
Artificial Transmission Lines for RF and Microwave Applications
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Artificial Transmission Lines for RF and Microwave Applications
About this book
This book presents and discusses alternatives to ordinary transmission lines for the design and implementation of advanced RF/microwave components in planar technology. This book is devoted to the analysis, study and applications of artificial transmission lines mostly implemented by means of a host line conveniently modified (e.g., with modulation of transverse dimensions, with etched patterns in the metallic layers, etc.) or with reactive loading, in order to achieve novel device functionalities, superior performance, and/or reduced size. The author begins with an introductory chapter dedicated to the fundamentals of planar transmission lines. Chapter 2 is focused on artificial transmission lines based on periodic structures (including non-uniform transmission lines and reactively-loaded lines), and provides a comprehensive analysis of the coupled mode theory. Chapters 3 and 4 are dedicated to artificial transmission lines inspired by metamaterials, or based on metamaterial concepts. These chapters include the main practical implementations of such lines and their circuit models, and a wide overview of their RF/microwave applications (including passive and active circuits and antennas). Chapter 5 focuses on reconfigurable devices based on tunable artificial lines, and on non-linear transmission lines. The chapter also introduces several materials and components to achieve tuning, including diode varactors, RF-MEMS, ferroelectrics, and liquid crystals. Finally, Chapter 6 covers other advanced transmission lines and wave guiding structures, such as electroinductive-/magnetoinductive-wave lines, common-mode suppressed balanced lines, lattice-network artificial lines, and substrate integrated waveguides. Artificial Transmission Lines for RF and Microwave Applications provides an in-depth analysis and discussion of artificial transmission lines, including design guidelines that can be useful to researchers, engineers and students.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1
