
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Statistics is confusing, even for smart, technically competent people. And many students and professionals find that existing books and web resources don't give them an intuitive understanding of confusing statistical concepts. That is why this book is needed. Some of the unique qualities of this book are:
• Easy to Understand: Uses unique "graphics that teach" such as concept flow diagrams, compare-and-contrast tables, and even cartoons to enhance "rememberability."
• Easy to Use: Alphabetically arranged, like a mini-encyclopedia, for easy lookup on the job, while studying, or during an open-book exam.
• Wider Scope: Covers Statistics I and Statistics II and Six Sigma Black Belt, adding such topics as control charts and statistical process control, process capability analysis, and design of experiments. As a result, this book will be useful for business professionals and industrial engineers in addition to students and professionals in the social and physical sciences.
In addition, each of the 60+ concepts is covered in one or more articles. The 75 articles in the book are usually 5–7 pages long, ensuring that things are presented in "bite-sized chunks." The first page of each article typically lists five "Keys to Understanding" which tell the reader everything they need to know on one page. This book also contains an article on "Which Statistical Tool to Use to Solve Some Common Problems", additional "Which to Use When" articles on Control Charts, Distributions, and Charts/Graphs/Plots, as well as articles explaining how different concepts work together (e.g., how Alpha, p, Critical Value, and Test Statistic interrelate).
ANDREW A. JAWLIK received his B.S. in Mathematics and his M.S. in Mathematics and Computer Science from the University of Michigan. He held jobs with IBM in marketing, sales, finance, and information technology, as well as a position as Process Executive. In these jobs, he learned how to communicate difficult technical concepts in easy - to - understand terms. He completed Lean Six Sigma Black Belt coursework at the IASSC - accredited Pyzdek Institute. In order to understand the confusing statistics involved, he wrote explanations in his own words and graphics. Using this material, he passed the certification exam with a perfect score. Those statistical explanations then became the starting point for this book.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
ALPHA,
Summary of Keys to Understanding

- In Inferential Statistics, p is the Probability of an Alpha (“False Positive”) Error.

- Alpha is the highest value of p that we are willing to tolerate and still say that a difference, change, or effect observed in the Sample is “Statistically Significant.”

- Alpha is a Cumulative Probability, represented as an area under the curve, at one or both tails of a Probability Distribution. p is also a Cumulative Probability.
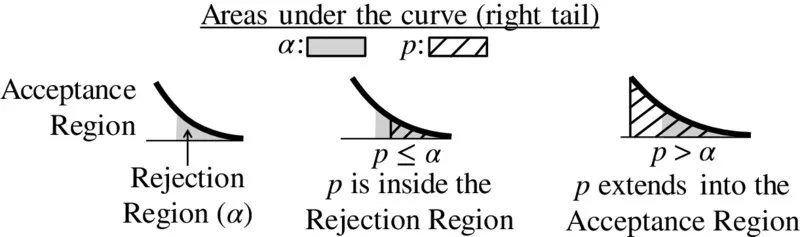

- In Hypothesis Testing, if p ≤ α, Reject the Null Hypothesis. If p > α, Accept (Fail to Reject) the Null Hypothesis.

- Alpha defines the Critical Value(s) of Test Statistics, such as z, t, F, or Chi-Square. The Critical Value or Values, in turn, define the Confidence Interval.
Explanation

- In Inferential Statistics, p is the Probability of an Alpha (“False Positive”) Error.
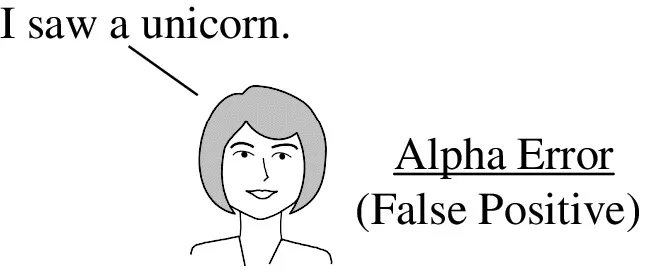
- Erroneously concluding that there is a difference in the Means of two Populations, when there is not, or
- Erroneously concluding that there has been a change in the Standard Deviation of a Process, when there has not, or
- Erroneously concluding that a medical treatment has an effect, when it does not. ...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title page
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Other Concepts Covered in the Articles
- Why This Book is Needed
- What Makes this Book Unique?
- How to Use This Book
- ALPHA,
- Binomial Distribution
- Charts/Graphs/Plots – Which to Use When
- Degrees of Freedom
- Errors – Types, Uses, and Interrelationships
- F
- Hypergeometric Distribution
- Inferential Statistics
- Margin of Error
- Nonparametric
- p, p-Value
- r, Multiple R, r2, R2, R Square, R2 Adjusted
- Sample, Sampling
- t – The Test Statistic and Its Distributions
- Variables
- Which Statistical Tool to Use to Solve Some Common Problems
- Z
- How to Find Concepts in This Book
- EULA