
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Java Programming for Android Developers For Dummies
About this book
Develop the next killer Android App using Java programming!
Android is everywhere! It runs more than half the smartphones in the U.S.—and Java makes it go. If you want to cash in on its popularity by learning to build Android apps with Java, all the easy-to-follow guidance you need to get started is at your fingertips. Inside, you'll learn the basics of Java and grasp how it works with Android; then, you'll go on to create your first real, working application. How cool is that?
The demand for Android apps isn't showing any signs of slowing, but if you're a mobile developer who wants to get in on the action, it's vital that you get the necessary Java background to be a success. With the help of Java Programming for Android Developers For Dummies, you'll quickly and painlessly discover the ins and outs of using Java to create groundbreaking Android apps—no prior knowledge or experience required!
- Get the know-how to create an Android program from the ground up
- Make sense of basic Java development concepts and techniques
- Develop the skills to handle programming challenges
- Find out how to debug your app
Don't sit back and watch other developers release apps that bring in the bucks! Everything you need to create that next killer Android app is just a page away!
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Getting Started with Java Programming for Android Developers
All about Java and Android


www.kantarworldpanel.com/global/smartphone-os-market-share/article): “The latest smartphone OS data … for the three months ending March 2016 shows Android continuing to grow sales across the EU5, US, and Urban China. There were solid gains in the EU5 (Great Britain, Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), up 7.1% points to 75.6%. In the US, Android share increased 7.3% points to 65.5%, and in China, it rose nearly 6% points to over 77%.”1The Consumer Perspective
- Possibility #1: No mobile phoneAdvantages: Inexpensive; no interruptions from callers.Disadvantages: No instant contact with friends and family; no calls to services in case of emergencies.
- Possibility #2: A feature phoneThis type of mobile phone isn’t a smartphone. Though no official rule defines the boundary between feature phone and smartphone, a feature phone generally has an inflexible menu of Home screen options, compared with a smartphone's ″desktop″ of downloaded apps.Advantage: Less expensive than a smartphone.Disadvantages: Less versatile than a smartphone, not nearly as cool as a smartphone, and nowhere near as much fun as a smartphone.
- Possibility #3: An iPhoneAdvantages: Great-looking graphics.Disadvantages: Little or no flexibility with the single-vendor iOS operating system; only a handful of models to choose from.
- Possibility #4: A Windows phone or another non-Android, non-Apple smartphoneAdvantage: Having a smartphone without having to belong to a crowd.Disadvantage: The possibility of owning an orphan product when the smartphone wars come to a climax.
- Possibility #5: An Android phoneAdvantages: Using a popular, open platform with lots of industry support and powerful market momentum; writing your own software and installing it on your own phone (without having to post the software on a company's website); publishing software without having to face a challenging approval process.Disadvantages: Security concerns when using an open platform; dismay when iPhone users make fun of your phone.
The Many Faces of Android
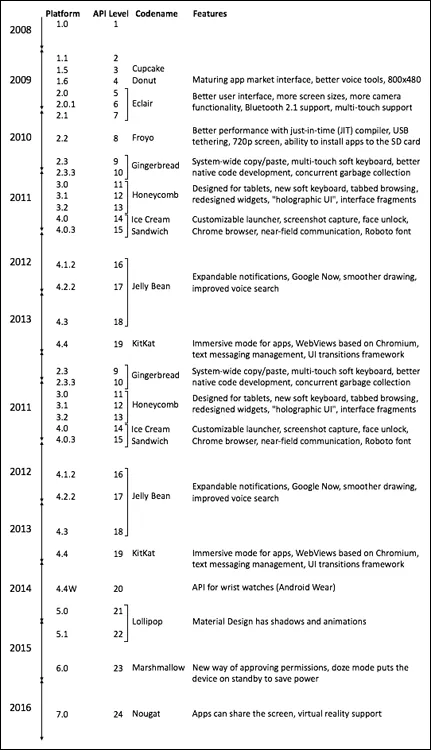
- The platform number is of interest to the consumer and to the company that sells the hardware.If you’re buying a phone with Android 5.1, for example, you might want to know whether the vendor will upgrade your phone to Android 6.0.
- The API level (also known as the SDK version) is of interest to the Android app developer.For example, the word MATCH_PARENT has a specific meaning in Android API Levels 8 and higher. You might type MATCH_PARENT in code that uses API Level 7. If you do (and...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Part 1: Getting Started with Java Programming for Android Developers
- Part 2: Writing Your Own Java Programs
- Part 3: Working with the Big Picture: Object-Oriented Programming
- Part 4: Powering Android with Java Code
- Part 5: The Part of Tens
- About the Author
- Advertisement Page
- Connect with Dummies
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app