
Handbook of Polymers for Pharmaceutical Technologies, Processing and Applications
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Handbook of Polymers for Pharmaceutical Technologies, Processing and Applications
About this book
Polymers are one of the most fascinating materials of the present era finding their applications in almost every aspects of life. Polymers are either directly available in nature or are chemically synthesized and used depending upon the targeted applications. Advances in polymer science and the introduction of new polymers have resulted in the significant development of polymers with unique properties. Different kinds of polymers have been and will be one of the key in several applications in many of the advanced pharmaceutical research being carried out over the globe.
This 4-partset of books contains precisely referenced chapters, emphasizing different kinds of polymers with basic fundamentals and practicality for application in diverse pharmaceutical technologies. The volumes aim at explaining basics of polymers based materials from different resources and their chemistry along with practical applications which present a future direction in the pharmaceutical industry. Each volume offer deep insight into the subject being treated.
- Volume 1: Structure and Chemistry
- Volume 2: Processing and Applications
- Volume 3: Biodegradable Polymers
- Volume 4: Bioactive and Compatible Synthetic/Hybrid Polymers
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Chapter 1
Particle Engineering of Polymers into Multifunctional Interactive Excipients
Abstract
1.1 Introduction
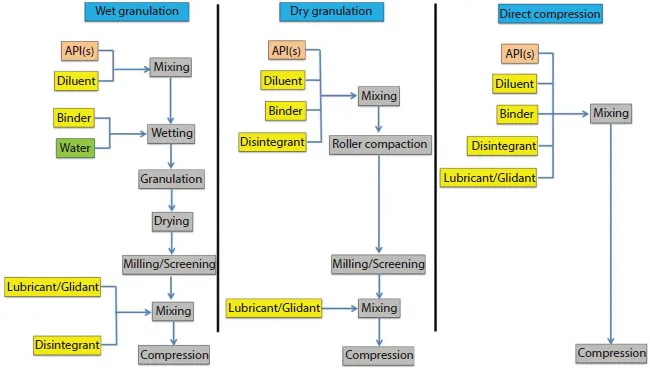
1.2 Polymers as Excipients
| Polymeric Excipient | Source | Functionality |
| Natural | ||
| Zein | Extracted from corn gluten | Binder, Coating agent |
| Cellulose | Extracted from fibrous plant material | Diluent, Disintegrant |
| Alginic acid | Extracted from various species of brown seaweed | Binder, Disintegrant |
| Acacia | Exudate from the stems and branches of Acacia Senegal | Binder |
| Guar gum | Extracted from the endosperm of the Cyamopsis tetragonolobus | Binder, Disintegrant |
| Inulin | Extracted from the tubers of Dahlia variabilis, Helianthus | Binder |
| Chitosan | Extracted from shells of crustaceans such as shrimps and crabs | Binder, Coating agent |
| Semi-synthetic | ||
| Sodium alginate | By neutralized alginic acid with sodium bicarbonate | Binder, Disintegrant |
| Calcium alginate | By treating sodium alginate with calcium salts | Disintegrant |
| Methyl cellulose | By treating wood pulp with alkali followed by methylation | Binder, Disintegrant, Coating agent |
| Carboxymethyl cellulose sodium | By treating wood pulp with alkali followed by reaction with sodium monochloroacetate | Binder, Disintegrant |
| Carboxymethyl cellulose calcium | By treating wood pulp with alkali followed by methylation and then converting to calcium salt | Disintegrant |
| Cellulose acetate | By treating cellulose with acid catalysis and acetic anhydride | Diluent, Coating agent |
| Cellulose acetate phthalate | By reacting cellulose acetate with phthalic anhydride | Coating agent |
| Microcrystalline cellulose | By controlled hydrolysis of cellulose with mineral acid | Binder, Diluent, Disintegrant |
| Hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose | By treating alkali cellulose with chloromethane and propylene oxide | Binder, Coating agent |
| Hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose acetate succinate | By the esterification of hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose with acetic anhydride and succinic anhydride | Film coating, Enteric coating |
| Hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose phthalate | By the esterification of hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose with phthalic anhydride | Enteric coating |
| Ethylcellulose | By ethylation of the alkali cellulose with chloroethane | Binder, Diluent, Coating agent |
| Low substituted-hydroxypropyl cellulose | By reacting alkaline cellulose with propylene oxide | Binder, Disintegrant |
| Ethyl cellulose | By ethylation of the alkali cellulose with chloroethane | Binder, Diluent, Coating a... |
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title page
- Title page
- Copyright page
- Dedication
- Preface
- About the Editors
- Chapter 1: Particle Engineering of Polymers into Multifunctional Interactive Excipients
- Chapter 2: The Art of Making Polymeric Membranes
- Chapter 3: Development of Microstructuring Technologies of Polycarbonate for Establishing Advanced Cell Cultivation Systems
- Chapter 4: In-Situ Gelling Thermosensitive Hydrogels for Protein Delivery Applications
- Chapter 5: Polymers as Formulation Excipients for Hot-Melt Extrusion Processing of Pharmaceuticals
- Chapter 6: Poly Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) Copolymer and Its Pharmaceutical Application
- Chapter 7: Pharmaceutical Applications of Polymeric Membranes
- Chapter 8: Application of PVC in Construction of Ion-Selective Electrodes for Pharmaceutical Analysis: A Review of Polymer Electrodes for Nonsteroidal, Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
- Chapter 9: Synthesis and Preservation of Polymer Nanoparticles for Pharmaceutical Applications
- Chapter 10: Pharmaceutical Applications of Maleic Anhydride/Acid Copolymers
- Chapter 11: Stimuli-Sensitive Polymeric Nanomedicines for Cancer Imaging and Therapy
- Chapter 12: Artificial Intelligence Techniques Used for Modeling of Processes Involving Polymers for Pharmaceutical Applications
- Chapter 13: Review of Current Pharmaceutical Applications of Polysiloxanes (Silicones)
- Chapter 14: Polymer-Doped Nano-Optical Sensors for Pharmaceutical Analysis
- Chapter 16: Polymeric Materials in Ocular Drug Delivery Systems
- Index