
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Financial Markets for Commodities
About this book
Agricultural, energy or mineral commodities are traded internationally in two market categories: physical markets and financial markets. More specifically, on the financial markets, contracts are negotiated, the price of which depends on the price of a commodity. These contracts are called derivatives (futures, options contracts, swaps). This book presents, on the one hand, the characteristics of these derivatives and the markets on which they are traded and, on the other hand, those transactions that typically combine an action on the physical market and a transaction on the corresponding financial market. The understanding of commodity financial markets mainly relies on the resources of economic analysis, especially the financial economy, because the use of this discipline is essential to understanding the major operations that are conducted daily by the operators of these markets: traders, producers, processors, financiers.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
General Observations on the Physical Trading of Commodities
1.1. The standardization of commodities and commercial contracts
“The Paris Syndicate [for Commerce and Seed Industries] establishes and diffuses the models for buying and selling contracts adapted to European commerce around primary agricultural products. These agreements are characterized by a balance between the interests of the buyer and those of the seller. These documents, known as the ‘Incograin formulae’ (for example: the Paris formulae) are periodically revised to take into account the evolution of commerce and uses, as well as of arbitrage decisions”3.
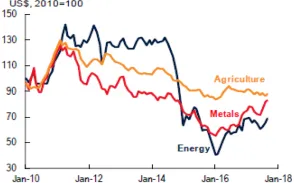
1.2. Price volatility of commodities
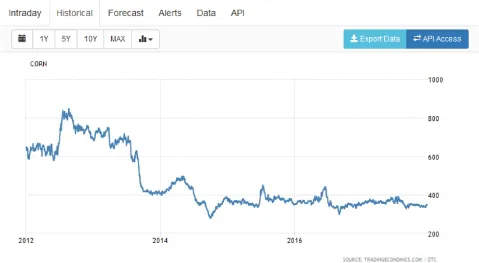
- – the prices of commodities sometimes see large variations over the medium and long term, as can be observed from the graph shown in Figure 1.2, which represents changes in the price of corn between 2012 and 2017;
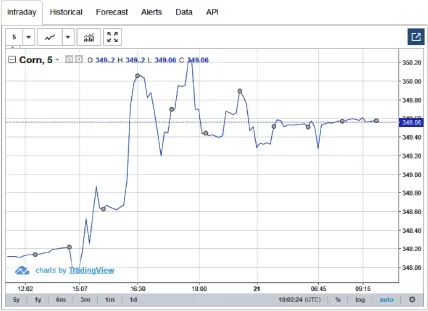
- – the prices of commodities also see multiple fluctuations in the short term, as can be seen in the evolution of the price of corn over 24 h, knowing that evolutions similar to those represented here are perfectly normal.
- – putting in place measures that aim to stabilize prices;
- – making available to operators the tools that are needed for private risk management as concerns prices.
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Introduction
- 1 General Observations on the Physical Trading of Commodities
- 2 The Financial Commodity Markets
- 3 Futures Contracts and Forward Contracts
- 4 The Storage and Term Structure of Commodity Futures Prices
- 5 Options Markets
- 6 A Selective Review of Classic Literature in Economics
- 7 A Very Selective Review of Modern Literature in Economics
- 8 Questions Surrounding Regulation
- Appendix: The Cox, Ross and Rubinstein model
- References
- List of Authors
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app