
eBook - ePub
Prognostics and Health Management of Electronics
Fundamentals, Machine Learning, and the Internet of Things
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Prognostics and Health Management of Electronics
Fundamentals, Machine Learning, and the Internet of Things
About this book
An indispensable guide for engineers and data scientists in design, testing, operation, manufacturing, and maintenance
A road map to the current challenges and available opportunities for the research and development of Prognostics and Health Management (PHM), this important work covers all areas of electronics and explains how to:
- assess methods for damage estimation of components and systems due to field loading conditions
- assess the cost and benefits of prognostic implementations
- develop novel methods for in situ monitoring of products and systems in actual life-cycle conditions
- enable condition-based (predictive) maintenance
- increase system availability through an extension of maintenance cycles and/or timely repair actions;
- obtain knowledge of load history for future design, qualification, and root cause analysis
- reduce the occurrence of no fault found (NFF)
- subtract life-cycle costs of equipment from reduction in inspection costs, downtime, and inventory
Prognostics and Health Management of Electronics also explains how to understand statistical techniques and machine learning methods used for diagnostics and prognostics. Using this valuable resource, electrical engineers, data scientists, and design engineers will be able to fully grasp the synergy between IoT, machine learning, and risk assessment.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Introduction to PHM
Michael G. Pecht and Myeongsu Kang
University of Maryland, Center for Advanced Life Cycle Engineering, College Park, MD, USA
As a result of intense global competition, companies are considering novel approaches to enhance the operational efficiency of their products. For some products, high in‐service reliability can be a means to ensure customer satisfaction. For other products, increased warranties, or at least reduced warranty costs, and a reduction in liability due to product failures, are incentives for manufacturers to improve field reliability and operational availability. 1
Electronics are integral to the functionality of most systems today, and their reliability is often critical for system reliability [1]. Interest has been growing in monitoring the ongoing health of electronics products, whether they be components, systems, or systems‐of‐systems, to provide advance warning of failure and assist in administration and logistics. Here, health is defined as the extent of degradation or deviation from an expected normal condition. Prognostics is the prediction of the future state of health based on current and historical health conditions [2]. This chapter provides a basic understanding of prognostics and health monitoring of products and the techniques being developed to enable prognostics for electronic products.
1.1 Reliability and Prognostics
Reliability is the ability of a product to perform as intended (i.e. without failure and within specified performance limits) for a specified time, in its life‐cycle environment [3]. Traditional reliability prediction methods for electronic products include Mil‐HDBK‐217 [4], 217‐PLUS, Telcordia [5], PRISM [6], and FIDES [7]. These methods rely on the collection of failure data and generally assume the components of the system have failure rates (most often assumed to be constant) that can be modified by independent “modifiers” to account for various quality, operating, and environmental conditions. There are numerous well‐documented concerns with this type of modeling approach [8–11]. The general consensus is that these handbooks should never be used, because they are inaccurate for predicting actual field failures and provide highly misleading predictions, which can result in poor designs and logistics decisions [9, 12]. In particular, a recent National Academy of Science study recommended that the use of Mil‐HDBK‐217 and its progeny be considered as discredited for being invalid and inaccurate: they should be replaced with physics‐of‐failure (PoF) methods and with estimates based on validated models [13].
The traditional handbook method for the reliability prediction of electronics started with Mil‐HDBK‐217A, published in 1965. In this handbook, there was only a single point failure rate for all monolithic integrated circuits (ICs), regardless of the stresses, the materials, or the architecture. Mil‐HDBK‐217B was published in 1973, with the RCA/Boeing models simplified by the US Air Force to follow a statistical exponential (constant failure rate) distribution. Since then, all the updates were mostly “band‐aids” for a modeling approach that was proven to be flawed [14]. In 1987–1990, the Center for Advanced Life Cycle Engineering (CALCE) at the University of Maryland was awarded a contract to update Mil‐HDBK‐217. It was concluded that this handbook should be canceled and the use of this type of modeling approach discouraged.
In 1998, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 1413 standard, IEEE Standard Methodology for Reliability Prediction and Assessment for Electronic Systems and Equipment, was approved to provide guidance on the appropriate elements of a reliability prediction [15]. A companion guidebook, IEEE 1413.1, IEEE Guide for Selecting and Using Reliability Predictions Based on IEEE 1413, provided information and an assessment of the common methods of reliability prediction for a given application [16]. It is shown that the Mil‐HDBK‐217 is flawed. There is also discussion of the advantage of reliability prediction methods that use stress and damage PoF techniques.
