
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
ABC of Diabetes
About this book
ABC of Diabetes provides primary care practitioners with a practical guide to all aspects of diabetes including the aetiology, diagnosis and management of Types 1 and 2 diabetes, detection and prevention, and the organization of care and support.
Advances in diabetes care take place at a rapid rate and this new edition is updated throughout to cover the latest evidence-based information for contemporary practice. A new chapter describes the management of severe and complex obesity complicated by diabetes and the management of patients through bariatric surgery.
It also covers the growing number of devices and digital technology, including health informatics, that can assist in diabetes care and provides evidence of their benefit. With more links to useful websites and resources online, it is now easier than ever to keep up-to-date with changes.
Drawing on the professional and teaching experience of an expert author team, ABC of Diabetes is an essential guide for general practice, primary care practitioners, diabetes specialist nurses, as well as for medical students and those training in diabetes as a specialty.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
CHAPTER 1
Diagnosing Diabetes
OVERVIEW
- Diabetes produces a variety of clinical presentations, from acute to gradual onset.
- The diagnosis should be based on two separate tests, unless the patient is clearly symptomatic, in which case only one positive test is required.
- A combination of genetic and environmental factors contribute to the risk of diabetes.
- Impaired glucose regulation is an important risk factor, both for future diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
- Distinction between random and fasting samples is essential in interpreting the significance of borderline blood glucose levels.
Introduction
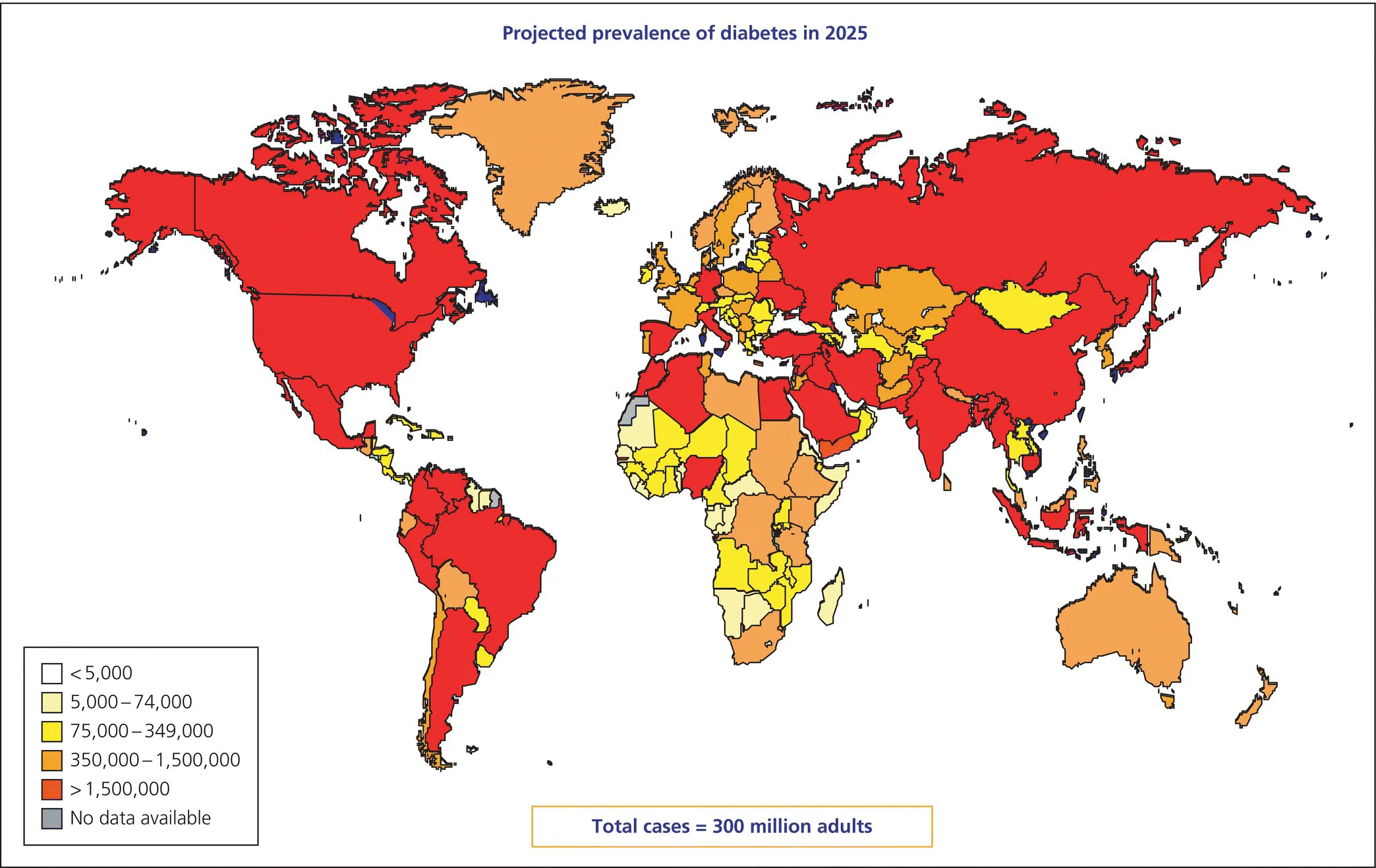
Prevalence of diabetes
Types of diabetes
Risk factors for diabetes
Genetics
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Table of Contents
- Contributors to this Book
- Foreword
- Preface
- Acknowledgements
- CHAPTER 1: Diagnosing Diabetes
- CHAPTER 2: Types of Diabetes
- CHAPTER 3: Helping People Live with Diabetes
- CHAPTER 4: Early Detection and Prevention of Diabetes
- CHAPTER 5: Obesity
- CHAPTER 6: Cardiovascular Disease
- CHAPTER 7: Management of Blood Glucose in Type 2 Diabetes
- CHAPTER 8: Hyperglycaemic Emergencies and Management of Diabetes in Hospital
- CHAPTER 9: Insulin Therapy
- CHAPTER 10: Hypoglycaemia
- CHAPTER 11: Self-Management of Diabetes
- CHAPTER 12: Surveillance for Complications
- CHAPTER 13: Kidney Disease in Diabetes
- CHAPTER 14: Eye Disease in Diabetes
- CHAPTER 15: The Diabetic Foot
- CHAPTER 16: Diabetic Neuropathy
- CHAPTER 17: Psychological Issues Related to Diabetes Care
- CHAPTER 18: Diabetes and Pregnancy
- CHAPTER 19: Organisation of Diabetes Care in General Practice
- CHAPTER 20: New and Emerging Therapies for Diabetes
- CHAPTER 21: Support for People Living with Diabetes
- Index
- End User License Agreement