
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Wi-Fi Integration to the 4G Mobile Network
About this book
The adoption of smartphones has had as a corollary the use of services that require streaming, such as video streaming, which is a constraint for the 4G mobile network. The integration of the network of Wi-Fi hotspots deployed by the operators adds capacity to the 4G mobile network.
The use of Wi-Fi technology in carrier networks is the result of developments coordinated by the IEEE, WFA and WBA standardization bodies. For its part, the 3GPP standardization body has been working to integrate Wi-Fi technology into the 4G mobile network.
The first part of this book presents the characteristics of the Wi-Fi radio interface. The different IEEE 802.11b / g / n / ac physical layers characterize the implementation in the 2.4 GHz ISM frequency bands and U- NII at 5 GHz. The MAC layer defines a number of media access procedures such as scanning, associating, or transferring data.
The second part of this book deals with the architecture of the 4G network based on the Wi-Fi interface. This architecture defines several models corresponding, on the one hand, to Wi-Fi access controlled or not, On the other hand, to a handover controlled by the network or by the mobile. The integration of Wi-Fi technology resulted in a redefinition of attachment and session set-up procedures.
Smartphones have the ability to activate simultaneously the two radio interfaces, LTE and Wi-Fi, which allows to direct certain services to one and / or the other of the interfaces. The ANDSF and HotSpot 2.0 functions provide the mobile with rules for network selection and traffic control to determine which traffic is to be routed to what type of interface.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1
Architecture Based on Wi-Fi Access
1.1. Functional architecture
- – Wi-Fi access is trusted or untrusted by the operator;
- – mobility is managed by the network or the mobile.
1.1.1. Architecture based on the S2a interface
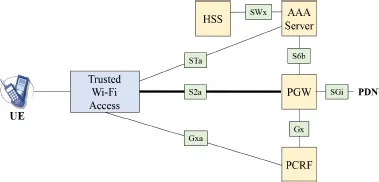
- – mutual authentication of the mobile and the AAA server via the interfaces SWx and STa. This authentication has the effect of opening Wi-Fi access to the mobile;
- – transfer of the mobile profile comprising a list of access point names (APN) and the quality of service (QoS) level of the S2a tunnel and Wi-Fi interface, to the PGW entity, via the interface S6b, and to trusted Wi-Fi access, via the STa interface.
- – WLAN AN: this feature includes Wi-Fi access points;
- – TWAG (Trusted WLAN Access Gateway): this function terminates tunnel S2a;
- – TWAP (Trusted WLAN AAA Proxy): this function terminates the STa interface.
- – in the case of a statefull configuration, the TWAG function acts as a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server;
- – in the case of a stateless configuration, the TWAG function broadcasts the prefix of the IPv6 address.
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Title
- Copyright
- List of Abbreviations
- Introduction
- 1 Architecture Based on Wi-Fi Access
- 2 MAC Layer
- 3 802.11a/g Interfaces
- 4 802.11n Interface
- 5 802.11ac Interface
- 6 Mutual Authentication
- 7 SWu Tunnel Establishment
- 8 S2a/S2b Tunnel Establishment
- 9 S2c Tunnel Establishment
- 10 Network Discovery and Selection
- 11 Carrier Aggregation
- 12 MPTCP Aggregation
- Bibliography
- Index
- End User License Agreement