
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Green communications is a very hot topic. As mobile networks evolve in terms of higher rates/throughput, a consequent impact on operating costs is due to (aggregate) network energy consumption. As such, design on 4G networks and beyond have increasingly started to focus on `energy efficiency' or so-called 'green' networks. Many techniques and solutions have been proposed to enhance the energy efficiency of mobile networks, yet no book has provided an in-depth analysis of the energy consumption issues in mobile networks nor has detailed theories, tools and solutions for solving the energy efficiency problems.
This book presents the techniques and solutions for enhancing energy efficiency of future mobile networks, and consists of three major parts. The first part presents a general description of mobile network evolution in terms of both capacity and energy efficiency. The second part discusses the advanced techniques to green mobile networks. The third part discusses the solutions that enhance mobile network energy efficiency as well as provides future directions. Whilst the reader is expected to have basic knowledge of wireless communications, the authors present a brief introduction of the evolution of mobile networks, providing the knowledge base for understanding the content of the book. In addition, complicated network problems are illustrated using simple examples. This will help the reader understand the concept and intuition of various techniques and solutions.
- Incorporates the latest research results from both academia and industry, providing an up-to-date overview of existing technologies and solutions on making mobile networks greener
- Consists of three sections with a gradually increasing technical depth on green mobile networks, providing the reader with a systematic view of the research area, and helping those with different technical backgrounds to better understand the content
- Covers existing enabling technologies for green mobile networking, including an innovative discussion of state-of-the-art solutions and algorithms
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Part I
Green Mobile Networking Technologies
1
Fundamental Green Networking Technologies
1.1 Energy Efficient Multi-cell Cooperation
1.2 Heterogeneous Networking
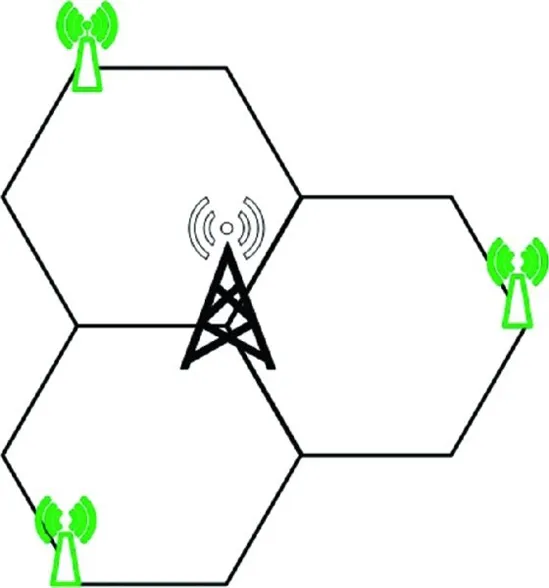
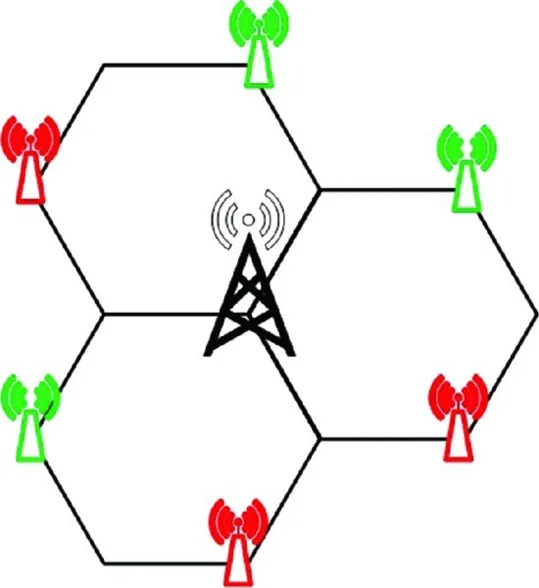
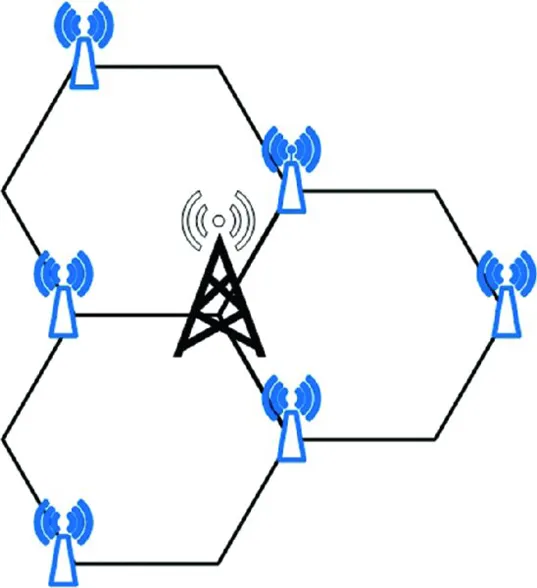
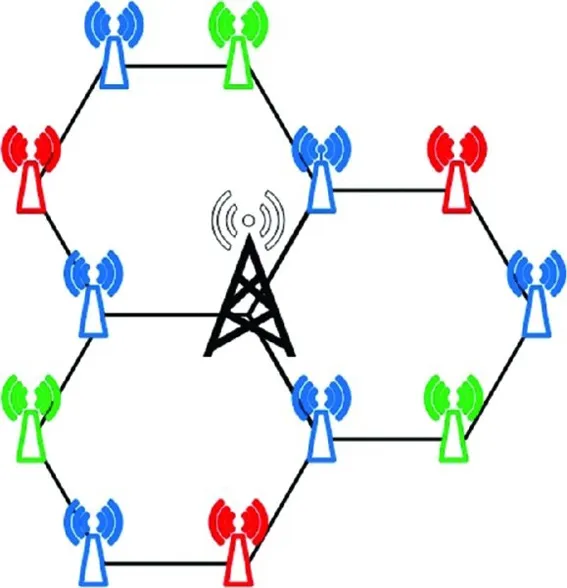
