
Open Innovation
New Product Development Essentials from the PDMA
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Open Innovation
New Product Development Essentials from the PDMA
About this book
A clear, practical guide to implementing Open Innovation for new product development
Open Innovation: New Product Development Essentials from the PDMA is a comprehensive guide to the theory and practice of the Open Innovation method. Written by experts from the Product Development and Management Association, the book packages a collection of Open Innovation tools in a digestible and actionable format. Real-world case studies drawn from the authors' own successes and failures illustrate the concepts presented, providing accurate representation of the opportunities and challenges of Open Innovation implementation. Key tools are presented with a focus on immediate applications for business, allowing NPD professionals to easily discern where this cutting edge development method can push innovation forward.
Open Innovation assumes that companies can and should use both internal and external ideas and paths to market, permeating the boundaries between firm and environment. Innovations transfer outward and inward through purchase, licensing, joint ventures, and spin-offs, allowing companies to expand beyond their own research and dramatically improve productivity through collaboration. PDMA Essentials provides practical guidance on exploiting the Open Innovation model to these ends, with clear guidance on all aspects of the new product development process. Topics include:
- Product platforming and idea competitions
- Customer immersion and interaction
- Collaborative product design and development
- Innovation networks, rewards, and incentives
Many practitioners charged with innovation have only a vague understanding of the specific tools available for Open Innovation, and how they might be applied. As the marketplace shifts dramatically to keep pace with changing consumer behaviors, remaining relevant increasingly means ramping up innovation processes. PDMA Essentials provides the tools NPD practitioners need to implement a leading innovation method, and drive continued growth.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Part 1
OPEN INNOVATION IN THE FUZZY FRONT END
- Manfred Stadlbauer and Gerhard Drexler focus on finding and using sources of technology capabilities that are external to the firm in Chapter 1. This chapter shows how to use the patent literature and social network analysis to find areas of technology in the early stages of development, uncover interconnections between those new technologies and other technologies, locate firms and individuals active in those technologies, and map their geographic location to help determine who might make appropriate technology development partners.
- Christiane Rau, Fiona Schweitzer and Oliver Gassmann present methods for using open foresight workshops to identify new opportunities for the firm. Rather than being merely technology-driven opportunities, these methods allow the firm to investigate at the overall market and general trends level. Chapter 2 shows firms how they can implement these types of workshops in “closed” or internally executed forms, but then also shows firms how to move step-by-step to using them in more and more open ways.
1
DE-BOTTLENECKING OPEN INNOVATION: TURNING PATENT-BASED TECHNOLOGY NETWORK ANALYSIS INTO VALUE
1.1 Methods of Patent Analysis and Data Mining
Patents as a Lead Indicator of Innovation
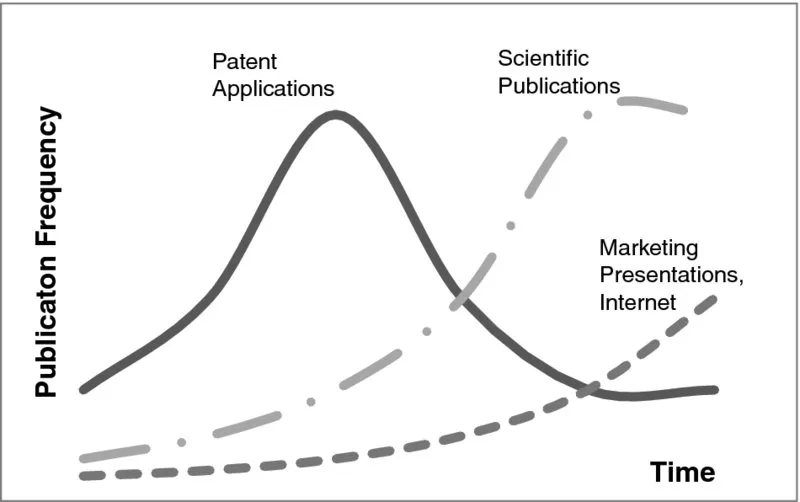
Table of contents
- Cover
- Titlepage
- Copyright
- Dedication
- INTRODUCTION THE JOURNEY INTO OPEN INNOVATION
- ABOUT THE EDITORS
- PART 1 OPEN INNOVATION IN THE FUZZY FRONT END
- PART 2 OPEN INNOVATION IN THE DEVELOPMENT STAGE
- PART 3 OPEN INNOVATION WITH UNIVERSITIES
- PART 4 OPEN INNOVATION FOR REALLY BIG INITIATIVES
- PART 5 BEST PRACTICES AND ADVICE FOR OPEN INNOVATION
- INDEX
- END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT