentials For Dummies to be an invaluable quick reference guide to the fundamentals of this often challenging course. Chemistry Essentials For Dummies contains content focused on key topics only, with discrete explanations of critical concepts taught in a typical two-semester high school chemistry class or a college level Chemistry I course, from bonds and reactions to acids, bases, and the mole. This guide is also a perfect reference for parents who need to review critical chemistry concepts as they help high school students with homework assignments, as well as for adult learners headed back into the classroom who just need to a refresher of the core concepts.
The Essentials For Dummies Series
Dummies is proud to present our new series, The Essentials For Dummies.Now students who are prepping for exams, preparing to study new material, or who just need a refresher can have a concise, easy-to-understand review guide that covers an entire course by concentrating solely on the most important concepts. From algebra and chemistry to grammar and Spanish, our expert authors focus on the skills students most need to succeed in a subject.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Matter and Energy: Exploring the Stuff of Chemistry





Knowing the States of Matter and Their Changes
Solids, liquids, and gases
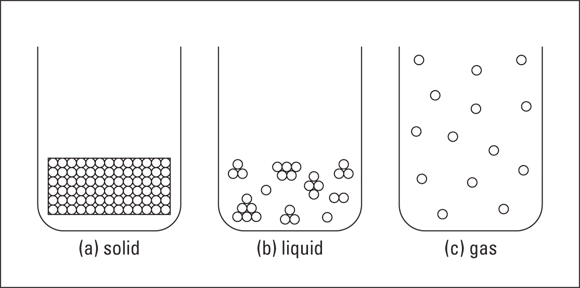
Solids
Liquids
Gases
Condensing and freezing
- Condensation: When a substance condenses, it goes from a gas to a liquid state. Gas particles have a high amount of energy, but as they’re cooled, that energy decreases. The attractive forces now have a chance to draw the particles closer together, forming a liquid. The particles are now in clumps, as is characteristic of particles in a liquid state.
- Freezing: A substance freezes when it goes from a liquid to a solid. As energy is removed by cooling, the particles in a liquid start to align themselves, and a solid forms. The temperature at which this occurs is called the freezing point (fp) of the substance.
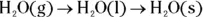
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Chapter 1: Matter and Energy: Exploring the Stuff of Chemistry
- Chapter 2: What’s in an Atom?
- Chapter 3: The Periodic Table
- Chapter 4: Nuclear Chemistry
- Chapter 5: Ionic Bonding
- Chapter 6: Covalent Bonding
- Chapter 7: Chemical Reactions
- Chapter 8: Electrochemistry: Using Electrons
- Chapter 9: Measuring Substances with the Mole
- Chapter 10: A Salute to Solutions
- Chapter 11: Acids and Bases
- Chapter 12: Clearing the Air on Gases
- Chapter 13: Ten Serendipitous Discoveries in Chemistry
- Index
- About the Author
- Connect with Dummies
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
