
Graph-related Optimization and Decision Support Systems
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Graph-related Optimization and Decision Support Systems
About this book
Constrained optimization is a challenging branch of operations research that aims to create a model which has a wide range of applications in the supply chain, telecommunications and medical fields. As the problem structure is split into two main components, the objective is to accomplish the feasible set framed by the system constraints. The aim of this book is expose optimization problems that can be expressed as graphs, by detailing, for each studied problem, the set of nodes and the set of edges. This graph modeling is an incentive for designing a platform that integrates all optimization components in order to output the best solution regarding the parameters' tuning. The authors propose in their analysis, for optimization problems, to provide their graphical modeling and mathematical formulation and expose some of their variants. As a solution approaches, an optimizer can be the most promising direction for limited-size instances. For large problem instances, approximate algorithms are the most appropriate way for generating high quality solutions. The authors thus propose, for each studied problem, a greedy algorithm as a problem-specific heuristic and a genetic algorithm as a metaheuristic.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Basic Concepts in Optimization and Graph Theory
1.1. Introduction
1.2. Notation
| Symbols | Description |
| n | the number of decision variables |
| k | the number of objectives |
| x = (x1,...,xn)T | the vector of decision variables |
| c(p,n) | the cost matrix |
| A | the matrix of constraints |
| B | Resources limitations |
| EO | The set of efficient solutions in the objective space |
| ED | The set of efficient solutions in the decision space |
1.3. Problem structure and variants
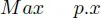
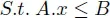
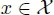
1.4. Features of an optimization problem
Table of contents
- Cover
- Contents
- Title Page
- Copyright
- List of Tables
- List of Figures
- List of Algorithms
- Introduction
- 1 Basic Concepts in Optimization and Graph Theory
- 2 Knapsack Problems
- 3 Packing Problems
- 4 Assignment Problem
- 5 The Resource Constrained Project Scheduling Problem
- 6 Spanning Tree Problems
- 7 Steiner Problems
- 8 A DSS Design for Optimization Problems
- Conclusion
- Glossary
- Bibliography
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app