FUNDAMENTALS OF PLANAR TRANSMISSION LINES
1.1 PLANAR TRANSMISSION LINES, DISTRIBUTED CIRCUITS, AND ARTIFICIAL TRANSMISSION LINES
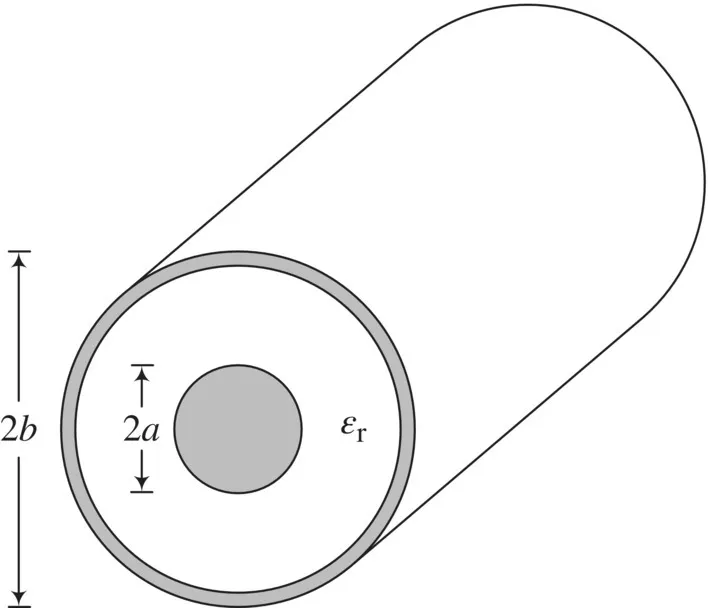
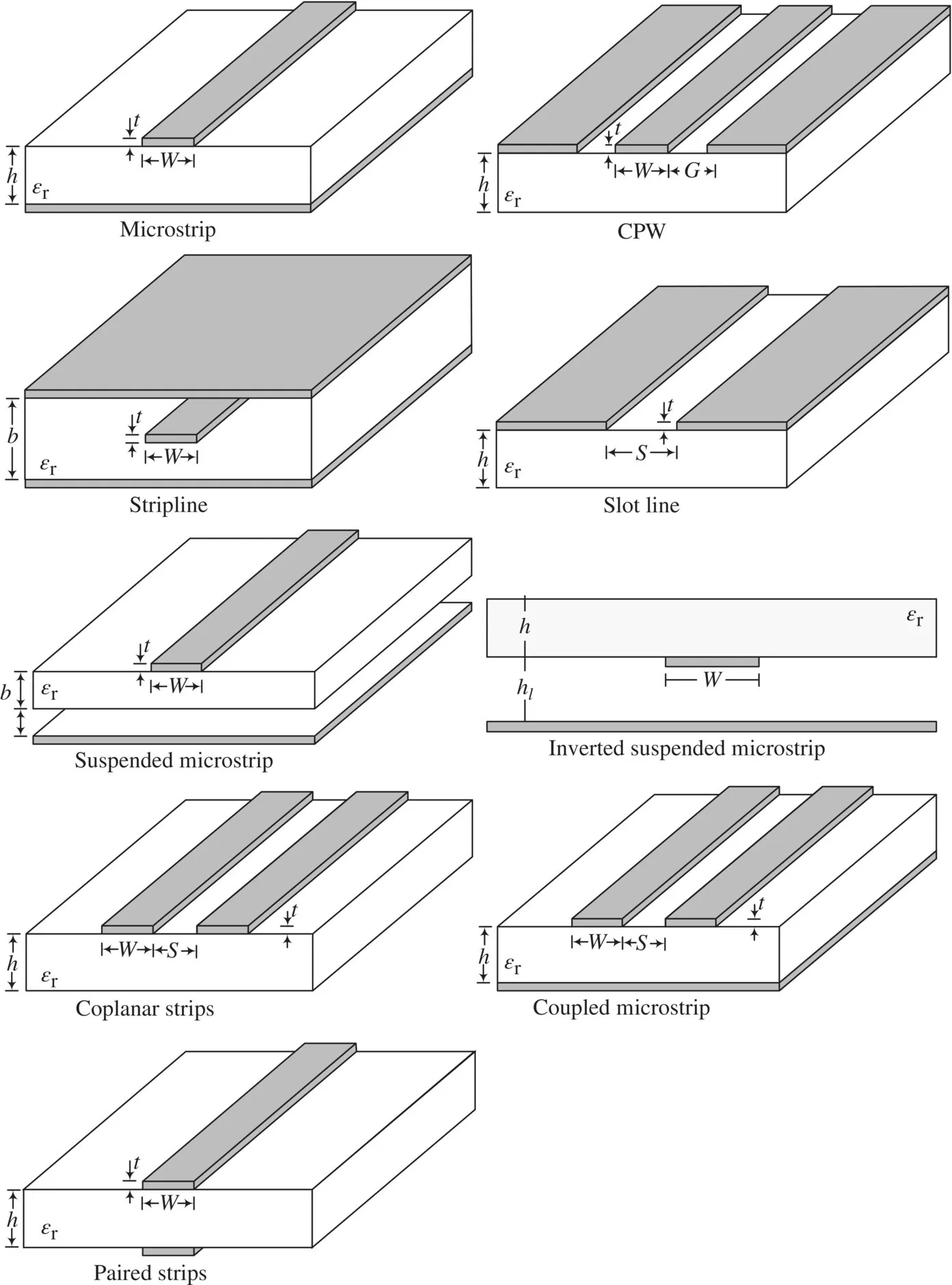
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- PREFACE
- ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- 1 FUNDAMENTALS OF PLANAR TRANSMISSION LINES
- 2 ARTIFICIAL TRANSMISSION LINES BASED ON PERIODIC STRUCTURES
- 3 METAMATERIAL TRANSMISSION LINES: FUNDAMENTALS, THEORY, CIRCUIT MODELS, AND MAIN IMPLEMENTATIONS
- 4 METAMATERIAL TRANSMISSION LINES: RF/MICROWAVE APPLICATIONS
- 5 RECONFIGURABLE, TUNABLE, AND NONLINEAR ARTIFICIAL TRANSMISSION LINES
- 6 OTHER ADVANCED TRANSMISSION LINES
- Appendix A EQUIVALENCE BETWEEN PLANE WAVE PROPAGATION IN SOURCE-FREE, LINEAR, ISOTROPIC, AND HOMOGENEOUS MEDIA; TEM WAVE PROPAGATION IN TRANSMISSION LINES; AND WAVE PROPAGATION IN TRANSMISSION LINES DESCRIBED BY ITS DISTRIBUTED CIRCUIT MODEL
- Appendix B THE SMITH CHART
- Appendix C THE SCATTERING MATRIX
- Appendix D CURRENT DENSITY DISTRIBUTION IN A CONDUCTOR
- Appendix E DERIVATION OF THE SIMPLIFIED COUPLED MODE EQUATIONS AND COUPLING COEFFICIENT FROM THE DISTRIBUTED CIRCUIT MODEL OF A TRANSMISSION LINE
- Appendix F AVERAGING THE EFFECTIVE DIELECTRIC CONSTANT IN EBG-BASED TRANSMISSION LINES
- Appendix G PARAMETER EXTRACTION
- Appendix H SYNTHESIS OF RESONANT-TYPE METAMATERIAL TRANSMISSION LINES BY MEANS OF AGGRESSIVE SPACE MAPPING
- Appendix I CONDITIONS TO OBTAIN ALL-PASS X-TYPE AND BRIDGED-T NETWORKS
- ACRONYMS
- INDEX
- WILEY SERIES IN MICROWAVE AND OPTICAL ENGINEERING
- END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT