
Recurrent Event Modeling Based on the Yule Process
Application to Water Network Asset Management
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Recurrent Event Modeling Based on the Yule Process
Application to Water Network Asset Management
About this book
This book presents research work into the reliability of drinking water pipes.
The infrastructure of water pipes is susceptible to routine failures, namely leakage or breakage, which occur in an aggregative manner in pipeline networks. Creating strategies for infrastructure asset management requires accurate modeling tools and first-hand experience of what repeated failures can mean in terms of socio-economic and environmental consequences.
Devoted to the counting process framework when dealing with this issue, the author presents preliminary basic concepts, particularly the process intensity, as well as basic tools (classical distributions and processes).
The introductory material precedes the discussion of several constructs, namely the non-homogeneous birth process, and further as a special case, the linearly extended Yule process (LEYP), and its adaptation to account for selective survival. The practical usefulness of the theoretical results is illustrated with actual water pipe failure data.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1
Introduction
- – either the distribution of successive inter-arrival times;
- – or the distribution of the number of events that occur in a given time interval.
1.1Notation
- – and
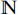 * respectively denote the sets of natural integers {0,1,2,…, ∞} and the set of strictly positive natural integers {1,2,…, ∞};
* respectively denote the sets of natural integers {0,1,2,…, ∞} and the set of strictly positive natural integers {1,2,…, ∞};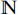
- – ,
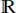 + and
+ and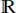 are the real sets ] − ∞, +∞[, [0, +∞[ and ]0, +∞[;
are the real sets ] − ∞, +∞[, [0, +∞[ and ]0, +∞[;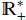
- – P (A) and P (A | B) respectively denote the probability of the event A, and the conditional probability of A given that the other event B occurs;
- – P (A ∩ B) and P (A, B) equivalently denote the joint probability of events A and B ;P (∩j Aj) more generally stands for the joint probability of events Aj;
- – t ∈ + is a positive time variable...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Title
- Copyright
- Preface
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Preliminaries
- 3 Non-homogeneous Birth Process
- 4 Linear Extension of the Yule Process
- 5 LEYP Likelihood and Inference
- 6 Selective Survival
- 7 LEYP2s Likelihood and Inference
- 8 Case Study Application of the LEYP2s Model
- 9 Conclusion and Outlook
- Appendices
- Bibliography
- Index