The PoF approach and design‐for‐reliability (DfR) methods have been developed by CALCE [17] with the support of industry, government, and other universities. PoF is an approach that utilizes knowledge of a product's life‐cycle loading and failure mechanisms to perform reliability modeling, design, and assessment. The approach is based on the identification of potential failure modes, failure mechanisms, and failure sites for the product as a function of its life‐cycle loading conditions. The stress at each failure site is obtained as a function of both the loading conditions and the product geometry and material properties. Damage models are then used to determine fault generation and propagation.
PoF is one approach to prognostics, but not the only approach. Prognostics and systems health management (PHM) is a multifaceted discipline for the assessment of product degradation and reliability. The purpose is to protect the integrity of the product and avoid unanticipated operational problems leading to mission performance deficiencies, degradation, and adverse effects on mission safety. More specifically, prognostics is the process of predicting a system's remaining useful life (RUL) by estimating the progression of a fault given the current degree of degradation, the load history, and the anticipated future operational and environmental conditions. Health management is the process of decision‐making and implementing actions based on the estimate of the state of health derived from health monitoring and expected future use of the product.
In general, PHM consists of sensing, anomaly detection, diagnostics, prognostics, and decision support, as shown in Figure 1.1. Sensing is to collect a history of time‐dependent operation of a product, the degradation of materials, and/or the environmental loads on the components of a product or the total product.
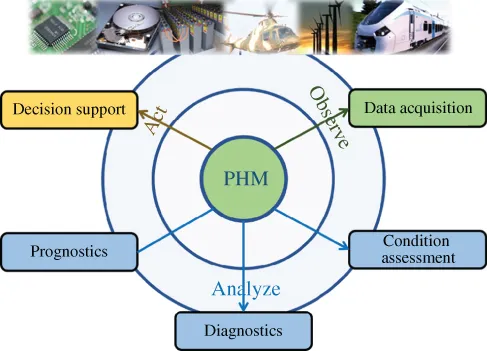
Figure 1.1 Framework for prognostics and health management.
The primary purpose of anomaly detection is to identify strange or unusual or unexpected (anomalous) behavior of the product by identifying deviations from nominally healthy behavior. The results from anomaly detection can provide advanced warnings of failure, often referred to as failure precursors. Note that anomalies do not necessarily indicate a failure because changes in operating and environmental conditions can influence sensor data to show anomalous behavior. However, even this type of anomaly information is valuable to product health management, because it can indicate an unexpected use.
Diagnostics enables the extraction of fault‐related information, such as failure modes, failure mechanisms, quantity of damage, and so forth, from sensor data caused by anomalies in the health of the product. This is a key piece of information that feeds into maintenance planning and logistics.
Prognostics refers to predicting a product's RUL within appropriate confiden...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Dedication
- About the Editors
- List of Contributors
- Preface
- About the Contributors
- Acknowledgment
- List of Abbreviations
- Chapter 1: Introduction to PHM
- Chapter 2: Sensor Systems for PHM
- Chapter 3: Physics‐of‐Failure Approach to PHM
- Chapter 4: Machine Learning: Fundamentals
- Chapter 5: Machine Learning: Data Pre‐processing
- Chapter 6: Machine Learning: Anomaly Detection
- Chapter 7: Machine Learning: Diagnostics and Prognostics
- Chapter 8: Uncertainty Representation, Quantification, and Management in Prognostics
- Chapter 9: PHM Cost and Return on Investment
- Chapter 10: Valuation and Optimization of PHM‐Enabled Maintenance Decisions
- Chapter 11: Health and Remaining Useful Life Estimation of Electronic Circuits
- Chapter 12: PHM‐Based Qualification of Electronics
- Chapter 13: PHM of Li‐ion Batteries
- Chapter 14: PHM of Light‐Emitting Diodes
- Chapter 15: PHM in Healthcare
- Chapter 16: PHM of Subsea Cables
- Chapter 17: Connected Vehicle Diagnostics and Prognostics
- Chapter 18: The Role of PHM at Commercial Airlines
- Chapter 19: PHM Software for Electronics
- Chapter 20: eMaintenance
- Chapter 21: Predictive Maintenance in the IoT Era
- Chapter 22: Analysis of PHM Patents for Electronics
- Chapter 23: A PHM Roadmap for Electronics-Rich Systems
- Appendix A: Commercially Available Sensor Systems for PHM
- Appendix B: Journals and Conference Proceedings Related to PHM
- Appendix C: Glossary of Terms and Definitions
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Prognostics and Health Management of Electronics by Michael G. Pecht, Myeongsu Kang, Michael G. Pecht,Myeongsu Kang in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Biomedical Science. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.