
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Lean Computing for the Cloud
About this book
Applies lean manufacturing principles across the cloud service delivery chain to enable application and infrastructure service providers to sustainably achieve the shortest lead time, best quality, and value
- Applies lean thinking across the cloud service delivery chain to recognize and minimize waste
- Leverages lessons learned from electric power industry operations to operations of cloud infrastructure
- Applies insights from just-in-time inventory management to operation of cloud based applications
- Explains how traditional, Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) and Enhanced Telecom Operation Map (eTOM) capacity management evolves to lean computing for the cloud
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
CHAPTER 1
Basics
Upon completion of this chapter the reader will understand:
- The standard definition, characteristics, and benefits of cloud computing
- The key roles in the cloud computing ecosystem
- Key concepts of application, demand, supply, quality, and fungibility
This section reviews the following key concepts that are used extensively in this work:
- Cloud computing fundamentals (Section 1.1)
- Roles in cloud computing (Section 1.2)
- Applications (Section 1.3)
- Demand, supply, capacity, and fungibility (Section 1.4)
- Demand variability (Section 1.5)
1.1 Cloud Computing Fundamentals
Cloud computing is defined by ISO/IEC 177881 as a “paradigm for enabling network access to a scalable and elastic pool of shareable physical or virtual resources with self-service provisioning and administration on-demand.” ISO/IEC 17788 specifies the following six key characteristics of cloud computing2:
- Broad network access – “A feature where the physical and virtual resources are available over a network and accessed through standard mechanisms that promote use by heterogeneous client platforms. The focus of this key characteristic is that cloud computing offers an increased level of convenience in that users can access physical and virtual resources from wherever they need to work, as long as it is network accessible, using a wide variety of clients including devices such as mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and workstations” (ISO/IEC 17788). Operationally, this means that end users access cloud-based application services via commonly available wireless and wireline IP networks.
- Measured service – “A feature where the metered delivery of cloud services is such that usage can be monitored, controlled, reported, and billed… The focus of this key characteristic is that the customer may only pay for the resources that they use. From the customers' perspective, cloud computing offers the users value by enabling a switch from a low efficiency and asset utilization business model to a high efficiency one” (ISO/IEC 17788). When cloud customers pay only for resources that are used, application services that are engineered so cloud resource usage tracks with application service usage which tracks with application revenue can reduce business risk by better linking application service provider's costs with application service revenues.
- Multi-tenancy – “A feature where physical or virtual resources are allocated in such a way that multiple tenants and their computations and data are isolated from and inaccessible to one another” (ISO/IEC 17788). Multi-tenancy enables infrastructure service providers to maximize resource sharing and boost their capacity utilization.
- On-demand self-service – “A feature where a cloud service customer can provision computing capabilities, as needed, automatically or with minimal interaction with the cloud service provider. The focus of this key characteristic is that cloud computing offers users a relative reduction in costs, time, and effort needed to take an action, since it grants the user the ability to do what they need, when they need it, without requiring additional human user interactions or overhead” (ISO/IEC 17788). This means that application service providers and/or automated systems working on behalf of those application operators can install, configure, and provision cloud resources to serve their applications in real time. On-demand self-service of capacity planning and fulfillment actions, coupled with rapid elasticity, enables significant reductions in fulfillment times for capacity change actions compared to traditional deployments.
- Rapid elasticity and scalability – “A feature where physical or virtual resources can be rapidly and elastically adjusted, in some cases automatically, to quickly increase or decrease resources. For the cloud service customer, the physical or virtual resources available for provisioning often appear to be unlimited and can be purchased in any quantity at any time automatically, subject to constraints of service agreements. Therefore, the focus of this key characteristic is that cloud computing means that the customers no longer need to worry about limited resources and might not need to worry about capacity planning” (ISO/IEC 17788). Application service providers and/or automated systems working on their behalf can allocate and release infrastructure resources on-the-fly, thereby enabling applications to transform from allocating and configuring capacity based on peak forecast demand (which may never even be approached) to just-in-time, demand-driven capacity configuration.
- Resource pooling – “A feature where a cloud service provider's physical or virtual resources can be aggregated in order to serve one or more cloud service customers… From the customer's perspective, all they know is that the service works, while they generally have no control or knowledge over how the resources are being provided or where the resources are located. This offloads some of the customer's original workload, such as maintenance requirements, to the provider” (ISO/IEC 17788). Resource pooling, coupled with multi-tenancy, enables cloud service providers (CSPs) to leverage economies of scale to boost operational efficiencies beyond what has traditionally been feasible.
Figure 1.1 offers a simplified view of cloud computing: many different applications simultaneously share a large and flexibly configured pool of compute, memory, storage, networking, and functional component resources offered by a CSP. Coupling on-demand self-service and rapid elasticity enables application service providers to fundamentally transform their businesses from configuring application capacity to meet peak forecast demand to just-in-time, demand-driven capacity management. Using measured service as the basis of charging application service providers for their resource usage enables at least a portion of the application provider's costs to shift from being fixed and independent of usage to variable so that resource charges are tied to resource usage, which is tied to application service usage, which should be tied to application revenue.
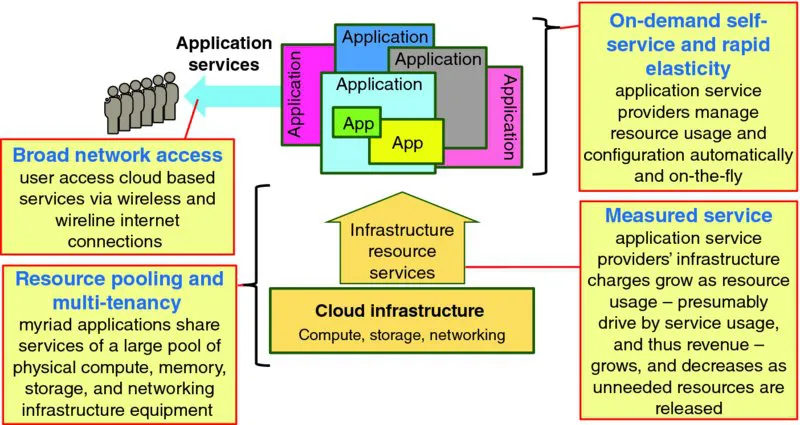
Figure 1.1 Cloud Computing in a Nutshell
Figure 1.2 visualizes key high-level business benefits of cloud computing:
- Lower infrastructure CapEx – the peak aggregate demand for compute, storage, and networking resources is smaller than the sum of peak demand of each individual application. Infrastructu...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Front matter
- Title page
- Copyright
- Introduction
- Acknowledgments
- Abbreviations
- 1 Basics
- 2 Rethinking Capacity Management
- 3 Lean Thinking on Cloud Capacity Management
- 4 Lean Cloud Capacity Management Strategy
- 5 Electric Power Generation as Cloud Infrastructure Analog
- 6 Application Capacity Management as an Inventory Management Problem
- 7 Lean Demand Management
- 8 Lean Reserves
- 9 Lean Infrastructure Commitment
- 10 Lean Cloud Capacity Management Performance Indicators
- 11 Summary
- References
- About the Author
- Index
- EULA
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Lean Computing for the Cloud by Eric Bauer in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Ciencia de la computación & Computación en la nube. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.