
Introduction to Bayesian Estimation and Copula Models of Dependence
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Introduction to Bayesian Estimation and Copula Models of Dependence
About this book
Presents an introduction to Bayesian statistics, presents an emphasis on Bayesian methods (prior and posterior), Bayes estimation, prediction, MCMC, Bayesian regression, and Bayesian analysis of statistical modelsof dependence, and features a focus on copulas for risk management
Introduction to Bayesian Estimation and Copula Models of Dependence emphasizes the applications of Bayesian analysis to copula modeling and equips readers with the tools needed to implement the procedures of Bayesian estimation in copula models of dependence. This book is structured in two parts: the first four chapters serve as a general introduction to Bayesian statistics with a clear emphasis on parametric estimation and the following four chapters stress statistical models of dependence with a focus of copulas.
A review of the main concepts is discussed along with the basics of Bayesian statistics including prior information and experimental data, prior and posterior distributions, with an emphasis on Bayesian parametric estimation. The basic mathematical background of both Markov chains and Monte Carlo integration and simulation is also provided. The authors discuss statistical models of dependence with a focus on copulas and present a brief survey of pre-copula dependence models. The main definitions and notations of copula models are summarized followed by discussions of real-world cases that address particular risk management problems.
In addition, this book includes:
• Practical examples of copulas in use including within the Basel Accord II documents that regulate the world banking system as well as examples of Bayesian methods within current FDA recommendations
• Step-by-step procedures of multivariate data analysis and copula modeling, allowing readers to gain insight for their own applied research and studies
• Separate reference lists within each chapter and end-of-the-chapter exercises within Chapters 2 through 8
• A companion website containing appendices: data files and demo files in Microsoft® Office Excel®, basic code in R, and selected exercise solutions
Introduction to Bayesian Estimation and Copula Models of Dependence is a reference and resource for statisticians who need to learn formal Bayesian analysis as well as professionals within analytical and risk management departments of banks and insurance companies who are involved in quantitative analysis and forecasting. This book can also be used as a textbook for upper-undergraduate and graduate-level courses in Bayesian statistics and analysis.
ARKADY SHEMYAKIN, PhD, is Professor in the Department of Mathematics and Director of the Statistics Program at the University of St. Thomas. A member of the American Statistical Association and the International Society for Bayesian Analysis, Dr. Shemyakin's research interests include informationtheory, Bayesian methods of parametric estimation, and copula models in actuarial mathematics, finance, and engineering.
ALEXANDER KNIAZEV, PhD, is Associate Professor and Head of the Department of Mathematics at Astrakhan State University in Russia. Dr. Kniazev's research interests include representation theory of Lie algebras and finite groups, mathematical statistics, econometrics, and financial mathematics.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Part I
Bayesian Estimation
1
Random Variables and Distributions
1.1 Conditional Probability
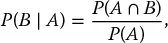
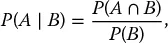
Table of contents
- Cover
- Titlepage
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Acknowledgments
- Acronyms
- Glossary
- About the Companion Website
- Introduction
- Part I: Bayesian Estimation
- Part II: Modeling Dependence
- Index
- EULA