
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Human Emerging and Re-emerging Infections
About this book
Emerging and re-emerging pathogens pose several challenges to diagnosis, treatment, and public health surveillance, primarily because pathogen identification is a difficult and time-consuming process due to the "novel" nature of the agent. Proper identification requires a wide array of techniques, but the significance of these diagnostics is anticipated to increase with advances in newer molecular and nanobiotechnological interventions and health information technology.
Human Emerging and Re-emerging Infections covers the epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnostics, clinical features, and public health risks posed by new viral and microbial infections. The book includes detailed coverage on the molecular mechanisms of pathogenesis, development of various diagnostic tools, diagnostic assays and their limitations, key research priorities, and new technologies in infection diagnostics. Volume 1 addresses viral and parasitic infections, while volume 2 delves into bacterial and mycotic infections.
Human Emerging and Re-emerging Infections is an invaluable resource for researchers in parasitologists, microbiology, Immunology, neurology and virology, as well as clinicians and students interested in understanding the current knowledge and future directions of infectious diseases.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Chapter 1
Pathogenesis of the Old World Arenaviruses in Humans
1.1 The Old World arenaviruses: taxonomic and zoonotic introduction
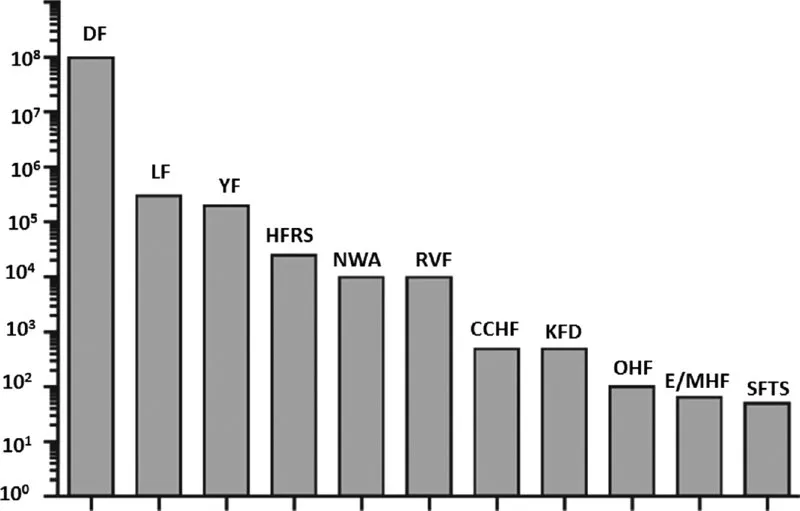
1.2 Genome structure
1.2.1 Arenavirus genome structure
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title page
- Copyright
- Dedication
- List of Contributors
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- About the Editor
- Chapter 1 Pathogenesis of the Old World Arenaviruses in Humans
- Chapter 2 Pathogenesis of New World Arenaviruses in Humans
- Chapter 3 Pathogenesis of Emerging and Novel Bunyaviruses in Humans
- Chapter 4 Pathogenesis of Rift Valley Fever in Humans
- Chapter 5 Pathogenesis of Hantavirus Infections
- Chapter 6 Molecular Pathogenesis of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infection
- Chapter 7 Dengue Virus Infection in Humans: Epidemiology, Biology, Pathogenesis, and Clinical Aspects
- Chapter 8 Pathogenesis of West Nile Virus in Humans
- Chapter 9 Overview on Chikungunya Virus Pathogenesis
- Chapter 10 Nipah Virus Infections in Humans
- Chapter 11 Pathogenesis of Hendra Virus in Humans
- Chapter 12 Pathogenesis of Rotavirus in Humans
- Chapter 13 Pathogenesis of Papillomaviruses in Humans
- Chapter 14 Kaposi's Sarcoma–Associated Herpesvirus Pathogenesis
- Chapter 15 Microsporidiosis in Humans
- Chapter 16 Pathogenesis of Toxoplasma gondii in Humans
- Chapter 17 Pathogenesis of Human African Trypanosomiasis
- Chapter 18 Pathogenesis of Leishmaniasis in Humans
- Chapter 19 Pathogenesis of Chagas Disease in Humans
- Chapter 20 Pathogenesis of Cryptosporidium in Humans
- Chapter 21 Pathogenesis of Malarial Parasites in Humans
- Chapter 22 Pathogenesis of Trichomonas vaginalis in Humans
- Chapter 23 Loa loa Pathogenesis in Humans
- Chapter 24 Nematode Larva Migrans
- Chapter 25 Pathogenesis of Human Schistosomiasis
- Chapter 26 Vector-Borne Parasitic Zoonotic Infections in Humans
- Index
- List of Contributors
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- About the Editor
- Chapter 27 Pathogenesis of Haemophilus influenzae in Humans
- Chapter 28 Campylobacter jejuni: Molecular Mechanisms and Animal Models of Colonization and Disease
- Chapter 29 Pathogenesis of Francisella tularensis in Humans
- Chapter 30 Pathogenesis of Yersinia pestis in Humans
- Chapter 31 Pathogenesis of Legionella pneumophila in Humans
- Chapter 32 Pathogenesis of Kingella kingae Infections
- Chapter 33 Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori in Humans
- Chapter 34 Pathogenesis of Chlamydia trachomatis in Humans
- Chapter 35 Pertussis or Whooping Cough
- Chapter 36 Pathogenesis of Human Ehrlichioses
- Chapter 37 Neisseria gonorrhoeae: The Pathogen, Diagnosis, and Antimicrobial Resistance
- Chapter 38 Pathogenesis of Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Corynebacterium ulcerans
- Chapter 39 Pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus in Humans
- Chapter 40 Pathogenesis of Listeria monocytogenes in Humans
- Chapter 41 Anthrax Infection
- Chapter 42 Pathogenesis of Streptococcus in Humans
- Chapter 43 Pathogenesis of Clostridium botulinum in Humans
- Chapter 44 Mycobacterium ulcerans and Buruli Ulcer
- Chapter 45 Challenges Associated with Diagnostics, Drug Resistance, and Pathogenesis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Chapter 46 Pathogenesis of Orientia tsutsugamushi Infection in Humans
- Chapter 47 Lyme Borreliosis
- Chapter 48 NDM-Type Carbapenemases in Gram-Negative Rods
- Chapter 49 Pathogenesis of Cryptococcosis in Humans
- Chapter 50 Candida albicans: Clinical Relevance, Pathogenesis, and Host Immunity
- Chapter 51 Pathogenesis of Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia
- Chapter 52 Pathogenesis of Aspergillosis in Humans
- Index
- EULA