
eBook - ePub
ECG from Basics to Essentials
Step by Step
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
This brand new guide assists students, interns and residents in developing a functional understanding of the set-up, workings and interpretation of ECGs
- Step-by-step graphics and short, bite-sized explanations
- Covers all major cardiac abnormalities including hypertrophy, arrhythmias, conduction blocks, and pre-excitation syndromes
- Begins with a section on physiology of the heart and the basic set up of ECG recording
- Features top tips on what to look for, complete with illustrated examples
- Supported by a companion website featuring additional practice tracings
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
CHAPTER 1
ANATOMY AND BASIC PHYSIOLOGY
- What is an ECG?
- Blood circulation – the heart in action
- The conduction system of the heart
- Myocardial electrophysiology
- About cardiac cells
- Depolarization of a myocardial fiber
- Distribution of current in myocardium
- Recording a voltage by external electrodes
- The resultant heart vector during ventricular depolarization
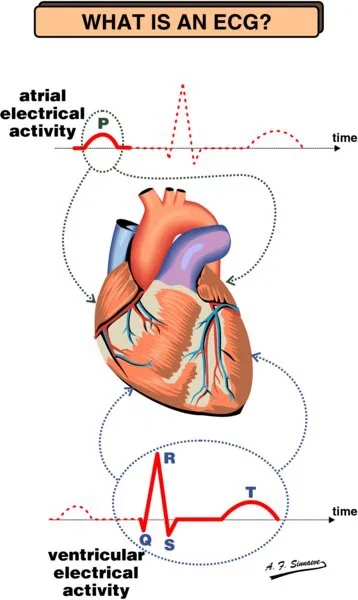

The ECG provides information on:
- the heart rate or cardiac rhythm
- position of the heart inside the body
- the thickness of the heart muscle or dilatation of heart cavities
- origin and propagation of the electrical activity and its possible aberrations
- cardiac rhythm disorders due to congenital anomalies of the heart
- injuries due to insufficient blood supply (ischemia, infarction, ...)
- malfunction of the heart due to electrolyte disturbances or drugs
History
The Dutch physiologist Willem Einthoven was one of the pioneers of electrocardiography and developer of the first useful string galvonometer. He labelled the various parts of the electrocardiogram using P, Q, R, S and T in a classic article published in 1903. Professor Einthoven received the Nobel prize for medicine in 1924.
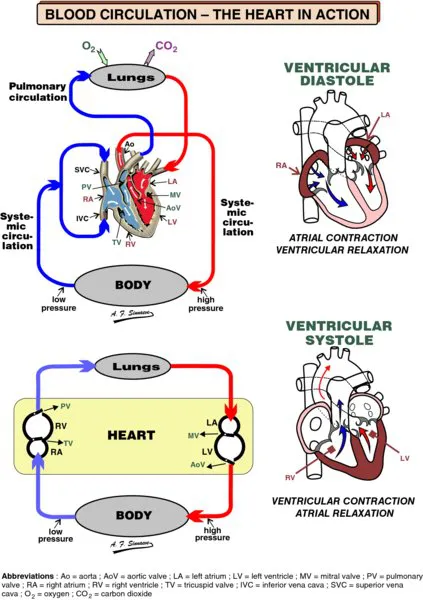
The heart is a muscle consisting of four hollow chambers. It is a double pump: the left part works at a higher pressure, while the right part works on a lower pressure.
The right heart pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation (i.e. the lungs). The left heart drives blood through the systemic circulation (i.e. the rest of the body).
The right atrium (RA) receives deoxygenated blood from the body via two large veins, the superior and the inferior vena cava, and from the heart itself by way of the coronary sinus. The blood is transferred to the right ventricle (RV) via the tricuspid valve (TV). The right ventricle then pumps the deoxy- genated blood via the pulmonary valve (PV) to the lungs where it releases excess carbon dioxide and picks up new oxygen.
The left atrium (LA) accepts the newly oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins and delivers it to the left ventricle (LV) through the mitral valve (MV). The oxygenated blood is pumped by the left ventricle through the aortic valve (AoV) into the aorta (Ao), the largest artery in the body.
The blood flowing into the aorta is further distributed throughout the body where it releases oxygen to the cells and collects carbon dioxide from them.

