
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Computing
About this book
Step-by-step instructions enable chemical engineers to master key software programs and solve complex problems
Today, both students and professionals in chemical engineering must solve increasingly complex problems dealing with refineries, fuel cells, microreactors, and pharmaceutical plants, to name a few. With this book as their guide, readers learn to solve these problems using their computers and Excel, MATLAB, Aspen Plus, and COMSOL Multiphysics. Moreover, they learn how to check their solutions and validate their results to make sure they have solved the problems correctly.
Now in its Second Edition, Introduction to Chemical Engineering Computing is based on the author's firsthand teaching experience. As a result, the emphasis is on problem solving. Simple introductions help readers become conversant with each program and then tackle a broad range of problems in chemical engineering, including:
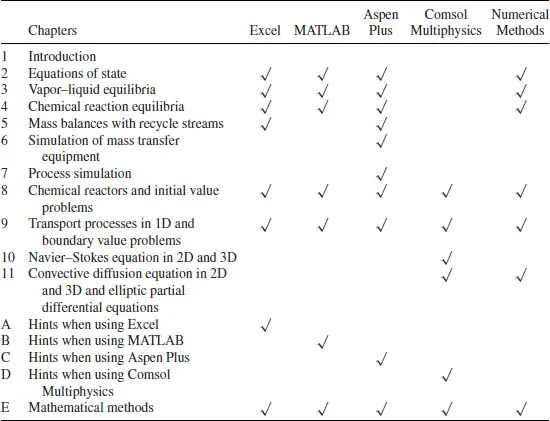
- Equations of state
- Chemical reaction equilibria
- Mass balances with recycle streams
- Thermodynamics and simulation of mass transfer equipment
- Process simulation
- Fluid flow in two and three dimensions
All the chapters contain clear instructions, figures, and examples to guide readers through all the programs and types of chemical engineering problems. Problems at the end of each chapter, ranging from simple to difficult, allow readers to gradually build their skills, whether they solve the problems themselves or in teams. In addition, the book's accompanying website lists the core principles learned from each problem, both from a chemical engineering and a computational perspective.
Covering a broad range of disciplines and problems within chemical engineering, Introduction to Chemical Engineering Computing is recommended for both undergraduate and graduate students as well as practicing engineers who want to know how to choose the right computer software program and tackle almost any chemical engineering problem.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
INTRODUCTION
- Illustrate the problems that you as chemical engineers may need to solve.
- Compare the types of computer programs you can use and illustrate which ones are best for certain applications.
- Describe how to check your work to ensure you have solved the problems correctly.
- Solve the problem
- Validate your work
- Understand how you reached that answer
ORGANIZATION
Algebraic Equations
Process Simulation
Differential Equations
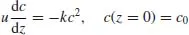
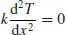

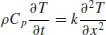
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Contents
- Preface
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Equations of State
- 3 Vapor–Liquid Equilibria
- 4 Chemical Reaction Equilibria
- 5 Mass Balances with Recycle Streams
- 6 Thermodynamics and Simulation of Mass Transfer Equipment
- 7 Process Simulation
- 8 Chemical Reactors
- 9 Transport Processes in One Dimension
- 10 Fluid Flow in Two and Three Dimensions
- 11 Heat and Mass Transfer in Two and Three Dimensions
- Appendix A Hints When Using Excel®
- Appendix B Hints When Using MATLAB®
- Appendix C Hints When Using Aspen Plus®
- Appendix D Hints When Using Comsol Multiphysics®
- Appendix E Mathematical Methods
- References
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app