
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Bookkeeping For Dummies, UK Edition
About this book
Britain's number-one guide to mastering the art and science of bookkeeping
Accurate bookkeeping is crucial to the success of every business—but few people relish in this highly detailed task. Luckily, this new edition of Bookkeeping For Dummies simplifies every aspect of financial record keeping, walking you through the basic skills you need to make numbers your minion. From tracking transactions and keeping ledgers to producing balance sheets and year-end reports, this straight-talking guide takes the intimidation out of bookkeeping and shows you how to make it your best friend in business.
Fully updated to include the latest coverage of accounting practices and bookkeeping software, this new edition of Bookkeeping For Dummies features tons of practical exercises to get you up and running with what you need to keep your books balanced, your finances in order and the tax inspector off your back.
- Find updated bookkeeping templates and resources available via download
- Manage day-to-day records like sales and purchases
- Produce Profit and Loss Statements and Balance Sheets
- Prepare year-end documents with confidence and ease
From the importance of keeping a paper trail to the best ways to keep payroll rolling—and everything in between—this is the ideal resource for anyone looking to learn the bookkeeping ropes.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Basic Bookkeeping: Why You Need It




So You Want to Do the Books



Delving into Bookkeeping Basics
Looking at basic accounting methods
- If you choose cash-based accounting, you only record transactions when cash changes hands.
- If you use accrual accounting, you record a transaction on its completion, even if cash doesn’t change hands.
Understanding assets, capital and liabilities
- Assets include everything the business owns, such as cash, stock, buildings, equipment and vehicles.
- Capital includes the claims that owners have on the assets based on their portion of ownership in the business.
- Liabilities include everything the business owes to others, such as supplier bills, credit card balances and bank loans.
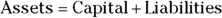
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Part I: Basic Bookkeeping: Why You Need It
- Part II: Recording Day-to-Day Business Operations
- Part III: Preparing the Books for Year- (or Month-) End
- Part IV: Reporting Results and Starting Over
- Part V: Payroll Preparation and Online Accounts Tools
- Part VI: The Part of Tens
- Appendix: Glossary
- About the Authors
- Cheat Sheet
- Advertisement Page
- Connect with Dummies
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app