- The users located at the edge of a macro cell usually experience bad radio channels due to excessive channel fading. In order to provide service to these users, MBSs could increase their transmit power, but this will result in a low energy efficiency. In a heterogeneous network deployment, SCBSs can be deployed at the edge of macro cells as shown in Figures 1.1–1.4. Depending on the traffic capacity demand, different SCBS deployment strategies can be adopted. For example, when the traffic capacity demand is relatively low, one SCBS may be deployed at the edge of a macro cell to serve the cell edge users as shown in Figure 1.1. As the traffic increases, additional SCBSs can be deployed at the cell edge as shown in Figs. 1.2 and 1.3. When the traffic capacity demand is very high, additional SCBSs should be deployed. For example, five SCBSs are deployed for enhancing the energy efficiency of serving cell edge users in Figure 1.4. The number of SCBSs that are deployed to enhance the energy efficiency of serving users located at the edges of macro cells should be optimized based on traffic capacity demand at the cell edge.
- When the traffic capacity demand in mobile networks is inhomogeneous, deploying SCBSs at the edges of macro cells may not be optimal. Instead, SCBSs can be deployed in areas where there is high traffic capacity demand such as shopping areas, stadiums, and public parks. We define such areas as hotspots. Owing to proximity to the users, SCBSs can provide very high capacity at hotspots and serve the traffic demand with low energy consumption. In order to deploy SCBSs at traffic hotspots to enhance energy efficiency, the distribution of traffic capacity demand should be understood from network measurements. In addition, the traffic capacity demand should be localized so that a large portion of the traffic demand can be offloaded to SCBSs. In the ideal case, MBSs are only serving users with high moving speed while all the other users are served by SCBSs. If the high traffic demand occurs indoors, the indoor deployment of SCBSs can significantly enhance the energy efficiency of mobile networks.
1.3 Mobile Traffic Offloading
1.3.1 Infrastructure Based Mobile Traffic Offloading
Table of contents
- Cover
- Titlepage
- Copyright
- Preface
- List of Abbreviations
- Part I: Green Mobile Networking Technologies
- Part II: Green Mobile Networking Solutions
- References
- Index
- EULA
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app