
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Data Science Strategy For Dummies
About this book
All the answers to your data science questions
Over half of all businesses are using data science to generate insights and value from big data. How are they doing it? Data Science Strategy For Dummies answers all your questions about how to build a data science capability from scratch, starting with the "what" and the "why" of data science and covering what it takes to lead and nurture a top-notch team of data scientists.
With this book, you'll learn how to incorporate data science as a strategic function into any business, large or small. Find solutions to your real-life challenges as you uncover the stories and value hidden within data.
- Learn exactly what data science is and why it's important
- Adopt a data-driven mindset as the foundation to success
- Understand the processes and common roadblocks behind data science
- Keep your data science program focused on generating business value
- Nurture a top-quality data science team
In non-technical language, Data Science Strategy For Dummies outlines new perspectives and strategies to effectively lead analytics and data science functions to create real value.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Optimizing Your Data Science Investment
Framing Data Science Strategy




Establishing the Data Science Narrative
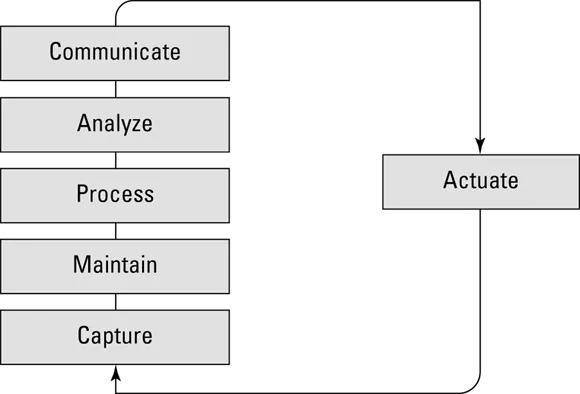
Capture
- Translating ambiguous business requests into concrete, well-defined problems or opportunities
- Deep-diving into the context of the requests to better understand what a potential solution could look like, including which data will be needed
- Outlining (if possible) strategic business priorities set by the company that might impact the data science work
- Managing data ownership and securing legal rights to data capture and usage
- Handling of personal information and securing data privacy through different anonymization techniques
- Using hardware and software for acquiring the data through batch uploads or the real-time streaming of data
- Determining how frequently data will need to be acquired, because the frequency usually varies between data types and categories
- Mandating that the preprocessing of data occurs at the point of collection, or even before collection (at the edge of an IoT device, for example). This includes basic processing, like cleaning and aggregating data, but it can also include more advanced activities, such as anonymizing the data to remove sensitive information. (Anonymizing refers to removing sensitive information such as a person's name, phone number, address and so on from a data set.)In most cases, data must be anonymized before being transferred from the data source. Usually a procedure is also in place to validate data sets in terms of completeness. If the data isn’t complete, the collection may need to be repeated several times to achieve the desired data scope. Performing this type of validation early on has a positive impact on both process speed and cost.

- Managing the data transfer process to the needed storage point (local and/or global). As part of the data transfer, you may have to transform the data — aggregating it to make it smaller, for example. You may need to do this if you’re facing limits on the bandwidth capacity of the transfer links you use.
Maintain
- Data storage: Think of this as everything associated with what's happening in the data lake. Data storage activities include managing the different retention periods for different types of data, as well as cataloging data properly to ensure that data is easy to access and use.
- Data preparation: In the context of maintaining data, data preparation includes basic processing tasks such as second-level data cleansing, data staging, and data aggregation, all of which usually involve applying a filter directly when the data is put into storage. You don't want to put data with poor quality into your data lake.
Process
- Data classification: This refers to the process of organizing data into categories for even more effective and efficient...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Foreword
- Introduction
- Part 1: Optimizing Your Data Science Investment
- Part 2: Making Strategic Choices for Your Data
- Part 3: Building a Successful Data Science Organization
- Part 4: Investing in the Right Infrastructure
- Part 5: Data as a Business
- Part 6: The Part of Tens
- Index
- About the Author
- Connect with Dummies
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app

