
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Digital Signal Processing Using the ARM Cortex M4
About this book
Features inexpensive ARM® Cortex®-M4 microcontroller development systems available from Texas Instruments and STMicroelectronics.
This book presents a hands-on approach to teaching Digital Signal Processing (DSP) with real-time examples using the ARM® Cortex®-M4 32-bit microprocessor. Real-time examples using analog input and output signals are provided, giving visible (using an oscilloscope) and audible (using a speaker or headphones) results. Signal generators and/or audio sources, e.g. iPods, can be used to provide experimental input signals. The text also covers the fundamental concepts of digital signal processing such as analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog conversion, FIR and IIR filtering, Fourier transforms, and adaptive filtering.
Digital Signal Processing Using the ARM® Cortex®-M4:
- Uses a large number of simple example programs illustrating DSP concepts in real-time, in an electrical engineering laboratory setting
- Includes examples for both STM32F407 Discovery and the TM4C123 Launchpad, using Keil MDK-ARM, on a companion website
- Example programs for the TM4C123 Launchpad using Code Composer Studio version 6 available on companion website
Digital Signal Processing Using the ARM® Cortex®-M4 serves as a teaching aid for university professors wishing to teach DSP using laboratory experiments, and for students or engineers wishing to study DSP using the inexpensive ARM® Cortex®-M4.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
ARM® CORTEX®-M4 Development Systems
1.1 Introduction
1.1.1 Audio Interfaces
http://www.wiley.com/go/Reay/ARMcortexM4.1.1.2 Texas Instruments TM4C123 LaunchPad and STM32F407 Discovery Development Kits
http://www.wiley.com/go/Reay/ARMcortexM4.
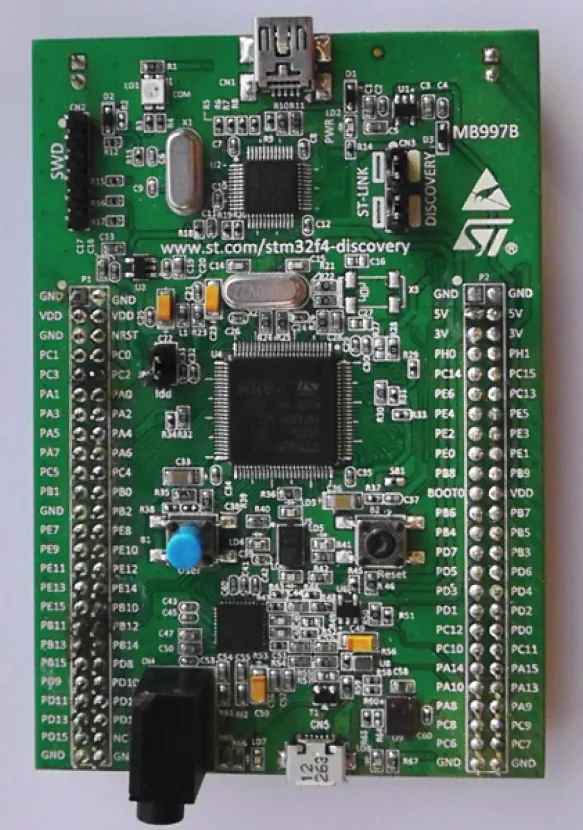
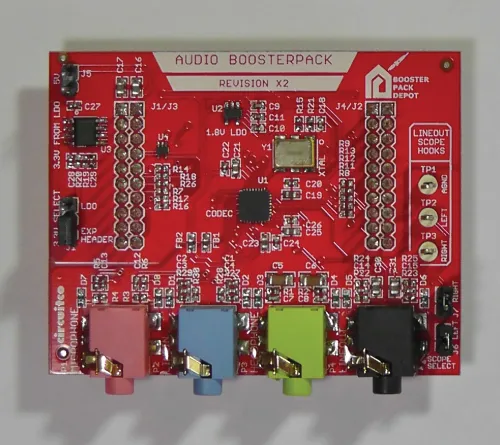
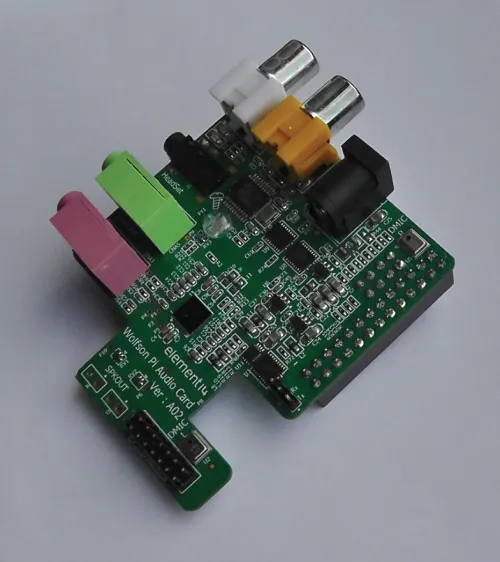
http://www.wiley.com/go/Reay/ARMcortexM4. and before progressing to the next chapter of this book will need to install MDK-ARM, including the “packs” appropriate to the hardware platform being used and including the CMSIS DSP library, download the program examples from the website, and become familiar with how to open a project in MDK-ARM, add and remove files from a project, build a project, start and stop a debug session, and run and halt a program running on the ARM Cortex-M4 processor.Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Table of Contents
- Dedication
- Preface
- Chapter 1: ARM® CORTEX®-M4 Development Systems
- Chapter 2: Analog Input and Output
- Chapter 3: Finite Impulse Response Filters
- Chapter 4: Infinite Impulse Response Filters
- Chapter 5: Fast Fourier Transform
- Chapter 6: Adaptive Filters
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app