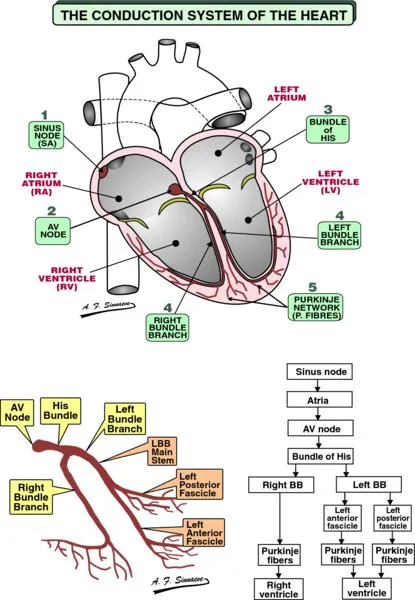
The contractions of the various parts of the heart have to be carefully synchronized. It is the prime function of the electrical conduction system to ensure this synchronization. The atria should contract first to fill the ventricles before the ventricles pump the blood in the circulation.
- The excitation starts in the sinus node consisting of special pacemaker cells. The electrical impulses spread over the right and left atria.
- The AV node is normally the only electrical connection between the atria and the ventricles. The impulses slow down as they travel through the AV node to reach the bundle of His.
- The bundle of His, the distal part of the AV junction, conducts the impulses rapidly to the bundle branches.
- The fast conducting right and left bundle branches subdivide into smaller and smaller branches, the smallest ones connec- ting to the Purkinje fibers.
- The Purkinje fibers spread out all over the ventricles beneath the endocardium and they bring the electrical impulses very fast to the myocardial cells.
All in all it takes the electrical impulses less than 200 ms to travel from the sinus node to the myocardial cells in the ventricles.
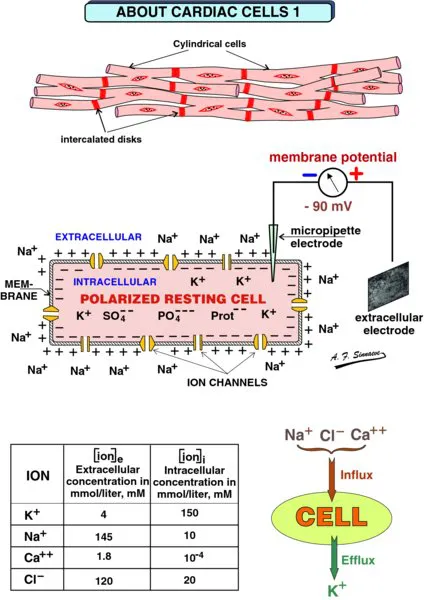
Cardiac muscle cells are more or less cylindrical. At their ends they may partially divide into two o...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Titlepage
- Copyright
- Preface
- About the companion website
- CHAPTER 1: ANATOMY AND BASIC PHYSIOLOGY
- CHAPTER 2: ECG RECORDING AND ECG LEADS
- CHAPTER 3: THE NORMAL ECG AND THE FRONTAL PLANE QRS AXIS
- CHAPTER 4: THE COMPONENTS OF THE ECG WAVES AND INTERVALS
- CHAPTER 5: P WAVES AND ATRIAL ABNORMALITIES
- CHAPTER 6: CHAMBER ENLARGEMENT AND HYPERTROPHY
- CHAPTER 7: INTRAVENTRICULAR CONDUCTION DEFECTS
- CHAPTER 8: CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE AND ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROMES
- CHAPTER 9: ACUTE PERICARDITIS
- CHAPTER 10: THE ECG IN EXTRA CARDIAC DISEASE
- CHAPTER 11: SINUS NODE DYSFUNCTION
- CHAPTER 12: PREMAT URE VENTRICULAR COMPLEXES (PVC)
- CHAPTER 13: ATRIOVENTRICULAR BLOCK
- CHAPTER 14: ATRIAL RHYTHM DISORDERS
- CHAPTER 15: VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIAS
- CHAPTER 16: VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION AND VENTRICULAR FLUTTER
- CHAPTER 17: PREEXCITATION AND WOLFF–PARKINSON–WHITE SYNDROME (WPW)
- CHAPTER 18: ELECTROLYTE ABNORMALITIES
- CHAPTER 19: ELECTROPHYSIOLOGIC CONCEPTS
- CHAPTER 20: ANTIARRHYTHMIC DRUGS
- CHAPTER 21: PA CEMAKERS AND THEIR ECGs
- CHAPTER 22: ERRORS IN ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY MONITORING, COMPUTERIZED ECG, OTHER SITES OF ECG RECORDING
- CHAPTER 23: HOW TO READ AN ECG
- Index
- EULA
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access ECG from Basics to Essentials by Roland X. Stroobandt,S. Serge Barold,Alfons F. Sinnaeve in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Medicine & Cardiology. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.